

![]() [1] In the ‘real world’ passports and ID cards identify people; crests or symbols identify institutions like the police or a hospital; and a seal or stamp authenticates a document [2]. In the Digital World, we use Digital Certificates to do the same thing.
[1] In the ‘real world’ passports and ID cards identify people; crests or symbols identify institutions like the police or a hospital; and a seal or stamp authenticates a document [2]. In the Digital World, we use Digital Certificates to do the same thing.
Digital certificates can be used for improved security where a username and password are used to login to any web application by introducing two factor authentication [3]; they can also be used to secure the connection to any server using SSL certificates [4]; and can be used for identity cards [5] and even national ID cards.
Digital signatures can be used for sign PDF [6] documents; a digital signature can be installed on a server for signing e-invoice [6], statement and other billing documents; and can also be used to secure the connection to authenticate legal transactions that occur over the internet.
In the ‘digital world’ the Digital Certificate is used to identify the person, authority, device, website, software and/or electronic file and it is a CA [7] that issues these Digital Certificates. The purpose of the CA is to provide digital identities of users, devices or files. The CA is configured and installed in accordance with the customer’s requirements and these requirements are documented in the Certificate Policy [CP] for the CA.
Every request for a Digital Certificate is validated and approved, or rejected, by the Registration Authority [RA]. A trained Administrator, again in accordance with the CP, can manually operate the RA or this function can be automated depending on the CA you choose.
Every Digital Certificate issued is unique and is delivered according to the CP.
Any network where information is stored electronically needs to be secured. Up to now, the most common way of protecting such data has been through the use of usernames and passwords. This is no longer considered ‘secure’.
A single unsecured transaction could result in significant losses to an organization. This alone makes a strong argument for using Digital Certificates. Digital Certificates remove this risk completely.
Even more compelling business arguments in favour of using Digital Certificates [Digi-IDs™] would include the reduction or removal of paper forms and workflow from an organization. Paper business processes can be computerized and digital signature [8] replace handwritten signatures using Digi-IDs™. The savings to organizations as a result of using this technology are well documented.
Two factor authentication [9], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD], secure email [8] national ID Cards [10], digital rights management, web access control, device-to-device authentication [9] and many other business processes can benefit from significant savings by using technology smartly. Integral to all of these processes, is the requirement for digital authentication [9], digital identification, digital encryption, digital stamping [11] and digital signing and being able to support these transactions with a legally binding infrastructure. This is what Digi-CA™ [12] provides to your organization. The online flash presentation of Digi-CA™ [13] explains the benefits in a simple and easy to understand manner.
![]() [1] If you are trying to migrate [14] an existing environment from another Traditional Certificate Authority [15] [CA] vendor to Digi-CA™ [12], there is a ready-to-go solution that works independently from the Traditional CA. The customer can provide the information manually or the Digi-CA Assistant™ can help minimize the migration process by using unobtrusive network scanning.
[1] If you are trying to migrate [14] an existing environment from another Traditional Certificate Authority [15] [CA] vendor to Digi-CA™ [12], there is a ready-to-go solution that works independently from the Traditional CA. The customer can provide the information manually or the Digi-CA Assistant™ can help minimize the migration process by using unobtrusive network scanning.
This is how it works:
These same offerings can be used in physical border control, building access, electronic signatures and any situation where truly knowing the other person/device is a necessity to securing the transaction.
![]() [1] Consider the following questions carefully:
[1] Consider the following questions carefully:
Remember, the Digi-ID™ [18] can be used in a variety of different security situations, however the most common uses are for proving identity, digitally signing/sealing files and encrypting data or two factor authentication [9].
This is how the Digi-ID™ answers the above questions:
If the Bank is serious about security, they will use a Digi-SSL™ [19] Secure Web Server Certificate to prove its online web site identity.
Using a Digi-Code™ [20] Software/Code Signing Certificate, a pop up dialog box assures the user of the Publisher’s identity prior to download.
If the email is first encrypted using a Digi-ID™ for email [Digi-Mail™ [18]], then only the intended recipient can decrypt the email.
Passwords can be copied and misused, however, if each user has a Digi-ID™, using Digi-Access™ [3], security and identification is assured because this is strong two factor authentication [9].
The same Digi-SSL™ that confirms the identity of the website, automatically encrypts any data that is submitted through it.
Again using the Digi-ID™, because the identity of the owner has been verified, they can use it to sign any digital file.
Using a Digi-CA™ [12] combined with Digi-Access™, the systems can be secured and all users can be verified before offering them the correct access level.
![]() [1] The solution to the problem of online identification, two factor authentication [9] and privacy in computer based systems lies in the field of cryptography. Due to the non-physical nature of electronic communication, traditional methods of physically marking transactions with a seal or signature are useless. So an alternative mark must be coded into the information itself in order to identify the source and provide privacy against eavesdroppers.
[1] The solution to the problem of online identification, two factor authentication [9] and privacy in computer based systems lies in the field of cryptography. Due to the non-physical nature of electronic communication, traditional methods of physically marking transactions with a seal or signature are useless. So an alternative mark must be coded into the information itself in order to identify the source and provide privacy against eavesdroppers.
One widely used tool for privacy protection is what cryptographers call a "secret key." Log-on passwords and cash card PINs are examples of secret keys. Consumers share these secret keys only with the parties they want to communicate with, such as an online subscription service or a bank. Private information is then encrypted with this password, and it can only be decrypted by one of the parties holding that same password.
Despite its widespread use, this secret-key system has some serious limitations. As network communications proliferate, it becomes very cumbersome for users to create and remember different passwords for each situation. Moreover, the sharing of a secret key involves inherent risks. In the process of transmitting a password, it can fall into the wrong hands, or one of the sharing parties might use it maliciously and then deny all action or liability.
Digital Certificate [8] technology addresses these issues because it does not rely on the sharing of secret keys. Rather than using the same key to both encrypt and decrypt data, a Digital Certificate uses a matched pair of keys that are unique complements to one another. In other words, what is done by one key can only be undone by the other key in the matching pair?
Digi-CA™ [12] generates these Digital Certificates [8] using the patented Rivest, Shamir & Adelman [RSA] cryptographic algorithm. This algorithm is a mathematical formula that creates a dual key algorithm that is used to create the Digital Certificate.
Private and Public Key
In this type of Key-Pair system, the "Private Key" can only be accessed by you. Your "Public Key" gets widely distributed as part of the Digi-ID™ [18]. Customers, partners or employees who want to communicate privately with you can use the Public Key in your Digi-ID™ to encrypt information, and you are then the only one who can decrypt that information. Since the Public Key alone does not provide access to communications, you do not need to worry about who gets hold of this Key.
Your Digi-ID™ tells customers and correspondents that your Public Key in fact belongs to you. Your Digi-ID™ contains your name and identifying information, your Public Key and electronic signature as certification. The online flash presentation of Digi-CA™ [13] explains the benefits in a simple and easy to understand manner.
![]() [1] Every time a user sends an email it travels across the internet or world wide web. It is called the world wide web because the internet is made up of thousands of servers or a ‘web of servers’. Each and every communication visits a minimum of 8 and a maximum of 32 servers before it reaches its intended destination. Each of these points of contact represents a security risk. Scripts, viruses, hackers and other devices can intercept the data at any time and can copy or alter it unnoticed.
[1] Every time a user sends an email it travels across the internet or world wide web. It is called the world wide web because the internet is made up of thousands of servers or a ‘web of servers’. Each and every communication visits a minimum of 8 and a maximum of 32 servers before it reaches its intended destination. Each of these points of contact represents a security risk. Scripts, viruses, hackers and other devices can intercept the data at any time and can copy or alter it unnoticed.
Device-to-device authentication, two factor authentication [9], transaction signing and the inherent ‘digital identity’ within the Digital Certificate means that you know who and what you’re communicating with.

Encrypting information is only one aspect of security. The other is knowing the identity of the person. If two people choose to communicate by email, how can they be sure that any of the communications were transmitted without being tampered with? Equally, if a website owner wants to be sure that only a specific user gains access to secured information, how can this assurance be provided?
The simple answer is that Digital Certificates are the digital equivalent of a passport or signature.

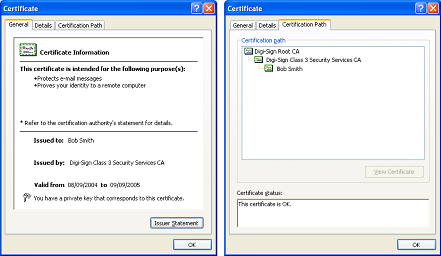
By opening a user’s Digital Certificate much of the information that would be available in a passport or drivers license can be viewed in the Certificate. The person’s name, the organization that they work for (or the organization that issued the Certificate) and other information is clearly legible. A Digital Certificate cannot be compromised or ‘cracked’, this provides the assurance necessary to assure the recipient that the person is genuinely who they claim to be.
Digital Certificates can be used to identify a person or a device. Once identification is established, the Certificate is most frequently used to prove one person’s, or device’s, identity to another person or device. Because of the RSA system, they both know each other. The Digital Certificate can now be used for signing and/or encrypting email or for providing two-factor strong authentication.
![]() [1] Using the dual-key cryptography algorithm, the Digital Certificates allow users to exchange Public Keys to secure and authenticate each other.
[1] Using the dual-key cryptography algorithm, the Digital Certificates allow users to exchange Public Keys to secure and authenticate each other.
There are two main uses for Digital Certificates are for:
And when considering using Digital Certificates you need to consider:
![]() [1] The rules, methods and guidelines that specify how the Digital Certificate is distributed to the end user are documented in the Certificate Policy [CP]. The CP is the ‘Who, What, Where and How’ document that describes the principles of the Digital Certificate usage and how they are to be distributed. This CP is agreed before the CA is operational and all Digital Certificates must be deployed in accordance with the CP.
[1] The rules, methods and guidelines that specify how the Digital Certificate is distributed to the end user are documented in the Certificate Policy [CP]. The CP is the ‘Who, What, Where and How’ document that describes the principles of the Digital Certificate usage and how they are to be distributed. This CP is agreed before the CA is operational and all Digital Certificates must be deployed in accordance with the CP.
The Registration Authority [RA] decides what users are permitted to receive a Digi-ID™ [18]. The RA can be a Systems Administrator or other responsible member of the organization, or the process can be automated using a database and a series of automated checks and controls, each one of which is designed to reduce the error possibility or the risk of deception.
![]() [1] There are three main types of Digital Certificates, they are:
[1] There are three main types of Digital Certificates, they are:
All Digital Certificates come from a Certificate Authority [7] which is a computer system that is capable of issuing the different types of Digital Certificate. The online flash presentation of Digi-CA™ [13] explains the benefits in a simple and easy to understand manner.
![]() [1] Digi-Sign offers three types of Digital Certificate and both types of CA (in fact Digi-CA™ Shared [22] is a third type of CA and is unique to Digi-Sign). With exception of Digi-Code™ [20], these are offered in three Classes depending on your requirements.
[1] Digi-Sign offers three types of Digital Certificate and both types of CA (in fact Digi-CA™ Shared [22] is a third type of CA and is unique to Digi-Sign). With exception of Digi-Code™ [20], these are offered in three Classes depending on your requirements.
The different types of Digital Certificate are:
And there are several Classes for each of these Certificates, e.g. Xs, Xp, Xe, Xg Xn, etc. The three standard Classes are the Xs, Xp and Xg, where Xs is the basic Class and offers no real flexibity to the user and Xg is at the other end of the spectrum and is the most flexible. Here is a breakdown of the most commont Certificate Type and Class combinations you are most likely to see:
Links:
[1] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-ca-pdf
[2] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digital+document
[3] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access
[4] http://www2.digi-sign.com/ssl
[5] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-card
[6] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-seal
[7] http://www2.digi-sign.com/certificate+authority
[8] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digital+certificate
[9] http://www2.digi-sign.com/two+factor+authentication
[10] http://www2.digi-sign.com/id+card
[11] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/time+stamp
[12] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca
[13] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/aacd
[14] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/migration
[15] http://www2.digi-sign.com/certificate+authority/traditional+ca
[16] http://www2.digi-sign.com/ssl+certificate
[17] http://www2.digi-sign.com/aacd
[18] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-id
[19] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ssl
[20] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-code
[21] http://www.digi-sign.com
[22] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/shared
[23] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-mail
[24] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-access-user-pdf
[25] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/approache
[26] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/total+trust+management
[27] http://www2.digi-sign.com/en/digi-access/compatibility
[28] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/digi-access#simple
[29] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/digi-access#bank
[30] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/digi-access#vpn
[31] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/approach#two-tier
[32] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/website
[33] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/configure
[34] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/customise
[35] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/distribute
[36] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access/distribute#approve
[37] http://www2.digi-sign.com/https
[38] http://www2.digi-sign.com/en/digi-ca
[39] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/service
[40] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/server
[41] http://www2.digi-sign.com/support/digi-access/index