

![]() [1] Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority [2] [CA] system for organisations that would like to own and manage their CA inside the organisation. The CA issues the Digital Certificates [3] that are used for two factor authentication [4], electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards [5], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD [6]], smart cards and ID Cards [5] and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
[1] Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority [2] [CA] system for organisations that would like to own and manage their CA inside the organisation. The CA issues the Digital Certificates [3] that are used for two factor authentication [4], electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards [5], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD [6]], smart cards and ID Cards [5] and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
The user online manual is the resource for the many different users of Digi-CA™ system and is suitable for both the technical and non-technical reader.
![]() [1] Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority [2] [CA] system for organisations that would like to own and manage their CA inside the organisation. The CA issues the Digital Certificates [3] that are used for two factor authentication [4], electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards [5], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD [6]], smart cards and ID Cards [5] and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
[1] Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority [2] [CA] system for organisations that would like to own and manage their CA inside the organisation. The CA issues the Digital Certificates [3] that are used for two factor authentication [4], electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards [5], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD [6]], smart cards and ID Cards [5] and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
Combining the consulting and professional services offered in the Digi-CAST™ [8] methodology with Digi-CA™ can meet all national and international standards [9] such as: Common Criteria, Sarbanes Oxley, SB 1386, BS 7799-3:2006, ISO 17799, FFIEC, HIPAA, ACSI 33, 1999/93/EC, ANSI, CWA 14167-1, ETSI 101 456, EAL, FIPS, RFC, ICAO, MRTD, CONOPS, ALGO, Gramm-Leach Bliley and many other compliance [9] and certification [9] requirements.
Small and medium sized businesses, large corporate, government, local government, Trust Centres [10], statutory bodies, security companies or any enterprise that wants to use Digital Certificates, should carefully examine the true benefits of using this radical new technology.
The Digi-CA™ system can issue, revoke, suspend and re-sign x.509v3 Certificates. The end user information and certificate request is entered through the web-based Registration Authority [RA] called the Digi-CA™ Control Centre. It is the Digi-CA™ Control Centre that is used to control all day-to-day administrative functions. Time stamping, Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] [11], customized Certificate Revocation Lists [CRLs] and many other options can be incorporated into Digi-CA™ on request.
The Digi-CA™ suite of CA systems offers the following benefits:
This online manual is the resource for the many different users of Digi-CA™ system and is suitable for both the technical and non-technical reader.
![]() [13] Multiple customized Root Certificates, Intermediate Root Certificates and EU Qualified Certificates can also be catered for. Every aspect of the Digital Certificate including Certificate fields can all be customized to meet any x.509 standard requirement.
[13] Multiple customized Root Certificates, Intermediate Root Certificates and EU Qualified Certificates can also be catered for. Every aspect of the Digital Certificate including Certificate fields can all be customized to meet any x.509 standard requirement.
Whether your requirement is for a simple to use and operate CA that is installed as software inside the organization or a totally outsourced service, Digi-CA™ can meet your precise requirements. Highly customized and complex CA environments and even a certified Trust Centre [10] that complies with international standards [9] can be built-to-order using Digi-CA™ Server. And you can also have almost all these same functionalities, no matter how complex, delivered as a service from outside the organization using the Digi-CA™ Service. No matter how it’s delivered, Digi-CA™ is the most flexible, efficient and cost effective CA system for you.
Digi-CA™ can be delivered exactly to your requirements. You can choose to have Digi-Sign do everything for you and ‘Fast Track’ your requirements, or you can be proactively involved at whatever level you like.
Implementing a Certificate Authority is not a ‘one size fits all’ project. Your requirement might be for a few hundred users with exceptionally high security parameters or you could be looking to authenticate several million hardware devices. The commercial organization’s requirements are typically related to cost, benefit, risk and return whilst the government project is more concerned with statutory requirements, IT standards and compliance [9].
No matter how small or large your requirement, you’ll have restrictions on what your current environment can cope with; availability of staff; budgetary constraints and other parameters within which you must choose the correct CA for your organization. You may want to be very ‘hands on’ at every stage of the project and even want to conduct some of the integration and even programming or you may decide you want us to do everything for you. Just as Digi-CA™ is totally flexible, so too is the Digi-Sign approach.
![]() [13] AACD™ System [14] ‘Fast Track’ is exactly as it sounds, you want everything done as quickly as possible and you want the professionals to do it for you. This is a total ‘turn key’ approach where we take your instructions, document them and deliver the entire solution back to you in the shortest possible time. Once the Digi-CA™ is delivered, you nominate personnel within your organization to take responsibility for it and we support them in the background.
[13] AACD™ System [14] ‘Fast Track’ is exactly as it sounds, you want everything done as quickly as possible and you want the professionals to do it for you. This is a total ‘turn key’ approach where we take your instructions, document them and deliver the entire solution back to you in the shortest possible time. Once the Digi-CA™ is delivered, you nominate personnel within your organization to take responsibility for it and we support them in the background.
This is where we not only ‘Fast Track your requirements through to delivery but actually assume responsibility for the total management of your CA environment for as long as you need us too.
Total Trust Management™ [TTM™] [15] is a unique offering from Digi-Sign (although some try to copy it) and it means that you Trust us to Totally Manage the Digi-CA™ for you. TTM™ is much more than a dedicated telephone support line, it’s a service where Digi-Sign personnel effectively work for you. We ensure that the CA technology is introduced to the end users with the minimum of fuss. All you do is agree how you want us to operate the Digi-CA™, and we do everything for you. It’s a bit like travelling First Class.
75% of our customers use TTM™ in the first year, at least, so that they can see how we do everything and then learn by watching us, see section 3.3 for more details.
You call us, we document your requirement, you sign the order and then we build, box and either ship it to you for installation or we host it for you so that it only needs to be activated.
If your requirements include integration work or customization, this is scheduled and delivery is subject to Production scheduling and all of this is agreed in advance.
The success or failure of any project can normally be traced back to the start, where bad planning will be found. This poor initial planning will either be as a result of bad management and leadership and to a lesser extent, the selection of technically inexperienced personnel. That is why Digi-Sign insists that no matter how much 'trouble' the project encounters en route, if it is properly planned initially, it will succeed.
Digi-CAST™ [8] is factual, high-quality, Digital Certificate and CA advice from experienced personnel that can show you how your CA should be implemented, integrated and maintained. The C-A-S-T method was pioneered by Digi-Sign in 2005 after many years of developing and deploying CAs around the world.
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ system is a complete system containing all of the necessary Operating System [OS], modules, directories and engines required to operate a fully functional CA system.
[16] The Digi-CA™ system is a complete system containing all of the necessary Operating System [OS], modules, directories and engines required to operate a fully functional CA system.
Digi-CA™ has been designed by some of the foremost experts in Internet Application Security. All modules are contained in one Linux / Unix based system. Specific care has been taken in the design of Digi-CA™ to ensure that no outside intrusion can take place and that all the private Keys for the Digi-CA™ are secure (if they are not stored on a HSM).
To ensure the uniqueness of the keys in the Digi-IDs™, Digi-CA™ uses its own entropy system. Digi-CA™ can create Key lengths up to 9192-bits. It can also support all key ciphers and signature algorithms.
Depending on the level of security required, Administrators must be authenticated by either a smart card [Digi-Card™], a USB Tokens [Digi-Tokens™] and/or a biometric reader.
The entire Digi-CA™ system infrastructure is formed mainly around x.509 certificates, produced with accordance to the internationally recognized RFC 2459 standard and is maintained in accordance to the same internationally recognized RFC 3647 standard.
The design of a typical x.509 Certificate includes the following cryptographic algorithms that are approved for commercial use by governments and related agencies and institutions around the world.
The Signature Algorithm uses RSA and DSA and as these algorithms are always used in conjunction with a one-way hash function, the following hash functions can be applied:
![]() [16] The Signature Key generation algorithms use RSA and DSA (Digi-CA™ Server only).
[16] The Signature Key generation algorithms use RSA and DSA (Digi-CA™ Server only).
The x.509 certificate can be used for many purposes, such as: electronic signature, two factor authentication [4], client authentication, email signing and encryption and many other applications.
The most common and most frequently used purposes can be included using further layers of security protocols and cryptographic algorithms, the most common of which are:
Digi-SSLs™ and Digi-Codes™ require browser compatibility. Digi-IDs™ require browser compatibility and email software compatibility when being used for Digi-Mail™ [18]
The following is a list of browsers that are compatible with Digi-SSLs™, Digi-Codes™ and Digi-IDs™:
The following is a list of browsers that are compatible with the Digi-IDs™ used for Digi-Mail™:
![]() [16] Number of certificates: 200 up to 200,000,000
[16] Number of certificates: 200 up to 200,000,000
Production speed: Without HSM up to 5,000 1024-bits Digi-IDs™/hour
With HSM up to 10,000 1024-bits Digi-IDs™/hour
Key length: Root and Intermediate Certificates 9196-1024 bits
Digi-IDs™ 1024-2048 bits
Symmetric Keys 56 to 256 bits
Key validity: Root Key 1 to 25 years
Intermediate Keys 1 to 10 years
Client Keys 1 to 10 years (as per Digi-ID™ Policy)
Key storage: Root Key off-line and stored in several separate pieces Intermediate (signing) keys access through HSM, biometric client certificates [3], smart card or USB tokens
Cryptographic Ciphers: AES, Blowfish, CAST5, DES, 3DES, IDEA, RC2, RC4, RC5 and RSA
Signature Algorithms: MD2, MD4, MD5, MDC2, SHA1 (DSSI) and RIPEMD-160
Entropy: 2127
![]() [16] The authentication, privacy and integrity of the Digi-ID™ is governed by several factors:
[16] The authentication, privacy and integrity of the Digi-ID™ is governed by several factors:
![]() [16] At the heart of every Digi-CA™ are at least one Root Key(s) or Root Certificate(s) and one Intermediate Root Certificate(s). Every Digi-CA™ Certificate is made from a Public and a Private Key. A Root Key Ceremony is a procedure where a unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated. Depending on the Certificate Policy, the generation of the Root Keys may require notarization, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples:
[16] At the heart of every Digi-CA™ are at least one Root Key(s) or Root Certificate(s) and one Intermediate Root Certificate(s). Every Digi-CA™ Certificate is made from a Public and a Private Key. A Root Key Ceremony is a procedure where a unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated. Depending on the Certificate Policy, the generation of the Root Keys may require notarization, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples:
Unless the information being accessed or transmitted is valued in terms of millions of dollars, it is probably sufficient that the Digi-CAST2™ Team [8] conduct the Root Key Ceremony within the security of the Digi-CAST2™ Laboratory. The customer may opt to have the Root Key stored on a Luna Card or HSM, but in most cases the safe storage of the Root Key on a CD or hard disk is sufficient. The Root Key is never stored on the Digi-CA™ server.
Example B: Machine Readable Travel Document [MRTD [6]] ID Card or e Passport [20]
This type of environment requires much higher security than a commercial one. When conducting the Root Key Ceremony, the Government or Organization will require rigorous security checks to be conducted on all personnel in attendance. Those that are normally required to attend the Key Ceremony will include a minimum of two Administrators from the organization, two signatories from the organization, one lawyer, a notary and two video camera operators in addition to the Digi-CAST2™ Team.
The actual Root Key-Pair generation is normally conducted in a secure vault that has no communication or contact with the outside world other than a single telephone line or intercom. Once the vault is secured, all personnel present must prove their identity using at least two legally recognized forms of identification. Every person present, every transaction and every event is logged by the lawyer in a Root Key Ceremony Log Book and each page is notarized by the notary. From the moment the vault door is closed until it is re-opened, everything is also video recorded. The lawyer and the two organization’s signatories must sign the recording and it too is then notarized.
Finally, as part of the above process, the Root Key is broken into as many as twenty-one parts and each individual part is secured in its own safe for which there is a key and a numerical lock. The keys are distributed to as many as twenty-one people and the numerical code is distributed to another twenty-one people.
Important Note: Example A and B are at opposite ends of the security spectrum and no two environments are the same. When considering the Root Key Ceremony, the Digi-CAST1™ Team [8] of professional advisors can assist you in deciding on the most efficient level of security to reflect the level of protection required.
![]() [16] A standard process for issuing a Digi-ID™ [21] Certificate involves the following stages:
[16] A standard process for issuing a Digi-ID™ [21] Certificate involves the following stages:
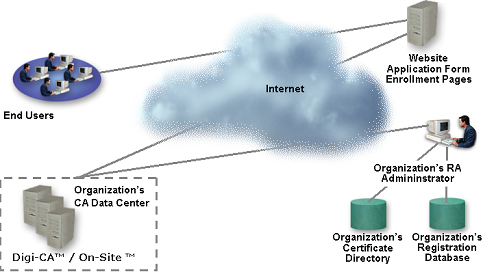
![]() [16] Digi-IDs™ are requested by the end user at the Enrollment Application Form or by the Administrator (on the users behalf) using the Digi-CA™ Control Centre.
[16] Digi-IDs™ are requested by the end user at the Enrollment Application Form or by the Administrator (on the users behalf) using the Digi-CA™ Control Centre.
From the Digi-CA™ Control Centre, all Digi-ID™ [21] requests are either entered into the database on an individual basis, using a batch upload file or automatically, depending on the Class of Digi-CA™ you are using. Similarly, all requests for Digi-IDs™ are accepted, rejected or deferred either manually or automatically, depending on the Class of Digi-CA™ you are own, using the RA Control Centre of the Digi-CA™.
The Digi-CA™ system automatically generates a Certificate Signing Request [CSR [22]] if the requesting party did not already supply one and then generates the Digi-ID™. The generation is done in batch processes according to schedules set in crontab. The default is to run the process every hour.
After generation, the Digi-ID™ is activated at the users PC or it can be delivered by email as a .p12 file. Storage of the Digi-ID™ can be on the PC or any suitable media such as a Digi-Card™ or a Digi-Token™. Similarly, the Administrator can pre-install the Digi-ID™ on the Digi-Card™ or Digi-Token™ prior to dispatch. This is particularly convenient where the Administrator wants ‘Zero Touch’ at the user’s location.
The method of distribution is set in the database at the time of the validation. The default is that Digi-IDs™ are distributed over the web, with the Digi-IDs™ holder getting an email containing a one-time password needed to pick it up.
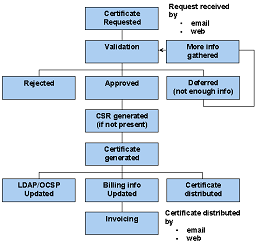
If the billing module is installed, this module is updated with information and then passed on to your billing system.

The following are the steps for issuing a Digi-ID™ Digital Signature:
The following are the steps for re-issuing/replacing an existing Digi-ID™ Digital Signature:
Typically the renewal process is simply a case of presenting the previous Digi-ID™ and a new one is issued to replace it

The Digi-CA™ [23] Certificate Authority [CA] system (that issues the Digi-ID™ end user digital signatures) can issue thousands of digital signatures every hour. This 'endless' capacity means that getting Digi-ID™ digital signatures to the end users can occur as quickly as your environment demands.
How the Digi-ID™ digital signatures are issued is set by the 'Enrolment Policy [24]'. The options within the Enrolment Policy are designed to be very flexible. They can be customised to meet almost any requirement with many different settings and combinations. The three basic options are:
Issuing the Digi-ID™ digital signatures is either a one or two stage process. Either the user receives an email inviting them to apply for their digital signature, or they are referred from an existing online site/system to the Digital Signature Application form.
However the user is prompted to get their digital signature, in the first stage, the Digi-CA™ Inviting 'action' requires the end user 'reaction' (completing an application form). In the second stage, the Digi-CA™ Approving 'action' requires the end user 'reaction' (activating the digital signature) and this completes the process. It is best understood as follows:
As stated, because the Enrolment Policy is very flexible, there are many different ways to invite and approve end users digital signatures. The following is a sample issuing process only. You may wish to include other options, as required.
Stage One 'Digi-CA™ Action' - Inviting Digi-ID™ Digital Signature Applications
Using the Digi-CA™ RA Management Console interface, the Administrator uploads a .CSV batch file inviting [25] as many users as required.

Stage One 'User Reaction' - Completing Enrolment Form
The Digi-CA™ system sends an email to each end user with a unique link to the Digi-ID™ digital signature enrolment form. Using the link provided in the email, the end user then completes the Digi-ID™ digital signature enrolment form.
Note:- this is the default Digi-ID™ End Entity Digital Signature Enrolment Form. This form uses basic HTML programming that can be altered [26] to match your specific design requirements.

Once the end user completes all the fields and submits the enrolment form to the Digi-CA™ system, the Administrator is notified. The Administrator then approves [24] each end user application using the Digi-ID™ Digital Signature Authorization Panel.
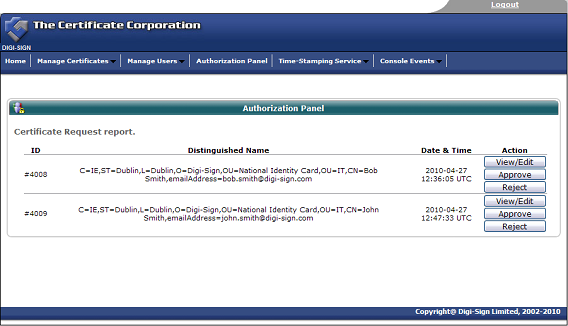
Stage Two 'User Reaction' - Activating the Digi-ID™ Digital Signature
Assuming the Administrator approves the application, the Digi-CA™ system sends a new email to the end user advising them that their application has been approved. Using the link provided in the email, the end user then activates [27] the Digi-ID™ digital signature and this completes the issuing process.
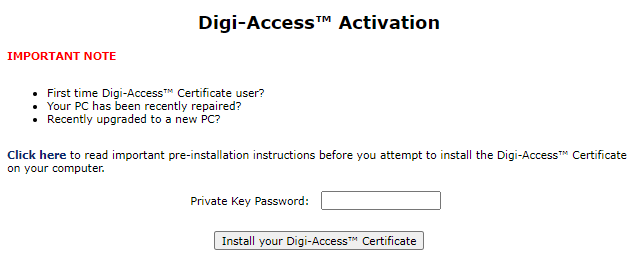

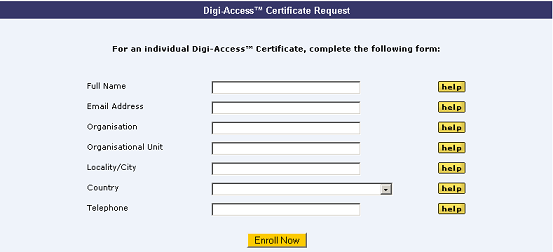
Once the enrolment form is completed and submitted by the end user, the Enrolment Policy enforces how the application is handled by the Digi-CA™ system. Learn more about the Enrolment Policy [24] options or browse the other pages below.


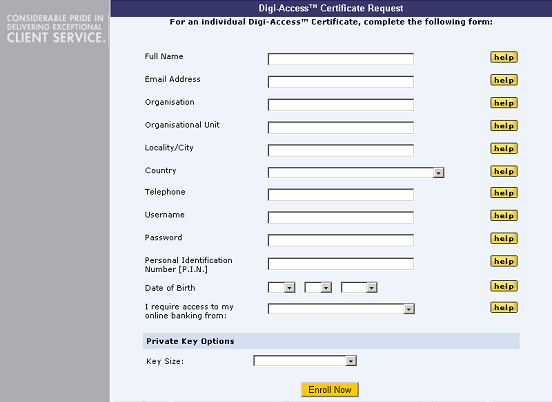
Once the invitation is issued, the end user must complete the enrolment form. View customised enrolment [26] forms or browse the other pages below.

The Enrolment Policy for Digi-ID™ controls the entire certificate issuing process. Enrolment Policy is set by the Certificate Policy [CP] for the Digi-CA™. This is a specialist subject and requires experienced knowledge of Certificate Authority [CA] systems and Public Key Infrastructure [PKI]. Keeping this complex topic simple, there are three basic options for Enrolment Policy:


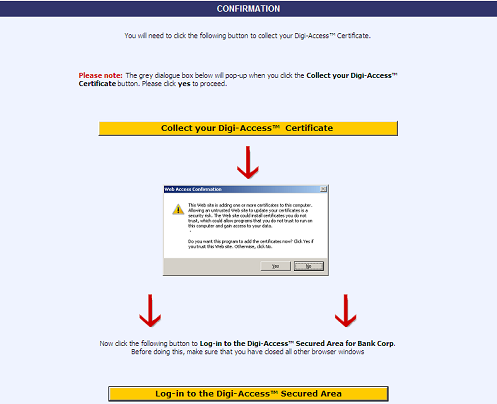
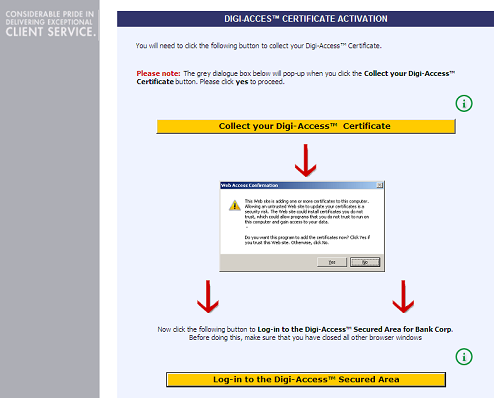
Once the enrolment form is completed and submitted by the end user, the Enrolment Policy enforces how the application is handled by the Digi-CA™ system. Learn more about the Enrolment Policy [24] options or browse the other pages below.

|
Microsoft® Internet Explorer® |
Mozilla/Firefox/Safari |
|
1. To view your Digi-ID™ digital signature in Microsoft® Internet Explorer®, use the Tools menu (you may have to press the 'Alt' button on your keyboard to view this menu) and then select Internet Options 2. In the Internet Options dialog box, select the Content tab and then click the Certificates button 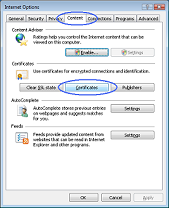 3. In the Certificates dialog box, select the certificate/digital signature you wish to examine and then click the View button 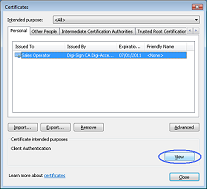 4. The chosen digital signature will be displayed where you will be able to see:
 |
1. To view your Digi-ID™ digital signature in Mozilla, Firefox or Safari, use the Tools menu and then select Options 2. In the Options dialog box, select the Encryption tab and then click the View Certificates button 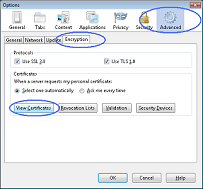 3. In the Certificate Manager dialog box, select the certificate/digital signature you wish to examine and then click the View button  4. The chosen digital signature will be displayed where you will be able to see:
 |


|
Microsoft® Internet Explorer® |
Mozilla Firefox |
|
1. To view your Digi-ID™ digital signature in Microsoft® Internet Explorer®, use the Tools menu (you may have to press the 'Alt' button on your keyboard to view this menu) and then select Internet Options 2. In the Internet Options dialog box, select the Content tab and then click the Certificates button  3. In the Certificates dialog box, select the certificate/digital signature you wish to examine and then click the View button  4. The chosen digital signature will be displayed where you will be able to see:
 5. Once you have viewed and confirmed this is the Digi-ID™ digital signature you wish to remove, return to the Certificates dialog box, select the certificate/digital signature and click the Remove button |
1. To view your Digi-ID™ digital signature in Mozilla Firefox, use the Tools menu and then select Options 2. In the Options dialog box, select the Encryption tab and then click the View Certificates button  3. In the Certificate Manager dialog box, select the certificate/digital signature you wish to examine and then click the View button  4. The chosen certificate/digital signature will be displayed where you will be able to see:
 5. Once you have viewed and confirmed this is the Digi-ID™ digital signature you wish to delete, return to the Certificate Manager dialog box, select the digital signature and click the Delete button |
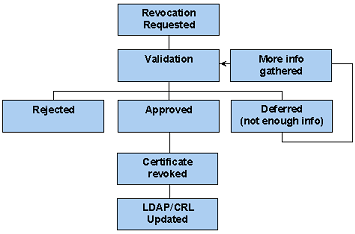
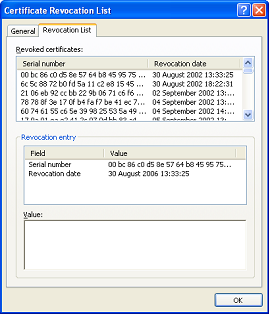
![]() [16] All Digi-ID™ revocations are initiated either by the user or by the Administrator. Revocations are required for a number of reasons, for example:
[16] All Digi-ID™ revocations are initiated either by the user or by the Administrator. Revocations are required for a number of reasons, for example:
1. the user has lost the PC or media where the Digi-ID™ was stored.
2. the user no longer has any affiliation with the organisation that issued the Digi-ID™.
3. the user changed position in the organisation and no longer has any right to the Digi-ID™.
4. the Administrator believes a Digi-ID™ has been misused.
5. the Administrator believes a Digi-ID™ used to misrepresent the organization that issued the Digi-ID™.
The following sub sections detail how Revocation requests are made and the resulting actions and uses for this important feature.
The following diagram explains the events that occur within the Digi-CA™ and how a revocation request is executed:
![]() [16] The digital signature [3] and message encryption implementation on email messages is achieved by mechanisms implemented directly in the email client software and that follows the S/MIME standard.
[16] The digital signature [3] and message encryption implementation on email messages is achieved by mechanisms implemented directly in the email client software and that follows the S/MIME standard.
Both S/MIME message encryption and Digital Signatures are based on encryption technologies. Message body encryption creates a completely unreadable message body and Digital Signature. The diagram below shows how the encryption process generates a one-time Symmetric Key (also called a Session Key) that encrypts the message body.
The Symmetric Key is then encrypted with each recipient’s Public Key so that only the recipient can decrypt the Symmetric Key. The message is then sent. On the recipient end, the Private Key is used to decrypt the Symmetric Key, which is then used to decrypt the message. This process is transparent to the user and is performed with no interaction between clients. Symmetric encryption is much faster than asymmetric encryption. The reason is because symmetric encryption encrypts the data (message body) in bulk.
The following diagram describes how email encryption is achieved:
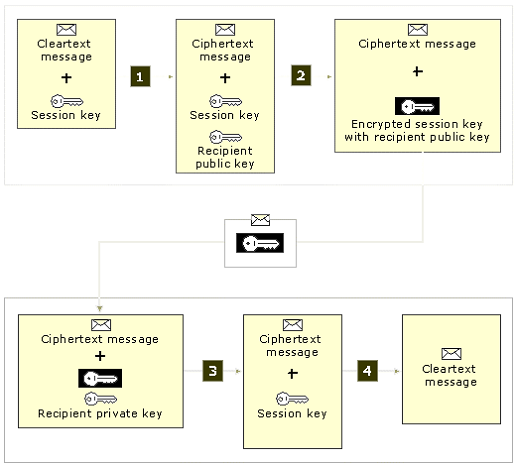
The diagram illustrates the message encryption and decryption process. The four main steps detailed in the illustration are as follows:
2. Session Key is encrypted with recipient’s Public Key.
3. After encrypted message is received, recipient decrypts Session Key with the recipient’s Private Key.
4. Message is decrypted with Session Key.
When you add a Digital Signature to a message, a hash value of the message contents is computed. User Keys aren’t used to compute the hash value and the hash doesn’t identify anyone. The hash is only a small, unique digital fingerprint of the message. This hash value is then encrypted with the sender’s Private Key, and can be decrypted with the Public Key found in the sender’s certificate.
The recipient decrypts the original hash value with the sender’s Public Key, which might be sent with the signed message or can be found in the sender’s certificate. Your client verifies signatures. For encrypted messages, it decrypts the message first. The client computes a new hash value based on the text received and compared to the original hash value. If they match, you can trust the content’s integrity and the sender’s identity.
The Digi-CA™ system can create multiple instances of unique CAs in a single Digi-CA™ system. The Digi-CA™ model imposes delegation of trust downwards from CAs to their Subordinate Certification Authorities [Sub-CAs]. The same Digi-CA™ system also enables any CA or Sub-CA to be signed or cross signed by an external third party CA. And any number of CAs can have any number of cross signed Sub-CAs. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CA™ model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI requirement from the smallest to the largest.
Digi-CA™ replaces older Traditional PKI [28] technology and CA systems using the latest in CA technology. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Traditional CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level. Digi-CA™ can also be ‘dropped’ on top of these Traditional CA environments and seamlessly migration [29] the older system’s users into this more modern and flexible replacement.
At its core, the Digi-CA™ system works on Unix/Linux operating systems and was written using C programming language for the low application level and PHP at the high level. The design philosophy was that the simplicity of the complete system should also be capable of large scale enterprise or national CA system, so that it could be delivered and scaled, easily. This critical design component has not changed in the past seven years.
To enable this, the modular design of Digi-CA™ allows easy and flexible service distribution to multiple numbers of servers, thus achieving high level of service availability. Each system component [30], for example the Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP], and all system modules [31] can be installed and operated on a multiple number of servers that can further be configured in a variety of high availability modes such as fail over, cluster and load balanced.
In each case, software or hardware high availability solution can be independently implemented to achieve best option suitable for your environment. And even more importantly, Digi-CA™ has the ability to scale, easily and without interrupting the live production environment at any stage during the life of your system.
The Digi-CA™ System can issue, revoke, suspend, de-suspend and re-sign x.509v3 Digital Certificates. Time-Stamping, Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP], Certificate Revocation Lists [CRLs] and many other features of a PKI system can be activated as required using the administration console of the system.
End user information and certificate requests are entered through the web based Registration Authority [RA] Management Console [32]. This powerful RA Management Console manages the entire Certificate Life cycle. Basic Certificate issuing and revocation by Operatives can be further delegated through a basic and modified RA Management Console interface called the Digi-CA™ Control Centre. It is the Digi-CA™ Limited RA [LRA] - Control Centre [33] that is used by the RA Operator on a day-to-day basis.
Unlike any other CA system in the market, Digi-CA™ is specifically designed to easily migrate any other existing PKI system. By design Digi-CA™ [23], as a entirely self dependent system, allows its easy migration from one data centre to another in an almost seamless manner. The transfer can be accomplished either physically through hardware transportation or by secure software and data migration whereby all software and database data is securely migrated in an encrypted format from one location to another.
The key features necessary for running your existing framework PKI infrastructure are already embedded in the Digi-CA™ System as standard. It additionally offers a much wider scale of possibilities in using PKI throughout your entire organisation. Where Traditional CA [28]s offer most modules as add-ons (and at additional cost), Digi-CA™ offers these 'as standard' and provides alternative key generation, certificate enrolment and certificate installation features, with policy based controls, in compliance with most current commercial and open standards. Digi-CA™ also supports a large variety of third party software and cryptographic hardware devices such as smart cards, USB tokens and Hardware Security Modules [HSMs].
In conjunction with your existing on line applications and PKI infrastructure, features provided by Digi-CA™ can introduce and add enhanced support and security to inbound and outbound email exchange communications through the use of S/MIME. Also, web server and web client strong and multi factor authentication using Public Key Certificates and SSL/TLS communication protocols, signing of application code, authentication of network routers, firewalls and Virtual Private Network [VPN] devices and many other business-to-client and business-to-business PKI aware solutions too.
To migrate your system, the Digi-CAST™ [36] methodology, you will experience a smooth transition process from your current PKI framework. The Digi-CAST™ Team consists of highly qualified, expert IT engineers responsible for providing analysis, planning and implementation services to meet the your requirements and allows you to completely 'off load' all activities in these areas. The Digi-CAST™ method will provide for a detailed migration plan that outlines all phases of the migration process and provides estimated delivery schedules for each phase of the project, leaving no space for omissions or lengthy implementation delays by providing best Digi-CAST™ guaranteed quality of service.
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ system is built in several modules. Each module communicates with other modules either directly through a programmable socket interface or an API interface. The system design is such that no access is allowed to the system Certificate Engine core level, except through the web based interface panel or through SSH for power low level administrators only [super users].
[16] The Digi-CA™ system is built in several modules. Each module communicates with other modules either directly through a programmable socket interface or an API interface. The system design is such that no access is allowed to the system Certificate Engine core level, except through the web based interface panel or through SSH for power low level administrators only [super users].
There is one operating system and four principle modules in the Digi-CA™ and how they are implemented for your requirements depends on the Certificate Policy:
As an option the following sub-systems can also be installed:
The above options are available subject to consultation and are listed here for indicative purposes only.
Digi-CA™ has been designed and is built for Unix / Linux compatible operating system platforms. Typical installations use FreeBSD 5.4+ Unix or a RedHat Enterprise Linux based operating system.
The main module of the system is the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core that is used for the creation and revocation of Certificates based on the system Certificate Policy. It uses a direct interface to the Digi-CA™ Information Database that contains information about all Digi-ID™ [21] Certificate holders and the issued (or pending to be issued, suspended or revoked) Certificates. Output from the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core is directed to:
The Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core is designed so that no Administrator intervention is necessary. Using a daemon server, important maintenance tasks occur automatically.
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ This module is used for storing:
[16] The Digi-CA™ This module is used for storing:
The database is SQL based and by default the system is installed with MySQL database server. At an additional cost, the Administrator can define what database to use (PostGRE SQL, Oracle®, DB2®, SQL Server®, Websphere®, etc).
Based on information stored in the database, the system generates requests for creation, suspension (if enabled) and revoking of Digi-ID™ [21] certificates to the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core.
The Digi-CA™ Directory stores Digi-ID™ Certificates and user data according to current international RFC standards. The schemas used are core, cosine and internetperson. The schemas are stored in a directory. Access to the directory is available through an LDAP compatible client.
The Digi-CA™ Control Centre is the Administrators’ interface for controlling the day-to-day operation of the Digi-CA™ system. The Digi-CA™ Control Centre provides all of the deployment and life cycle management functions of the Digi-IDs™ and any other Digital Certificates [3] the system issues. One or more Administrators can manage the Digi-CA™ Control Centre. Depending on the level of security required, Administrators must be authenticated using Digi-Access™ [40], Digi-Card™, Digi-Token™ and/or a biometric reader.
Digi-CA™ uses the x.509 standard Certificate Revocation List [CRL] format so that Digi-ID™ information can be made publicly available at a designated web address. This is the repository for all issued Digi-IDs™ and enables integration of Digi-IDs™ into third party or custom applications an easy task.
Recent ANSI, ETSI and ICAO guidelines have recommended the use of Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] [11] for certain environments. Offering OCSP as a service can cause considerable traffic on your network and should only be considered where there is a statutory or compliance [9] requirement.
In all other cases, the CRL service is the preferred method of communicating the status of the Digi-ID™.
![]() [16] After the environment has been prepared and the Certificate Policy (and in the case of Xg the Digi-Sign Certificate Practice Statement [12]) agreed, the software is configured. Software configuration may be as simple as designing the SSRoot & Intermediate Certificates or it can be a complex environment requiring compliance and standards, integration and application development.
[16] After the environment has been prepared and the Certificate Policy (and in the case of Xg the Digi-Sign Certificate Practice Statement [12]) agreed, the software is configured. Software configuration may be as simple as designing the SSRoot & Intermediate Certificates or it can be a complex environment requiring compliance and standards, integration and application development.
A simple configuration can be completed in 2-3 days with full-scale projects running into several months of configuration, documentation and implementation. The following descriptions are provided here as guidelines only:
Configuration Time: 2 Days
Configuration Time: 25 Days
Configuration Time: 5 Days
Configuration Time: 90+ Days
Once the software is configured, installation of the Digi-CA™ can begin. Subject to project scheduling, and Digi-CAST2™ [8] availability, the following are indicative installation times. You should also note that the installation also includes Administrator and RA training:
As Digi-CA™ Xg is usually a highly customized setup [41], the following sections focus on the installation of the Xs and Xp environments for Digi-CA™ Server and Digi-CA™ Service.
![]() [16] Ordering and operating a Digi-CA™ Service Xs or Xp couldn’t be simpler. All you require is a single internet enabled PC with Internet Explorer 5.5+ and the Digi-CAST2™ Team [8] will either send you a Digi-Card™ and smart card reader or a Digi-Token™ USB token that enables you to access the Service or you will be permitted to store the Administrator’s Digi-ID™ [21] in the Certificate Store of the PC.
[16] Ordering and operating a Digi-CA™ Service Xs or Xp couldn’t be simpler. All you require is a single internet enabled PC with Internet Explorer 5.5+ and the Digi-CAST2™ Team [8] will either send you a Digi-Card™ and smart card reader or a Digi-Token™ USB token that enables you to access the Service or you will be permitted to store the Administrator’s Digi-ID™ [21] in the Certificate Store of the PC.
Whoever logs into the system first is assigned PRIMARY Administrator status with access to all areas and functions of the system. The PRIMARY can invite other Administrators onto the system and may even reassign PRIMARY status to another person.

The Digi-CA™ Service ‘ownership’ is strictly controlled so that the identity of the PRIMARY Administrator is a carefully monitored process. Once the identity of this Administrator is Validated, they are invited to enroll for the Administrator’s Digi-ID™ and this used as two factor authenticated access to the Service. The first time this Administrator logs into the system, they must agree to the Terms & Conditions of the service by clicking the ‘I Agree’ log in button on the index page (see Appendix V.iii). This acceptance uses the electronic signature capability of the Digi-ID™ to sign the Digi-CA™ Service contract with Digi-Sign before permitting access to the system. All subsequent Administrators, regardless of their status, must also digitally sign the same contract but ultimate responsibility resides with the very first Administrator to access the system.
There are no other hardware, software or contracts required by the Administrators of the Digi-CA™ Service and, subject to the Digi-CAST2™ [8] Production Schedule, they can usually order and receive their required system in a few days.
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ Server, by nature of the fact that it is installed software (usually at the customer site), is a more involved process with hardware, software, documentation and installation requirements. The basic requirements for every Digi-CA™ Server installation are the same and in most instances, Digi-CAST2™ [8] install the Digi-CA™ Server system on your server(s). As more sophisticated environments arise for Digi-CA™ Server Xp or Digi-CA™ Server Xg, the requirements increase accordingly.
[16] The Digi-CA™ Server, by nature of the fact that it is installed software (usually at the customer site), is a more involved process with hardware, software, documentation and installation requirements. The basic requirements for every Digi-CA™ Server installation are the same and in most instances, Digi-CAST2™ [8] install the Digi-CA™ Server system on your server(s). As more sophisticated environments arise for Digi-CA™ Server Xp or Digi-CA™ Server Xg, the requirements increase accordingly.
The following sections describe the basic requirements for installing the three classes of Digi-CA™ Server and the three main components are detailed in each case:
The Digi-CA™ Server Xs is usually installed on a single server and if the correct internet connection and secure Virtual Private Network [VPN] can be provided to the server, it is possible that the installation of the software can be carried out virtually.
The benefit of this is that it reduces the cost of travel and accommodation. When examining each of the following three sub sections you can consult with the Digi-CAST2™ Team at any time to check configurations and access for you.
These are the minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
![]() [16] These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
[16] These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
Digi-CA™ Server Xs is supplied complete and ready for total install on the server. There is no requirement for any Operating System [OS] or pre-configuration, whatsoever. In fact, if the Server is not completely free of any OS or software, it must be formatted to return it to its original ‘as manufactured’ state.
During the installation, the Digi-CA™ Server will use versions of the following software that will be hardened and modified by the Digi-CAST2™ [8] Team during their installation work:
The previous list is provided for information purposes only.
These are the minimum requirements for the correct installation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ Server Xp is usually installed on two servers and if the correct internet connection and a VPN can be provided to the servers, it is possible that the installation of the software can be carried out virtually.
[16] The Digi-CA™ Server Xp is usually installed on two servers and if the correct internet connection and a VPN can be provided to the servers, it is possible that the installation of the software can be carried out virtually.
The benefit of this is that it reduces the cost of travel and accommodation. When examining each of the following three sub sections you can consult with the Digi-CAST2™ Team [8] at any time to check configurations and access for you.
These are the minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp:
Digi-CA™ Server Xp is supplied ready for total installation on the two servers. There is no requirement for any Operating System [OS] or pre-configuration, whatsoever. In fact, if the servers are not completely free of any OS or software, they must be formatted to return them to their original ‘as manufactured’ state.
During the installation, the Digi-CA™ [23] will use versions of the following software that will be hardened and modified by the Digi-CAST2™ Team during their installation work:
The above list is provided for information purposes only.
These are the minimum requirements for the correct installation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp:
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ Server Xg is completely customizable and can be installed across many servers, even if they are in different locations. A Trust Centres [10] example would use four servers and if the correct internet connection and a VPN can be provided to the server, it is possible that much of the installation of the software can be carried out virtually. However, the Digi-CA™ Server Xg will require at least one site visit from a Digi-CAST™ Team Member [8] to conduct certain specialist tasks.
[16] The Digi-CA™ Server Xg is completely customizable and can be installed across many servers, even if they are in different locations. A Trust Centres [10] example would use four servers and if the correct internet connection and a VPN can be provided to the server, it is possible that much of the installation of the software can be carried out virtually. However, the Digi-CA™ Server Xg will require at least one site visit from a Digi-CAST™ Team Member [8] to conduct certain specialist tasks.
The benefit of using the VPN connection as much as possible is that it reduces the cost of travel and accommodation. When examining each of the following three sub sections you can consult with the Digi-CAST2™ Team at any time to check configurations and access for you.
These are the minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the multiple server Digi-CA™ Server Xg:
These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the multiple server Digi-CA™ Server Xg:
Digi-CA™ Server Xg is supplied ready for total installation on the desired number of servers. There is no requirement for any Operating System [OS] or pre-configuration, whatsoever. In fact, if the servers are not completely free of any OS or software, they must be formatted to return them to their original ‘as manufactured’ state.
During the installation, the Digi-CA™ [23] will use versions of the following software that will be hardened and modified by the Digi-CAST2™ Team during their installation work:
The above list is provided for information purposes only.
These are the minimum requirements for the correct installation of the multiple server Digi-CA™ Server Xg:
![]() [16] Once the Certificate Policy Requirements are documented and available, the project process can begin. The Digi-CA™ project can be sub-divided into five separate undertakings:
[16] Once the Certificate Policy Requirements are documented and available, the project process can begin. The Digi-CA™ project can be sub-divided into five separate undertakings:
The Certificate Policy sets out the system design, RA function and overall workflow of the system and also the Root Certificate(s) and Intermediate Root Certificate(s) design. As explained in the Requirements section of this document, the Digi-CA™ is pre-configured prior to delivery at the customer site.
During the software configuration, the Digi-CAST2™ Team [8] will produce test Root Certificate(s) and Intermediate Certificates(s) for your approval. Again, depending on the Certificate Policy, the actual Root(s) and Intermediate Certificate(s) may be generated prior to delivery. Other workflow and processes may also need to be verified. Finally, all the interfaces for the End User and Administrators can be customized to reflect the organization’s identity and/or local language.
Once the configuration is complete it is compiled, complete with ‘hardened’ Operating System [OS] and software, and delivered on a CD or DVD to the customer site.
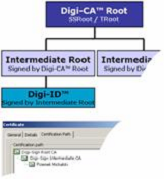
At the heart of every Digi-CA™ are at least one Root Key or Root Certificate and one Intermediate Root Certificate(s). Every Digi-CA™ Certificate is made from a Public and a Private Key. A Root Key Ceremony is a procedure where a unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated. Depending on the Certificate Policy, the generation of the Root Keys may require notarization, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples:
The Root Certificate is only ever used to sign the Intermediate Root Key(s). After signing this Key(s) the Root Key is 3-DES encrypted and split into a minimum of 4 Key shares that are each stored on 3-DES encrypted smartcard and signed with SHA-1. All Key shares will have a unique password and should be stored separately in different secure locations (bank vault, safety deposit box, attorney’s office, etc). A Key generation log is kept in the system and in a separate physical log.
Important Note: the Root Certificate should not exceed a 25-Year life duration.
The Intermediate Root Certificate is protected by 3-DES encryption and all key shares have unique passwords.
Important Note: the Root Certificate should not exceed a 25-Year life duration.
In order to create Digi-IDs™ from the system, at least one self-signed Digi-CA™ Root Certificate must be generated. There is a possibility in the system, depending on ordered options, to create any number of Digi-CA™ Root Certificates and Digi-CA™ Intermediate Roots with different policies and validity. The figure below represents a theoretical relationship between Digi-CA™ Root Certificates. Please consult Digi-CAST1™ before setting up your specific schema.
![]() [16] Digi-CA™ is normally installed by Digi-CAST2™ [8] but in the case of a very basic Digi-CA™ Xs installation (and based on the availability of experienced Network Engineers), you may be capable of installing the Digi-CA™ Xs using its documentation and simple telephone support from a Digi-CAST2™ Team member.
[16] Digi-CA™ is normally installed by Digi-CAST2™ [8] but in the case of a very basic Digi-CA™ Xs installation (and based on the availability of experienced Network Engineers), you may be capable of installing the Digi-CA™ Xs using its documentation and simple telephone support from a Digi-CAST2™ Team member.
The basic Digi-CA™ Xs installation can be completed in three to five days. See Appendix II for two examples of a Single Server and a Dual Server installation. The following is a brief installation schedule:
A Digi-CA™ Xs customized installation may take additional time to configure and a Digi-CA™ Xp or Digi-CA™ Xg installation, using the basic outline as described above, takes longer.
The system activation of the Digi-CA™ is also an integral part of the installation process and is completed, checked and approved by the customer before the Digi-CAST2™ Team leaves the customer site. The online flash presentation of Digi-CA™ [42] explains the benefits in a simple and easy to understand manner.
![]() [16] The Digi-CA™ is probably the most flexible and capable CA system available in the market today. Unlike the other Traditional CA [28]s, Digi-CA™ takes advantage of the many advances in technology over the past seven years and you benefit by getting the most flexible, cost effective and easily integrated and/or migrated [43] CA system you need.
[16] The Digi-CA™ is probably the most flexible and capable CA system available in the market today. Unlike the other Traditional CA [28]s, Digi-CA™ takes advantage of the many advances in technology over the past seven years and you benefit by getting the most flexible, cost effective and easily integrated and/or migrated [43] CA system you need.
The Digi-CA™ still uses Unix in its Certificate Engine core but by using Open Source PKI technology in other modules, Professional Services and upgrade costs are substantially less than those normally associated with the complex and costly modifications of the less flexible Unix Traditional CAs.
In the larger or more complex environment, the organization may require a workflow process to control the use of the Digi-CA™ usage from a cost, security or for general management reasons. The following is an example of a customization currently in use by a Digi-Sign customer for issuing Digi-SSLs™:
This type of customization is not unusual but it does add to the initial cost of deploying a Digi-CA™ system.
Every aspect of the Digi-CA™ can be automated. Examples of this would be where the Digi-IDs™ are being used to replace Usernames and Passwords for login to a secure website, to replace hardware tokens like SecurID®, to issue Digi-IDs™ for secure email [3] on a closed network or to replace an existing Traditional CA with Digi-CA™.
Using the Digi-CA™ technology and its capabilities, it is possible to use existing LDAPs or other databases such as Oracle®, Active Directory® or any other SQL or flat file format to automate the Digi-ID™ [21] issuing, renewal, suspension and revocation processes.
Using the authentication and validation Certificate Policies from your Traditional CA, Digi-CA™ can migrate users automatically without requiring any IT resources or Administrators’ time.
![]() [16] The entire Digi-CA™ system and all of the interfaces used by the Administrators and users can be completely customized on request. Typical reasons for the graphical changes are for integrating Digi-CA™ into a larger application to make a complete package or the simpler integration of the Digi-CA™ into the organization’s web systems or extranet.
[16] The entire Digi-CA™ system and all of the interfaces used by the Administrators and users can be completely customized on request. Typical reasons for the graphical changes are for integrating Digi-CA™ into a larger application to make a complete package or the simpler integration of the Digi-CA™ into the organization’s web systems or extranet.
The specification of the Digi-CA™ at the time of going to print is available in Appendix IV. All specification updates and technical help files are updated using the online support section of the Digi-Sign website located at www.digi-sign.com [44].
As is the case with sub section 6.5, Digi-CA™ offers the capability to completely localize all interfaces, help files and user screens into your local language(s). This is particularly important to organizations where English is not used. It is also possible to have multiple interfaces with multiple languages for the same system. The following two samples show the Digi-CA™ Control Centre screen in Chinese and the user enrollment screen where users can apply for a [21]Digi-ID™ in Turkish.
The importance of the capability to produce the Digi-CA™ in the local language(s) cannot be over stated. It will result in faster training of the RA personnel and will significantly reduce the Help Desk Support calls (where users are seeking help to with translations from English rather than actual technical support related issues).
It is also possible to have a single Digi-CA™ configured in multiple languages so that different Digi-RAs™ in different countries can use the same Digi-CA™ Control Centre in their native language. Similarly, the users requesting Digi-IDs™ can do so from the same system but again in their native language.
To have your Digi-CA™ localized in your language, the system files and instructions are available in Appendix V.
The following are sample Digi-CA™ installation diagrams, schedule and technical schematics for review.
![]() [45] The following diagram explains the ideal environment for running the Digi-CA™ Server Xs single server system. The Strong Room/locked server cabinet should be a secured with biometric access, ideally with main power supply and a backup power supply with at least one reliable internet connection. Access to this area should be restricted to Administrators only. Two trusted and approved Administrators should be present at all times when the area is being accessed.
[45] The following diagram explains the ideal environment for running the Digi-CA™ Server Xs single server system. The Strong Room/locked server cabinet should be a secured with biometric access, ideally with main power supply and a backup power supply with at least one reliable internet connection. Access to this area should be restricted to Administrators only. Two trusted and approved Administrators should be present at all times when the area is being accessed.
![]() [45] The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![]() [45] The following is the time required to install a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following is the time required to install a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
Days Project Part Persons Description
0.5 Server Configurations
0.5 RA Core configuration, Digi-CA™, RA and Public services configuration
0.5 Network connectivity and service accessibility tests
0.5 Root and Intermediate CA Key Ceremony
0.5 Digi-CA™ Administration Training
0.5 RA Training
3 Total Project Installation Time
Note: This installation can be conducted by two personnel, a qualified IT person and a Network Engineer. Alternatively, Digi-CAST2™ can conduct the installation and in some cases this can occur from outside the environment using virtual access (this means there is no on site visit required).
![]() [45] The following is the time required to install a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following is the time required to install a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
Days Project Part Persons Description
0.5 Server Configurations
0.5 Digi-CA™ Core configurations
0.5 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services configuration
1 HSM configuration
0.5 Network connectivity and service accessibility tests
0.5 Root and Intermediate CA Key Ceremony
0.5 Digi-CA™ Administration Training
0.5 RA Training
4.5 Total Project Installation Time
![]() [45] The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![]() [45] The following diagram explains the ideal environment for running the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system. The Strong Room/locked server cabinet should be a secured with biometric access, ideally with two power supplies and two separate internet connections from two different providers. Access to this area should be restricted to Administrators only. Two trusted and approved Administrators should be present at all times when the area is being accessed.
[45] The following diagram explains the ideal environment for running the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system. The Strong Room/locked server cabinet should be a secured with biometric access, ideally with two power supplies and two separate internet connections from two different providers. Access to this area should be restricted to Administrators only. Two trusted and approved Administrators should be present at all times when the area is being accessed.
![]() [45] The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![]() [45] The following is the time required to install a dual server Digi-CA™ Xp system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following is the time required to install a dual server Digi-CA™ Xp system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
Days Project Part Persons Description
1 Server Configuration
1 RA Core configuration
1 Digi-CA™ Server Failover and Database Replication configuration
1 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services configuration
0.5 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services redundancy configuration
1 Network connectivity and service accessibility tests
0.5 Root and Intermediate CA Key Ceremony
0.5 Digi-CA™ Administration Training
0.5 RA Training
7 Total Project Installation Time
![]() [45] The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![]() [45] The following is the time required to install a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
[45] The following is the time required to install a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
Days Project Part Persons Description
1 Server Configuration
1 Digi-CA™ Core configuration
1 Digi-CA™ Server Failover and Database Replication
1 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services configuration
0.5 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services redundancy configuration
1 HSM configuration
1 Network connectivity and service accessibility tests
0.5 Root and Intermediate CA Key Ceremony
0.5 Digi-CA™ Administration Training
0.5 RA Training
8 Total Project Installation Time
![]() [45] The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a multi-server Digi-CA™ Server Xg, full redundancy system with a HSM and optional HSM Fail Over (not shown).`
[45] The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a multi-server Digi-CA™ Server Xg, full redundancy system with a HSM and optional HSM Fail Over (not shown).`
![]() [45] The following is the time required to install a multi-server Digi-CA™ Server Xg full redundancy system with an HSM.
[45] The following is the time required to install a multi-server Digi-CA™ Server Xg full redundancy system with an HSM.
Days Project Part Persons Description
2 Server Configuration
1 Digi-CA™ Core configuration
1 Digi-CA™ Server Failover and Replication
1 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services configuration
0.5 Digi-CA™ RA and Public services redundancy configuration
1 HSM configuration
1 Network connectivity and service accessibility tests
0.5 Root and Intermediate CA Key Ceremony
0.5 Digi-CA™ Administration Training
0.5 RA Training
9 Total Project Installation Time
Implementing a Public Key Infrastructure [PKI], a Certificate Authority [CA] and then using Digital Certificates requires extensive technical knowledge and experience. In a single Digi-CA™ [23] project, often there is a requirement to comply with more than 70 standards [46] and this list of regulatory requirements is constantly being updated.
In addition to the complexities of the technology and the need for extensive experience, the commercial sensitivity of any tri-party relationship (i.e. Customer - ARP Member - Digi-Sign) and the importance of a strong ARP management system cannot be over stated. This is not necessary in the case of an ARP Affiliate [47], but with the ARP Reseller or Partner [47], closer co-operation and empowerment is essential.
Technical 'know how' and compliance are only one aspect of any project and although they may be important, there are many other aspects of the project that must be considered if it is to be successful. For example:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/knowledgebase.png)
This guide is intended to assist buyers in selecting [51] the correct Digi-CA™ Certificate Authority [CA] system for their environment. It is assumed that the audience and readers of this guide have a basic understanding of the concepts of information technology, CA systems and the use of digital certificates and signatures.
Organisations choose to use a CA for many reasons and ultimately it relates to using the internet to improve efficiency, reduce costs and/or increase market reach. In almost every instance, using the internet in these ways encounters security issues of identifying users, authenticating of transactions, events and times, the need for secure servers, digital document and workflow signing and related matters.
Whilst a CA cannot address every conceivable security issue, it solves most of them. There are several recognised CA providers, but few can compete with the ease-of-use and management capabilities offered by Digi-CA™ [51].
A CA issues digital certificates and digital signatures for use by end users or servers. They are used for securing servers (i.e. https:// and the ‘little yellow lock’ that is seen when making payments online) and also for:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ is the complete CA system for organisations that would like to have their own CA or would like to own and manage a Public Key Infrastructure [PKI] for digital certificates, inside the organisation, or over the Internet. Digi-CA™ generates and manages digital public key certificates that are used for a variety of different purposes, most commonly for secure server connection [51], electronic signatures, natural person and/or device authentication and for secure email.
The Digi-CA™ system can create multiple instances of independent CAs in a single Digi-CA™ system deployment. The Digi-CA™ model imposes delegation of trust downwards from Root CAs to their Subordinate CAs using a concept called ‘layered hierarchy’. The same Digi-CA™ system also enables a CA to be cross signed by an external third party CA. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CA™ model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI requirement from the smallest to the largest.
Digi-CA™ can be delivered as an installed Software CA, or as a Managed CA service [59]. Uniquely, both the Managed Digi-CA™ Service and the installed Digi-CA™ Server software [60] use the same common, core technology. This is important because in selecting Digi-CA™ it is possible to begin with Digi-CA™ Service and migrate to Digi-CA™ Server with ease.
It is possible to use the distributed architectural design of Digi-CA™ to implement the concept of a ‘Shared CA’ where different modules of the system are hosted and managed in separate geographical locations.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ replaces older Legacy CA systems using the latest in CA and PKI technologies and benefits from combining commercial and open source software initiatives. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Legacy CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level.
By combining the consulting and professional services [51] offered by Digi-CAST™ with the functions provided by Digi-CA™, can bring an organisation to a highly professional PKI level, meeting the criteria for internationally recognised accreditation standards such as WebTrust® and ISO 27001 certifications.
| Compliance to international standards | Digi-CAST™ follows the international industry standards for PKI and CA systems [61] so that is can easily fit into almost any certificated IT infrastructure and work seamlessly within that environment. This compliance to standards is important when considering current requirements and potential future requirements too | |
| Programming language | All components of the Digi-CAST™ [51] system kernel have been developed in C on Unix and this is considered the most stable, secure and efficient language and operating system for the development of PKI & CA systems | |
| Centralised Management | Web based ‘system management centre’ for all operated CAs, RAs & LRAs makes it ideal for operation as an installed standalone CA system or as a Managed CA [51] | |
| ‘‘futureproof’ | By its very design, the entire Digi-CAST™ system can be in house, totally out sourced or a combination of the two and this can be decided at any stage during the life of the system. So you can purchase [51] what it needs today, safe in the knowledge that you can easily migrate and move all or part of the system to the Managed CA alternative to meet your future demands | |
| Ease of integration | Whether now or in the future, because it is LDAPv3 compliant, Digi-CAST™ can publish X.509 certificates and certificate Revocation [62] Lists [CRL] to other directories. This is a significant factor when considering integration with existing or future environments | |
| Scalability | Digi-CAST™ can scale, easily and with minimal/no interrupting of live operations. This is important when considering the future growth of your requirements. It is also possible to add additional hardware [63] to expand the system capacity and services and to conduct cross certification | |
| Continuous operation | When considering the future growth of your requirements, live production can continue uninterrupted while adding more CAs, RAs and LRAs. These capabilities ensure the CA remains operational and without interruption throughout | |
| Customisation to your requirements | Custom multi-layer CA hierarchy, RA and LRA distribution can be modified, extended and changed at any stage and again, this can be done without affecting the operation of the live environment | |
| ‘look & feel’ customisation | The entire Digi-CAST™ system interfaces and all its levels can be easily changed using Cascade Style Sheet [CSS]. This ability to completely change the ‘look and feel’ of the system eases the deployment to your end users because they know you but may not be familiar with the CA vendor. It also helps with integrating into web sites and other online systems seamlessly | |
| Multiple Languages | Language localisation is “plug n’ play” for displaying all interfaces in your desired language(s). This further helps the deployment to end users and reduces ‘help desk calls’ (where users are really looking for translation of help files, etc) | |
| Custom profile, enrolment & DN capabilities supplied as | Certificate profiles and enrolment policies can be customised and therefore full custom certificate subject Distinguished Name [DN] attributes and certificate extensions are possible. This is particularly important | |
| standard | when meeting national & international standards and the cost of providing these capabilities from other systems can be considerable | |
| CA Flexibility | Ability to operate multiple independent CA hierarchies from a single system instance without the need of installing multiple software applications on multiple server computers to run each CA hierarchy | |
| RA Flexibility | Multiple independent Registration Authority [RA] instances from a single system without needing to install multiple applications on multiple servers to run each RA | |
| 100% browser independent | 100% certificate enrolment web browser platform and operating system independency | |
| Root CA cross certification | Digi-CAST™ offers the capability of cross certification between the your Root CA and any other CA | |
| Trusted Root capability | Also it can be cross certified by a Trusted Root CA of issuing trusted SSLs and secure, signed and/or encrypted email | |
| Best training & knowledge transfer | With the largest online searchable PKI & CA KnowledgeBase, the extensive documentation offered, the Digi-TaSC system and the many different types of training offered, this proposal offers the most comprehensive that programme for your personnel | |
| Overall most capable & most competitively priced | Digi-CAST™ achieves the best blend of meeting your current requirements and possible future ones too. It’s highly customisable and flexible features means it will meet future demands easily, without incurring downtime, service interruption or unwieldy costs | |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
The simplicity of the design of the complete Digi-CA™ system means that the same system can be purchased initially as a service [64]. Later, if needed, the software [65] version can be deployed and later scaled for enterprise, large scale and even national PKI use, with minimum or no disruption. This is made possible by the modular architecture used in the development of the Digi-CA™ system.
The modular architecture of Digi-CA™ provides its components in Service Modules [64]. Here is the list of modules currently available (for further details, refer to the Digi-CA™ Deployment Guide).
| Module Name | Code | Services Provided |
| Cryptographic Service Provider | CSP | Certificate & CRL Generation Services |
| Time-Stamping Gateway | TSG | Digital Time-Stamping Service |
| OCSP Gateway | OCSPG | Real time Revocation Status Service |
| CA Application Service | CAAS | TSG and OCSPG gateway services connector |
| CA Management Console | CAMC | Web based Certification Authority management |
| RA Management Console | RAMC | Web based Registration Authority management |
| Entity Registration Service | ERS | Web based End Entity Registration management |
| Content Dissemination Service | CDS | Certificate and CRL dissemination management |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/deployment.png)
The above diagram shows each module of Digi-CA™ [64] distributed across multiple servers for use in a large scale enterprise/government PKI.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
This modular architecture permits Digi-CA™ to meet almost any requirement. The principal delivery models are:
| Digi-CA™ Service - Managed CA [59] | ||
| Digi-CA™ Server - CA Software [60] | ||
| Digi-CA™ Shared - Dedicated CA [61] |
It is possible to build [66] a custom Digi-CA™ solution that will meet all your requirements. This sophisticated online shopping cart assist you in selecting the correct Digi-CA™ and also demonstrates the many add-ons available to meet those requirements. For further information use this URL:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-service_0.png)
Digi-CA™ Service is the Managed CA [59] and is the service that is provided online using the Application Service Provider [ASP] or Software-as-a-Service [SaaS] delivery model. There is no hardware or software requirement at the customer site.
Unless there is a very specific reason why your organisation must own and locate its own CA system [51], then Digi-CA™ Service will most probably meet all of your requirements. As a service offering it is more cost effective both financially and from a human resource/time consumption perspective.
Digi-CA™ Service is charged on an annual recurring fee that is based on the number of digital certificates [51] issued each year. The annual fee covers all maintenance, administration and day-to-day system support that is required to keep the Digi-CA™ operational. For further information use this URL:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
Digi-CA™ Server is the CA Software that is installed on a server in a data centre [60] or at the customer site. Digi-CA™ charges a ‘once off’ initial license fee that is based on the cost of the software, its configuration and installation and then the number of certificates required over the life of the product's use.
Unless there is a very specific reason why your organisation must own and locate its own CA system, then Digi-CA™ Service [59]will most probably meet all of your requirements. If ownership and specific geographic location are specific requirements, the Digi-CA™ Server is probably your best choice.
Once personnel are properly trained, they should be able to manage and administer the system with ease. Digi-CA™ Server also has the ability to be accessed using a highly secure Virtual Private Network [VPN] connection, where Digi-CAST™ personnel can assist with escalated technical matters using direct access to the system.
Apart from the initial license fee, the only other fees you pay are the annual license fee to cover upgrades, patches and application telephone support and optional annual support fees that can be purchased in ‘blocks of tickets’ where a single support case uses one support ticket until the case is solved.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
When considering a centralised or distributed deployment model of Digi-CA™ [60], one must consider the fact, that Digi-CA™ requires a pre-established network infrastructure that is a key objective to a successful deployment of this system.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/deployment.png)
Although Digi-CA™ does not require, or rely on, a specific network design, careful network architecture planning [51] is strongly recommended prior to the deployment of this system. Diagrams below – as an example only - illustrate two most common deployment methodologies, one with all Service Modules centralised on a single server and the other with distributed services as an alternative.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/considerations.png)
As an installed Software CA [60], Digi-CA™ Server will require at least one, if not multiple servers, networking and at least one internet connection. The minimum software and hardware requirement to deploy a standard Digi-CA™ on a single server device is as follows:
| Component | Minimum Requirements Specification |
| Server OS Platform | Unix®, Linux® [x86 / x86-64 / ia64] |
| Operating System | Red Hat Enterprise Linux® 4.x, 5.x ; FreeBSD® 5.x, 6.x, 7.x, 8.x |
| RAM Memory | 1GB RAM |
| Hard Disk Device | 15GB ATA/SCSI/SAS |
| CPU | Intel® Pentium® IV 2.4 MHz |
| Network Interface Card | Intel® compatible 10/100 Megabits NIC |
| Database server software | MySQL Community Server 5.0.45 |
For further information use this URL:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-shared.png)
Digi-CA™ [68] Shared was a concept conceived by Digi-Sign in 2006 that has only recently been acknowledged by potential customers as a real alternative to providing Digi-CA™ Service. Although implementations of this concept CA are limited, the capability and the option are important.
Typical enquiries come from large industry or government agencies where ownership of the entire CA is not a requirement, but ownership of specific components is preferred (e.g. data files, HSMs or the requirement to have a complete, hosted disaster recovery system). When considering Digi-CA™, the availability of this concept may not be of paramount importance, but its availability may be very useful during the continued growth and expansion of the total environment.
Digi-CA™ Shared can be a dedicated instance of the Digi-CA™ Service [69] that is completely separate from all other Digi-Sign systems; or it can be a combination of the Digi-CA™ Server system, hosted at a location of your choosing, with certain functions hosted by at one of our nominated data centres.
Estimating the annual charges and other cost considerations for Digi-CA™ Shared is calculated on a case-by-case basis. For further information use this URL:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
Digi-CA™ replaces older Legacy CA systems using the latest in CA and PKI technologies and benefits from combining commercial and open source software initiatives. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Legacy CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level.
The Digi-CA™ Team combine consulting and professional services with the functions provided by Digi-CA™ and can bring an organisation to a highly professional PKI level whilst meeting the criteria for internationally recognised accreditation standards such as WebTrust® and ISO 27001 certifications.
Advice on selecting the modules and services you may require are in the next section.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
This section of the Guide provides general information on the functional concepts for each Digi-CA™ Service Module and related Digi-CAST™ services to consider when selecting the correct Digi-CA™ system for your environment. As a guide, it is recommended that you familiarise yourself with the general concepts and then contact us directly for more information, or use the online shopping cart or more detailed information:
Regardless of what Digi-CA™ system you elect to use, the following service modules will always be active, albeit in some cases, transparent to the administrators or end users. These are:
| Cryptographic Service Provider | |
| CA Management Console [CAMC] | |
| RA Management Console [RAMC] | |
| Entity Registration Service [EERS] | |
| Certificate & CRL Dissemination Services [CCDS] |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
The Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP] Service Module is a software application that ultimately provides the most of cryptographic operations to the system and is effectively responsible for generating all public key certificates. Due to the high severity for the security of this module, it is not accessible through any network communications protocol. This design imposes an asynchronous certificate generation and distribution model.
The CA Management Console [CAMC] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] for managing Certification Authorities, Registration Authorities, Service Modules and other services provided within the Digi-CA™ system infrastructure.
The following table presents a general overview on the functionalities provided by CAMC.
| CAMC functionality overview | ||
| Management of CA accounts | Management of internal Master CA key pair | |
| CA Key Pair management | Management of Digi-CA™ system user accounts | |
| CA Certification and Cross-Certification management | Management of End Entity certificate policies | |
| Service Module Registration and Management | Management of Time-Stamping Authorities | |
| Digi-CA™ main configuration | Management of OCSP Validation Authorities | |
| Registration and management of X.509 certificate profiles | Digi-CA™ system status overview | |
| End Entity Certificate reporting | CSP cryptographic request queue reporting | |
| Management of RA accounts | Activity Dual Control authorization | |
The RA Management Console [RAMC] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] for operating Registration Authorities and managing End Entity Certificates.
The following table presents a general overview on the functionalities provided by RAMC.
| RAMC functionality overview | ||
| End Entity account management | Management of RA user accounts | |
| End Entity key pair life cycle management | Management of End Entity certificate policies | |
| End Entity certificate request registration | End Entity Validation | |
| End Entity certificate authorization | Activity Dual Control authorization | |
| End Entity certificate revocation | End Entity certificate reporting | |
| End Entity certificate suspension | End Entity certificate de-suspension | |
| End Entity certificate replacement (re-issuance) |
Management of TSA clients | |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
The Entity Registration Service [ERS] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] provided to End Entities for user account and certificate related activity registration purposes.
The following table presents a general overview on the functionalities provided by ERS.
| ERS functionality overview | ||
| End Entity initial account registration | End Entity certificate status reporting | |
| End Entity certificate request registration | End Entity certificate collection | |
| End Entity certificate revocation requests | End Entity certificate replacement (re-issuance) requests |
|
| End Entity certificate suspension requests | End Entity certificate de-suspension requests | |
| TSA client token reporting | ||
The Certificate & CRL Dissemination Services [CCDS] Module is a software application that ultimately provides dissemination service for End Entity Public Key Certificates, Key Pairs and Certificate Revocation Lists.
From an Operating System perspective, the CDS is a client application to the CA database server. It sustains a persistent connection to the database from where dissemination requests are loaded and subsequently served. The following table presents a general overview of the functionality the CDS module is designed to provide.
| CSP functionality overview | ||
| End Entity public key publication in LDAP directory | CRL publication in web repository | |
| End Entity public key distribution | CRL distribution | |
| End Entity certificate expiration notification | TSA Client notifications | |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
The following optional additional services are categorised as being available as follows:
| Unique to Digi-CA™ Service Only | ||
| Available on all Versions of Digi-CA™ | ||
| Restricted to Certain Versions of Digi-CA™ |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/ttm.png)
The following services are only available with Digi-CA™ Service
Total Trust Management™ is much more than direct telephone support line or a dedicated Account Manager. Total Trust Management™ is the total out sourcing of your Digi-CA™ Service management, where Digi-CAST™ personnel effectively work for you and every aspect of the certificate life-cycle management is done for you.
We pioneered the Total Trust Management™ [TTM™] in 2004 and have been offering this valuable service to our customers ever since. Under TTM™ we act as the Trusted Administrator of your Digi-CA™ Service and carry out all of the duties of the CAMC and RAMC operator on your system. TTM™ is an option that is only available with Digi-CA™ Service.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
Digi-CA™ Service automatically offers fail-over and load balancing as part of the standard service provisioning and strictly speaking, is not an optional addition. It is listed here for illustration purposes only.
Digi-CA™ Service automatically offers backup and disaster recovery as part of the standard service provisioning and strictly speaking, is not an optional addition. It is listed here for illustration purposes only.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
The following services are available on all versions of Digi-CA™.
When purchasing your Digi-CA™system, the initial order will contain a fixed number of digital certificates/signatures. In the case of Digi-CA™Service, the entire annual cost is based on the number of certificates in use. With Digi-CA™Server, the system is supplied, as standard, with 100 multi-use certificates.
Therefore, additional certificates must be ordered on an, as needed basis. Additional single use (e.g. for encryption only) or multi-use (e.g. authentication and digital signature, etc.) certificates must be ordered separately.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server_0.png)
When issuing large numbers of certificates in a single instance (e.g. several thousand in one hour or day) this will result in many users completing the online application form very soon after receiving the invitation email. Manually approving each request may not be possible and in such cases, RA Automation is the recommended option.
RA Automation can be as simple or as integrated as your environment requires and can be enabled on any version of Digi-CA™.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/tsa.png)
The TimeStamp Authority [TSA] provides digital TimeStamping network based services in compliance with RFC 3161 standard, Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure TimeStamp Protocol [TSP]. The TimeStamp Protocol, or TSP, is a cryptographic protocol for certifying timestamp tokens using X.509 public key certificates and public key infrastructure.
The timestamp token is the signer's assertion that a piece of electronic data existed at, or before, a particular time. TimeStamp tokens are effectively used to provide evidence data in the process of validating long-term electronic signatures applied to digital communication or payment transactions and electronic documents such as Adobe® Acrobat® PDF.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/ocsp_0.png)
The OCSP Gateway [OCSPG] Service Module is intended to provide digital
Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] network based services in compliance with RFC 2560 standard, X.509 Internet Public Key Infrastructure Online Certificate Status Protocol - OCSP.
The OCSP is an Internet protocol used for obtaining the revocation status of an X.509 digital public key certificate. It was created as an alternative to Certificate Revocation Lists [CRL], specifically addressing certain problems associated with using CRLs in a public key infrastructure [PKI].
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-dr.png)
A CA or PKI, although not mission critical, must ensure that all its data is protected and available at all times. Using fail-over may ensure that no data is lost, but the best option is to ensure that there is a back-up system that is completely separate from the main system.
This is referred to as disaster recovery and in high security situations, this backup disaster recovery is usually located at a separate geographic location from the main system.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-dr.png)
The following services are only required on certain versions of Digi-CA™Server. This is because in the case of Digi-CA™Server Xg, fail-over and load balancing are component parts of the overall system delivery and parts of the overall system delivery of Digi-CA™Service.
Fail-over is where a second system is enabled so that if the primary system ceases to function for any reason, the fail-over, or second system, temporarily assumes the primary role until normal service can resume. As Digi-CA™Server Xp and Xg are automatically supplied with fail-over, this is the only version of Digi-CA™Server where fail-over must be ordered separately (and is a good reason why most customers order Digi-CA™Server Xp).
Load balancing is where a minimum of two machines are configured so that all traffic across the system is balanced equally across the machines to ensure the highest performance of the overall system. Load balancing is only required where high volumes, or high production peaks, are expected in the einvironment.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/images/key-ceremony.png)
A Key Ceremony is only required when your organisation wishes to achieve your own independent root, or intermediate, Certificate Authority. This typically occurs where an organisation wants to create and own its own Root CA for reasons relating to compliance to specific standards (e.g. ISO 27001, WebTrust, EU Qualified Certificates, etc).
A Root Key Ceremony is a procedure where a unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated. Depending on your requirements and specifications, the generation of the Root Keys may require notarisation, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples:
Unless the information being accessed or transmitted is valued in terms of millions of dollars, it is probably sufficient that the Digi-CAST2™ Team conduct the Root Key Ceremony within the security of the Digi-CAST2™ Laboratory. The customer may opt to have the Root Key stored on a Luna Card or HSM, but in most cases the safe storage of the Root Key on a CD or hard disk is sufficient. The Root Key is never stored on the Digi-CA™server.
This type of environment requires much higher security than a commercial one. When conducting the Root Key Ceremony, the Government or Organization will require rigorous security checks to be conducted on all personnel in attendance. Those that are normally required to attend the Key Ceremony will include a minimum of two Administrators from the organisation, two signatories from the organisation, one lawyer, a notary and two video camera operators in addition to the Digi-CAST2™ Team.
The actual Root key-pair generation is normally conducted in a secure vault that has no communication or contact with the outside world other than a single telephone line or intercom. Once the vault is secured, all personnel present must prove their identity using at least two legally recognised forms of identification. Every person present, every transaction and every event is logged by the lawyer in a Root Key Ceremony Log Book and each page is notarized by the notary. From the moment the vault door is closed until it is re-opened, everything is also video recorded. The lawyer and the two organisation’s signatories must sign the recording and it too is then notarized.
Finally, as part of the above process, the Root Key is broken into as many as twenty-one parts and each individual part is secured in its own safe for which there is a key and a numerical lock. The keys are distributed to as many as twenty-one people and the numerical code is distributed to another twenty-one people.
Example A and B are at opposite ends of the security spectrum and no two environments are the same. When considering the Root Key Ceremony, the Digi-CAST1™ Team of professional advisors can assist you in deciding on the most efficient level of security to reflect the level of protection required.
![]() [70] This Guide is intended to provide general information on the basic concepts, design, deployment and use of the Digi-CA™ Public Key Infrastructure [PKI] system. It is assumed that the audience and readers of this guide have a basic understanding of the concepts of information technology, PKI and the use of X.509 digital public key certificates.
[70] This Guide is intended to provide general information on the basic concepts, design, deployment and use of the Digi-CA™ Public Key Infrastructure [PKI] system. It is assumed that the audience and readers of this guide have a basic understanding of the concepts of information technology, PKI and the use of X.509 digital public key certificates.
If you are planning to deploy Digi-CA™ inside your organisation, ensure your read this document first, before attempting to perform a new standalone or distributed installation of this system.
In cryptography, a Certificate Authority or Certification Authority [CA] is an entity that issues digital certificates for use by other parties. It is an example of a trusted third party. A CA issues digital certificates that contain a public key and the identity of the public key owner. The matching private key is not similarly made available publicly, but kept secret by the end user who owns the key pair. The certificate is also an attestation by the CA that the public key contained in the certificate belongs to the person, organization, software or hardware device or other entity noted in the certificate. A CA's obligation in such schemes is to verify an applicant's credentials, so that users and relying parties can trust the information in the CA's certificates.
Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority system for organisations that would like to have their own CA, like to own and manage a PKI for digital certificates inside the organisation or over the Internet. Digi-CA™ generates and manages digital Public Key Certificates that are used for a variety of different purposes, most commonly for electronic signatures, natural person or device authentication and secure email.
The Digi-CA™ system can create multiple instances of independent Certification Authorities in a single Digi-CA™ system deployment. The Digi-CA™ model imposes delegation of trust downwards from Root CAs to their Subordinate CAs that meets the concepts of layered hierarchy. The same Digi-CA™ system also enables a CA to be cross signed by an external third party CA. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CA™ model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI requirement from the smallest to the largest.
The Digi-CA™ System provides a full scale of services necessary for the management of X.509 certificates. An overview of these services is presented in the table below.
|
Digi-CA™ service overview |
|||
| End Entity registration | Time-Stamping | ||
| Certificate issuance | Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] | ||
| Certificate re-signing | Multi-CA system engine | ||
| Certificate renewal | Cross-Certification management | ||
| Certificate dissemination | Certificate Revocation List [CRL] generation | ||
| Certificate revocation | CRL distribution & dissemination | ||
| Certificate suspension | Entity based multi-key management | ||
| Certificate de-suspension | Certificate profile management | ||
| Certificate expiration notification | Certificate Enrolment Policy Management | ||
| Event logging & auditing service | Support for hardware cryptographic module devices | ||
| Hierarchical CA operations | Support for Smart Cards and USB Tokens | ||
Table 0.1
As an addition, Digi-CA™ offers the following supplementary services:
The core and supplementary CA services are further described in the Digi-CA™ Service Modules [71]
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/knowledgebase.png)
This Guide is intended to provide general information on the basic concepts, design, deployment and use of the Digi-CA™ Public Key Infrastructure [PKI] system. It is assumed that the audience and readers of this guide have a basic understanding of the concepts of information technology, PKI and the use of X.509 digital public key certificates.
If you are planning to deploy Digi-CA™ inside your organisation, ensure your read this document first, before attempting to perform a new standalone or distributed installation of this system.
In cryptography, a Certificate Authority or Certification Authority [CA] is an entity that issues digital certificates for use by other parties. It is an example of a trusted third party. A CA issues digital certificates that contain a public key and the identity of the public key owner. The matching private key is not similarly made available publicly, but kept secret by the end user who owns the key pair. The certificate is also an attestation by the CA that the public key contained in the certificate belongs to the person, organization, software or hardware device or other entity noted in the certificate. A CA's obligation in such schemes is to verify an applicant's credentials, so that users and relying parties can trust the information in the CA's certificates.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/knowledgebase.png)
Digi-CA™is the complete Certificate Authority system for organisations that would like to have their own CA, like to own and manage a PKI for digital certificates inside the organisation or over the Internet. Digi-CA™generates and manages digital Public Key Certificates that are used for a variety of different purposes, most commonly for electronic signatures, natural person or device authentication and secure email.
The Digi-CA™system can create multiple instances of independent Certification Authorities in a single Digi-CA™system deployment. The Digi-CA™model imposes delegation of trust downwards from Root CAs to their Subordinate CAs that meets the concepts of layered hierarchy. The same Digi-CA™system also enables a CA to be cross signed by an external third party CA. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CA™model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI requirement from the smallest to the largest.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-service.png)
Digi-CA™can be delivered as an installed Software CA, or as a Managed CA service. Uniquely, both the Managed Digi-CA™Service and the installed Digi-CA™Server software use the same common, core technology. This is important because in selecting Digi-CA™it is possible to begin with Digi-CA™Service and migrate to Digi-CA™Server with ease.
It is possible to use the distributed architectural design of Digi-CA™to implement the concept of a Shared CA where different modules of the system are hosted and managed in separate locations.
The Digi-CA™System provides a full scale of services necessary for the management of X.509 certificates. An overview of these services is presented in the table below.
| Digi-CA™ service overview | ||
| End Entity registration | Time-Stamping | |
| Certificate issuance | Online Certificate Status Protocol | |
| Certificate re-signing | Multi-CA system engine | |
| Certificate renewal | Cross-Certification management | |
| Certificate dissemination | CRL generation | |
| Certificate revocation | CRL distribution and dissemination | |
| Certificate suspension | Entity based multi-key management | |
| Certificate de-suspension | Certificate Profile management | |
| Certificate Expiration Notification | Certificate Enrolment Policy Management | |
| Event logging and auditing service | Support for Hardware Cryptographic Module devices | |
| Hierarchical CA operations | Support for Smart Cards and USB Tokens | |
In principle and in compliance with internationally recognised PKI standards, Digi-CA™offers the following core Certification Authority services:
As an addition, Digi-CA™offers the following supplementary services:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
At its core, Digi-CA™ software was designed for Unix and Linux operating systems that provide a robust and stable operating environment. The simplicity of the architectural design of the complete Digi-CA™ system means that the same software can be deployed on a single server device and later scaled for enterprise or Internet PKI use with minimum or no disruption.
Typically, scaling may start from a 'handful' of servers acting in a basic
fail-over mode. Such basic setup can be later extended to reach greater capacity and performance by introducing additional servers as required. This scaling of the capacity can occur almost without, or completely without, interrupting the operation of the existing production environment. This is a critical component when deciding on a CA that may scale considerably over time and allows organisations to carefully plan their investment costs, whilst also achieving all functional goals.
The following table presents a minimum software and hardware requirement to deploy a standard Digi-CA™ on a single server device.
| Component | Minimum Requirements Specification | |
| Server OS Platform | Unix®, Linux® [x86 / x86-64 / ia64] | |
| Operating System | Red Hat Enterprise Linux® 4.x, 5.x ; FreeBSD® 5.x, 6.x, 7.x, 8.x | |
| RAM Memory | 1GB RAM | |
| Hard Disk Device | 15GB ATA/SCSI/SAS | |
| CPU | Intel® Pentium® IV 2.4 MHz | |
| Network Interface Card | Intel® compatible 10/100 Megabits NIC | |
| Database server software | MySQL Community Server 5.0.45 | |
Digi-CA™ software is a multi-application component based system for generating and managing cryptographic keys, digital X.509 public key certificates and providing supplementary PKI services. In this model, each application component, referred to as a "Service Module", provides a series of both cryptographic and non-cryptographic functionalities to other application components within the system’s infrastructure.
The following table presents a list of Service Modules currently available within Digi-CA™.
| Component | Code | Minimum Requirements Specification |
| Cryptographic Service Provider | CSP | Certificate & CRL Generation Services |
| Time-Stamping Gateway | TSG | Digital Time-Stamping Service |
| OCSP Gateway | OCSPG | Real time Revocation Status Service |
| CA Application Service | CAAS | TSG and OCSPG gateway services connector |
| CA Management Console | CAMC | Web based Certification Authority management |
| RA Management Console | RAMC | Web based Registration Authority management |
| Entity Registration Service | EERS | Web based End Entity Registration management |
| Content Dissemination Service | CCDS | Certificate and CRL dissemination management |
| a | where it is required to centralise all Module Services on a single dedicated server to reduce costs and where large certificate volumes are not a demand; | |
| b | in a most complex environment, for very high volume certificate processing and where all Module Services are distributed separately to a number of server devices, most often in combination with network hardware load balancing, database data replication as well as hardware and software fail-over that combine to form the so called ‘High Availability’ model. | |
This unique feature of Digi-CA™software provides not only a flexible range of possible configuration variations but allows organisations to slowly build their own PKI infrastructure from a very small environment and carefully control their expenditure related to purchasing and maintenance of hardware devices.
When considering a centralised or distributed deployment model of Digi-CA™, one must consider the fact, that Digi-CA™requires a pre-established network infrastructure that is a key objective to a successful deployment of this system. Although Digi-CA™does not require, or rely on, a specific network design, careful network architecture planning is strongly recommended prior to the deployment of this system. Diagrams below – as an example only - illustrate two most common deployment methodologies, one with all Service Modules centralised on a single server and the other with distributed services as an alternative.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/deployment.png)
Diagram 1.0: Digi-CA™with centralised Service Modules
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/considerations.png)
Diagram 2.0: Digi-CA™with distributed Service Modules
Digi-CA™replaces older Legacy CA systems using the latest in CA and PKI technologies and benefits from combining commercial and open source software initiatives. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Legacy CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level.
The Digi-CAST™ Team combine consulting and professional services with the functions provided by Digi-CA™and can bring an organisation to a highly professional PKI level whilst meeting the criteria for internationally recognised accreditation standards such as WebTrust® and ISO 27001 certifications.
Diagram 1.0: Digi-CA™with centralised Service Modules
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
This section of the Guide provides general information on the functional concepts for each Digi-CA™Service Module. More detailed information as well as usage instructions for these modules are available in the following associated documents:
The Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP] Service Module is a software application that ultimately provides the most of cryptographic operations to the system and is effectively responsible for generating all public key certificates. Due to the high severity for the security of this module, it is not accessible through any network communications protocol. This design imposes an asynchronous certificate generation and distribution model.
The only allowed control mechanism for this software module is manual, through the use of Operating System console command line interface [CLI]. CLI control options are limited to start, stop, key activation and general module configuration operations.
CSP in the overview of the CA core services acts as the Certificate Generation Service.
From an Operating System perspective, CSP is executed as a software daemon being also a client to the CA database server and Content Distributing Service. It sustains a persistent connection to the database from where cryptographic operation requests are loaded and subsequently served. The following table presents a general overview of the cryptographic functionality the CSP module is designed to provide.
| CSP functionality overview | ||
| CA Key Pair generation | End Entity Key Pair generation | |
| Root CA public key certification | End Entity public key certification | |
| Subordinate CA public key certification | Certificate Revocation List certification | |
| CA Public Key Cross-Certification | CA Private Key Storage in Software Security Module | |
| Table 3.0 | ||
Certified (digitally signed by the CA private key) public key certificates are instantly stored in a CA database and where immediate certificate dissemination is required, a Content Distributing Service is optionally called through an Uniform Resource Identifier [URI], further resulting in a certificate being distributed to the End Entity and, if necessary, published in a certificate LDAP directory.
CSP makes regular use of CA private keys and associated public key certificates and therefore it must have uninterrupted access to these keys at all times. Private keys used by CAs to certify public key certificates are by nature security sensitive. A CA must therefore provide sufficient security mechanisms and procedures to protect the CA private key from an illegitimate use by others.
CSP is designed to meet the highest security demands and simultaneously support two different types of Security Modules for secure private key access and storage:
The SSM is a CSP’s built-in cryptographic hardware-less feature. SSM uses PKCS#8 (Public Key Cryptography Standard) format to store private keys on a local file system in an encrypted manner. Private key encryption is accomplished by the use of encryption algorithm sets as defined in PKCS#5 standard.
Access to private keys in SSM is protected by a key activation password, which is used by the CSP to derive a "secret" further used to effectively encrypt CA private key information. Although a System Administrator or Security Officer may be aware of the SSM activation password, direct access to raw private key information is not likely possible, unless a successful attempt is made to reverse engineer the CSP source code in order to establish the precise secret derivation algorithms in use.
Once an instance of a CSP is launched, all private keys residing in the SSM private key repository configured for activation are loaded and remain in computer RAM memory until the CSP process is purposefully or unexpectedly terminated. Upon successful shutdown of the CSP process, the RAM memory area designated for private key storage is programmatically zeroed.
The SSM option for CA private key storage is designed to provide a cost-effective way of CA private key storage for small organisations, that intend to deploy Digi-CA™only for private use and where corporate security policies are actively maintained and followed by IT personnel and finally where the organisation has full control of the use of public key certificates.
Where greater CA private key protection mechanisms are a security demand, SSM option is strongly NOT recommended and this is where CSP offers a simultaneous use of hardware based cryptographic devices - HSMs - for secure private key storage and access.
HSMs introduce a very high level for private key protection and provide enhanced performance for cryptographic operations with the use of private keys, for example in the process of creating digital signatures.
There are two general types of HSM devices: host-attached and network-attached. The CSP supports both types of HSMs. A host-attached HSM device can be a device connected directly to a host server through a PCI, USB or SCSI interface. A network-attached HSM is a device connected to the host server over network using a Network Interface Card [NIC] attached to the server. Both types of HSM devices provide enhanced private key protection and meet the highest security criteria demand such as certification to FIPS 140-2 level 4 and/or Common Criteria EAL4+.
CSP communicates with the HSM device using a software library API, provided by the device vendor. When using HSM devices, private keys are physically stored and protected inside a hardware device and are never accessible as plain text. In fact, CSP has no real control over private keys stored on an HSM device as it merely makes the use of the hardware device layer to perform cryptographic operations.
HSM devices are therefore strongly recommended typically everywhere, where organisations intend to provide CA services to the public community or where the use of public key certificates is outside of the organisation’s exclusive control.
The table below presents example HSM models, that have been successfully tested with the CSP Service Module.
| Supported Hardware Security Modules |
| AEP Keyper Professional (FIPS 140-2 level 4) |
| AEP Keyper Enterprise (FIPS 140-2 level 4) |
| Thales nCipher NetHSM 500 (FIPS 140-2 level 3) |
| Thales nCipher NetHSM 2000(FIPS 140-2 level 3) |
| Thales nCipher nShield PCI (FIPS 140-2 level 3) |
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™Administrator Guide.
The CA Management Console [CAMC] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] for managing Certification Authorities, Registration Authorities, Service Modules and other services provided within the Digi-CA™system infrastructure.
The following table presents a general overview on the functionalities provided by CAMC.
| CAMC functionality overview | ||
| Management of CA accounts | Management of internal Master CA key pair | |
| CA Key Pair management | Management of Digi-CA™system user accounts | |
| CA Certification and Cross-Certification management | Management of End Entity certificate policies | |
| Service Module Registration and Management | Management of Time-Stamping Authorities | |
| Digi-CA™main configuration | Management of OCSP Validation Authorities | |
| Registration and management of X.509 certificate profiles | Digi-CA™system status overview | |
| End Entity Certificate reporting | CSP cryptographic request queue reporting | |
| Management of RA accounts | Activity Dual Control authorization | |
| Table 5.0 | ||
The CAMC is essentially a web based application designed to work with an instance of an Apache web server.
System users, such as CA Administrators can access the console interface only by using a web browser client application such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox.
CAMC provides support for a combination of two user authentication factors: traditional username and password and X.509 certificate based client authentication, which is a feature enabled by the use of SSL/TLS communication encryption protocol on the Apache web server. CAMC allows you to decide what authentication factor should be used to authenticate console users or whether to use both authentication factors at the same time.
The console is capable of supporting multiple language locales.
The great advantage of this module is that it allows different CA users to independently access separate CA accounts at the same time using the same console interface.
To store and retrieve information, the console uses an interface connection to the CA database. The fact it is a web based application, makes it easy to deploy and protect on a common installation of an Apache web server.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™Administrator Guide.
The RA Management Console [RAMC] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] for operating Registration Authorities and managing End Entity Certificates.
he following table presents a general overview on the functionalities provided by RAMC.
| RAMC functionality overview | ||
| End Entity account management | Management of RA user accounts | |
| End Entity key pair life cycle management | Management of End Entity certificate policies | |
| End Entity certificate request registration | End Entity Validation | |
| End Entity certificate authorization | Activity Dual Control authorization | |
| End Entity certificate revocation | End Entity certificate reporting | |
| End Entity certificate suspension | End Entity certificate de-suspension | |
| End Entity certificate replacement (re-issuance) |
Management of TSA clients | |
| Table 6.0 | ||
The RAMC is essentially a web based application designed to work with an instance of an Apache web server.
System users, such as RA Administrators and RA Operators can access the console interface only by using a web browser client application such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox.
The RAMC provides support for a combination of two user authentication factors: traditional username and password and X.509 certificate based client authentication, which is a feature enabled by the use of SSL/TLS communication encryption protocol on the Apache web server. RAMC allows you to decide what authentication factor should be used to authenticate console users or whether to use both authentication factors at the same time.
The console is capable of supporting multiple language locales.
The great advantage of this module is that it allows different RA users to independently access separate RA accounts at the same time using the same console interface.
To store and retrieve information, the console uses an interface connection to the CA database. The fact it is a web based application, makes it easy to deploy and protect on a common installation of an Apache web server.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™RA Operation Guide.
The Entity Registration Service [EERS] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] provided to End Entities for user account and certificate related activity registration purposes.
The following table presents a general overview on the functionalities provided by EERS.
| EERS functionality overview | ||
| End Entity initial account registration | End Entity certificate status reporting | |
| End Entity certificate request registration | End Entity certificate collection | |
| End Entity certificate revocation requests | End Entity certificate replacement (re-issuance) requests |
|
| End Entity certificate suspension requests | End Entity certificate de-suspension requests | |
| TSA client token reporting | ||
| Table 7.0 | ||
The EERS is essentially a web based application designed to work with an instance of an Apache web server.
End Entity users, such as Public Key Certificate subscribers or TSA Clients can access the module interface only by using a web browser client application, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox.
EERS provides support for traditional username and password based authentication. The console is capable of supporting multiple language locales.
To store and retrieve information, the module uses an interface connection to the CA database. The fact it is a web based application, makes it easy to deploy and protect on a common installation of an Apache web server.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™RA Operation Guide.
The Certificate & CRL Dissemination Services [CCDS] Module is a software application that ultimately provides dissemination service for End Entity Public Key Certificates, Key Pairs and Certificate Revocation Lists.
The CCDS, in the overview of the CA core services, acts as the Dissemination Service.
From an Operating System perspective, the CCDS is a client application to the CA database server. It sustains a persistent connection to the database from where dissemination requests are loaded and subsequently served. The following table presents a general overview of the functionality the CCDS module is designed to provide.
| CSP functionality overview | ||
| End Entity public key publication in LDAP directory | CRL publication in web repository | |
| End Entity public key distribution | CRL distribution | |
| End Entity certificate expiration notification | TSA Client notifications | |
| Table 8.0 | ||
Public Key Certificates generated by the CSP Service Module are stored in a CA database and CCDS is responsible for distributing the certificates to End Entities and if necessary, publishing these in a certificate LDAP directory.
For distribution, CCDS primarily uses Internet mail messaging [email], where public key certificates are attached to email messages. Another common method is to notify End Entities of a specific certificate collection web access point where End Entities can collect certificates by using a web browser, which is provided as part of the Entity Registration Service.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™Administrator Guide.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/tsa.png)
The TimeStamp Authority Gateway [TSAG] Service Module is intended to provide digital Time-Stamping network based services in compliance with RFC 3161 standard, Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Time-Stamp Protocol [TSP].
The Time-Stamp Protocol, or TSP, is a cryptographic protocol for certifying time-stamp tokens using X.509 public key certificates and public key infrastructure. The time-stamp token is the signer's assertion that a piece of electronic data existed at, or before, a particular time. Time-Stamp tokens are effectively used to provide evidence data in the process of validating long-term electronic signatures applied to digital communication or payment transactions and electronic documents such as Adobe® Acrobat® PDF.<,/
TSAG, in the overview of the CA supplementary services, acts as the Timestamping Service.
The term "Gateway" in the module name is purposely used to describe what the TSAG really does. It is essentially a network gateway between the TSP Client and TSP Server. The design concept for this Service Module arose from the results of security assessments applied to RFC 3161 standard.
A typical implementation model for a TSP Server allows that server to directly access the Timestamp Authority’s [TSA] Private Key designated for certifying TimeStamp tokens. Due to the fact that the TSP Server is very likely to be exposed for public use, the likelihood of the TSA’s private key accidental exposure to an illegitimate party is relatively high, regardless whether the TSA’s private key is stored in a Software or Hardware Security Module. The TSA forms a key party in the process of validating electronic signatures and non-repudiation and therefore an illegitimate exposure of the TSA’s private key in any form could lead to a potential risk of TSA signature forger that would further result in invalidation of any previously certified Time-Stamp tokens and further invalidation of any electronic signatures that these tokens would provide an evidence of.
TSAG was designed to eliminate the above risks. It is a software library built to work with an instance of an Apache web server software and it can be therefore considered as an Apache software module. Its functionality is limited to the following purposes:
| a. Optionally authenticate connecting TSP Clients against a database | ||
| b. Qualify correctly formatted TSP requests | ||
| c. Transparently pass TSP requests to the CA Application Service [CAAS] | ||
| d. Retrieve responses from CAAS | ||
| e. Transparently pass responses retrieved from CAAS to TSP Clients | ||
The TSP Clients can connect to the TSAG using standard HTTP or secure HTTPS [HTTP over SSL/TLS] protocol using a Uniform Resource Locator [URL] method. TSP requests are accepted either as HTTP POST or HTTP GET requests.
The optional Client Authentication is accomplished by the use of Simple HTTP Authentication where TSP Clients are requested to provide a username and password before their TSP request is accepted. To authenticate a TSP Client, the TSAG will transparently connect to a CA database, where End Entity account information is stored.
The TSAG module is configured and activated inside the Apache web server configuration and can be applied per site, virtual realm or per physical directory configuration. It is loaded the very moment the Apache web server is started.
Important Note: TSAG Service Module can place significant demands on your servers and IT hardware environment and should only be deployed and offered to relying parties if you have the correct infrastructure that meets the recommended model of High Availability.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™Administrator Guide.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/ocsp.png)
The Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] Gateway Service Module is intended to provide digital network based services in compliance with RFC 2560 standard, X.509 Internet Public Key Infrastructure Online Certificate Status Protocol - OCSP.
The OCSP is an Internet protocol used for obtaining the revocation status of an X.509 digital public key certificate. It was created as an alternative to Certificate Revocation Lists [CRL], specifically addressing certain problems associated with using CRLs in a public key infrastructure [PKI].
Messages communicated via OCSP are effectively used to provide real time certificate revocation status service in the process of validating a public key certificate. This service can greatly support the validation process of the long-term electronic signatures applied to digital communication or payment transactions and electronic documents, such as Adobe® Acrobat® PDF. OCSP, in the overview of the CA core services, acts as the Revocation Status Service.
The OCSP is provided in a Gateway mode and the term "Gateway" in the module name is purposefully used to describe what the OCSPG really does. It is essentially a network gateway between the OCSP Client and OCSP Responder. The design concept for this Service Module arose from the results of security assessments applied to RFC 2560 standard. A typical implementation model for an OCSP Responder allows that server to directly access the OCSP Validation Authority’s [VA] Private Key designated for certifying OCSP response messages. Due to the fact that the OCSP Responder is very likely to be exposed for public use, the likelihood of the VA’s private key accidental exposure to an illegitimate party is relatively high, regardless whether the VA’s private key is stored in a Software or Hardware Security Module. The VA forms a key party in the process of validating electronic signatures and non-repudiation and therefore an illegitimate exposure of the VA’s private key in any form could lead to a potential risk of VA signature forgery that would further result in invalidation of any previously certified OCSP responses and further invalidation of any electronic signatures that these responses would provide evidence of.
OCSPG was designed to eliminate the above risks. It is a software library built to work with an instance of an Apache web server software – it can be therefore considered as an Apache software module. Its functionality is limited to the following purposes:
| a. Qualify correctly formatted OCSP requests | ||
| b. Transparently pass OCSP requests to the CA Application Service [CAAS] | ||
| c. Retrieve responses from CAAS | ||
| d. Transparently pass responses retrieved from CAAS to OCSP Clients | ||
OCSP Clients can connect to OCSP Gateway using standard HTTP or secure HTTPS [HTTP over SSL/TLS] protocol using a Uniform Resource Locator [URL] method. OCSP request messages are accepted either as HTTP POST or HTTP GET requests.
OCSP Gateway module is configured and activated inside the Apache web server configuration and can be applied per site, virtual realm or per physical directory configuration basis. It is loaded the very moment the Apache web server is started.
Important Note: OCSP Gateway Service Module can place significant demands on your servers and IT hardware environment and should only be deployed and offered to relying parties if you have the correct infrastructure that meets the recommended model of High Availability.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™Administrator Guide.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/caas.png)
The CA Application Service [CAAS] Service Module is intended to provide target TSP Server and OCSP Responder services to the Time-Stamping Gateway and OCSP Gateway Service Modules.
The CA Application Service [CAAS] Service Module is intended to provide target TSP Server and OCSP Responder services to the Time-Stamping Gateway and OCSP Gateway Service Modules.
The design concept for this Service Module arose from the results of security assessments applied to RFC 3161 and RF 2560 standards and these concepts are further described in the above chapters 3.2 and 3.3.
CAAS has direct access and makes regular use of the TSA and OCSP VA Private Keys designated for certifying Time-Stamp tokens and OCSP response messages. Due to the fact that CAAS is NOT likely to be exposed for public access, the likelihood of the TSA or VA private key accidental exposure to an illegitimate party is relatively very small, regardless whether the TSA or VA private key is stored in a Software or Hardware Security Module.
CAAP was designed to remain in a protected network zone where public access is physically made impossible. It is a software library built to work with an instance of an Apache web server software – it can be therefore considered as an Apache software module. Its functionality is limited to the following purposes:
| a. Receive and serve Time-Stamp Requests | ||
| b. Receive and serve OCSP Requests | ||
| c. Respond to relevant requests by producing Time-Stamp tokens | ||
| d. Respond to relevant requests by producing OCSP responses | ||
Note: although CAAS will only accept legitimate requests from either of the Gateway Service Modules, it is still possible to setup the CAAS in combination with any of the Gateway Service Module in a traditional manner. Such a setup would allow you to install CAAS with TSG and/or OCSPG on a single server. This type of deployment is very useful in a closed private environment where volumes of requests are predictable and where corporate security policies are actively maintained and followed by IT personnel.
The CAAS uses the same private key storage and access techniques as the CSP Service Module and these techniques are described in more detail above.
Gateway Service Modules can connect to CAAS using secure HTTPS [HTTP over SSL/TLS] protocol with a Uniform Resource Locator [URL] method. Request messages are accepted as HTTP POST requests.
The CAAS module is configured and activated inside the Apache web server configuration and can be applied per site, virtual realm or per physical directory configuration basis. It is loaded the very moment the Apache web server is started.
Important Note: CAAS Service Module can place significant demands on your servers and IT hardware environment and should only be deployed and offered to relying parties if you have the correct infrastructure that meets the recommended model of High Availability.
Usage and configuration instructions for this module are available in the following associated documentation: Digi-CA™Administrator Guide.
Using a standalone deployment of Digi-CA™with basic Service Modules on a mid-spec Intel® processor based computer, Digi-CA™CSP Service Module has recorded the following performance data.
| CSP Performance Data | ||
| Number of Certificates | 500 up to 500,000,000+ | |
| Production speed | 5,000 1024-bits key signatures using SSM / hour 20,000 1024-bits key signatures using HSM / hour |
|
| Key lengths | 1024-8192 bits using SSM and HSM | |
| Signature algorithms | PKCS#1: RSA with SHA-1 | |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/testing.png)
Digi-CA™has been verified to comply with the following standards. For a complete and current list of standards, refer to the official Digi-Sign website URL:
www.digi-sign.com/about/compliance [72]
| Digi-CA™standard compliance list | ||
| RFC 5280, RFC 3647, RFC 2587, RFC 3161, RFC 3628, RFC 3629, RFC 2560 | RFC standards or standard candidates | |
| PKCS#1, PKCS#3, PKCS#5, PKCS#7, PKCS#8, PKCS#9, PKCS#10, PKCS#11, PKCS#12 | RSA Public Key Cryptography Standards | |
| FIPS 46, FIPS 180-2, FIPS 186-2, FIPS 197, FIPS 198 | US Federal Information Processing Standards | |
| ETSI TS 102 280, ETSI TS 102 042, ETSI TS 102 040, ETSI TS 102 023, ETSI TS 101 861 | European Telecommunications Standards Institute standards | |
| CWA 14167-1 | CEN Workshop Agreement standards | |
![]() [1] Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority [2] [CA] system for organisations that would like to own and manage their CA inside the organisation. The CA issues the Digital Certificates [3] that are used for two factor authentication [4], electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards [5], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD [6]], smart cards and ID Cards [5] and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
[1] Digi-CA™ is the complete Certificate Authority [2] [CA] system for organisations that would like to own and manage their CA inside the organisation. The CA issues the Digital Certificates [3] that are used for two factor authentication [4], electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards [5], Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD [6]], smart cards and ID Cards [5] and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
This online manual is the resource for many different users of Digi-CA™, from the most basic RA Operator [73] and RA Administrator [32], right through to the senior CA Manager [74].
![]() [1] The Digi-CA™ system can create multiple instances of unique CAs in a single Digi-CA™ system. The Digi-CA™ model imposes delegation of trust downwards from CAs to their Subordinate Certification Authorities [Sub-CAs]. The same Digi-CA™ system also enables any CA or Sub-CA to be signed or cross signed by an external third party CA. And any number of CAs can have any number of cross signed Sub-CAs. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CA™ model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI [7] requirement from the smallest to the largest. Also, the Digi-CA™ can be offered as a managed service outside your environment Digi-CA™ Service, or as the installed software Digi-CA™ Server.
[1] The Digi-CA™ system can create multiple instances of unique CAs in a single Digi-CA™ system. The Digi-CA™ model imposes delegation of trust downwards from CAs to their Subordinate Certification Authorities [Sub-CAs]. The same Digi-CA™ system also enables any CA or Sub-CA to be signed or cross signed by an external third party CA. And any number of CAs can have any number of cross signed Sub-CAs. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CA™ model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI [7] requirement from the smallest to the largest. Also, the Digi-CA™ can be offered as a managed service outside your environment Digi-CA™ Service, or as the installed software Digi-CA™ Server.
The Digi-CA™ System can issue, revoke, suspend, de-suspend and re-sign x.509v3 Digital Certificates [3]. Time-Stamping [75], Certificate Revocation Lists [CRLs], Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] [11] and many other features of a PKI system can be activated as required using the administration console of the system.
The end user information and certificate requests are entered through the web based Registration Authority [RA] Management Console. This powerful RA Management Console manages the entire Certificate Life cycle. Basic Certificate issuing and revocation by Operatives can be further delegated through a basic and modified RA Management Console interface called the Digi-CA™ Control Centre. It is the Digi-CA™ Control Centre or Limited Registration Authority [LRA] that is used by the RA Operator day-to-day.
Digi-CA™ replaces older Traditional PKI [28] technology and CA systems using the latest in CA technology. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Traditional CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level. The Digi-CA™ can even be ‘dropped’ on top of these Traditional CA environments and seamlessly migrate the older system’s users into this more modern and flexible replacement.
Combining the consulting and professional services [8] offered in the Digi-CAST™ methodology [8] with Digi-CA™ can meet all national and international standards [9] such as:
The remainder of this online manual is for use by Managers [74], Administrators [32] and Operators [73] of the Digi-CA™ system. If you have not already done so, please download and read the Digi-CA™ Manual [76], before proceeding further.
See the Digi-CA™ Flash Presentation [77] that explains the issues and benefits of using the system.
![]() [1] Digital Certificates [3] are issued and managed using a Certificate Authority or CA [2]. In the market, there are two main types of CA systems that are explained in more detail in the Digi-CA™ Manual download [45] or in the Managed CA – Digi-CA™ Service [78] and CA Software – Digi-CA™ Server [79] sub sections of the Certificate Authority online book.
[1] Digital Certificates [3] are issued and managed using a Certificate Authority or CA [2]. In the market, there are two main types of CA systems that are explained in more detail in the Digi-CA™ Manual download [45] or in the Managed CA – Digi-CA™ Service [78] and CA Software – Digi-CA™ Server [79] sub sections of the Certificate Authority online book.
Then there is the innovative CA combination that is unique to Digi-CA™ because of the principals used in the Core Design of Digi-CA™:
This unique offering is called the Shared CA: Digi-CA™ Shared
See the Digi-CA™ Flash Presentation [77] that explains the design principals that have made this innovation possible.
So with Digi-CA™ there are in fact three types of Certificate Authority system to choose from:
![]() [1] The Shared CA - Digi-CA™ Shared is a concept and capability that is unique to Digi-CA™. It is made possible by the component design and flexibility that is at the core design of Digi-CA™ and is not available from Traditional CA [28] vendors.
[1] The Shared CA - Digi-CA™ Shared is a concept and capability that is unique to Digi-CA™. It is made possible by the component design and flexibility that is at the core design of Digi-CA™ and is not available from Traditional CA [28] vendors.
The concept is simple: The benefits of outsourcing the entire CA to a Trusted Third Party [TTP] as a Managed CA [78] may meet most of your main business objectives. In a second scenario, your organization may require total ownership of the CA in which case Managed CA is suitable. But there is a third scenario where you want to own the critical assets but do not wish to manage everything internally. In this case, the Digi-CA™ Shared system is the solution.
In instances where critical assets, such as, the Hardware Security Modules [HSMs], databases, key storage and other functions must be retained by your organization and the day-to-day administration, support, help desk, ‘critical response’ and other ‘non critical’ components can be outside your organization, then Digi-CA™ will be your choice.
Digi-CA™ Shared offers all the technical backup and support components of your CA requirements and ‘fills in any gaps’ in your current environment. The external infrastructure, the team of professionals and specialist you require and other critical resources such as Disaster Recovery, critical response and Service Level Agreement [SLA], components can be outsourced with ease. At the same time, the principal assets and integrity you wish to own and control can remain inside your organization.
Digi-CA™ Shared can be designed and delivered to meet your precise requirements and can combine physical IT assets, personnel, help desk, internal and external networks and servers. For further details contact a member of the Digi-CAST1™ [8] Technical Advisor Team and they will advise you accordingly.
![]() [1] To decide on the best CA system for your environment, there are three key considerations you need to take into account and they are explained in the following sub sections of this online manual:
[1] To decide on the best CA system for your environment, there are three key considerations you need to take into account and they are explained in the following sub sections of this online manual:
When deciding on whether the Managed CA [78] or the Managed CA [79] is most suited to you, you should understand the difference between an open and a closed user group. From a CA perspective, this relates to the extent of end user control you have. If the CA exercises some degree of control over the end user’s environment then it is a closed user group and if it doesn’t, it is in an open group.
The following are examples of the two types of user group:
It is not always immediately obvious whether a group is open or closed and it is important that this is determined accurately if your CA is to meet your precise requirements. If there is any doubt, contact the Digi-CAST1™ Team [8] and ask them to advise you.
If the user group is closed, then you may be able to use either CA. There are two exceptions to this when you want to secure:
In 99% of cases an SSL Certificate [17] must be Trusted and if there is any possibility that the secure email [3] is required outside the closed group, then the Trusted Certificate is required here too. In both of these special cases, the Managed CA is your only choice.
The third consideration needed to help you select the correct CA for your organisation is the availability of the type of suitably trained and experienced technical personnel required to run and operate a CA. Most organisations don’t have this type of specialist staff within their organisation and therefore are best advised to use a Managed CA to deliver the required service.
![]() [1] The majority of the remainder of this online manual describes and explains the functionality and flexibility of the Digi-CA™ Server system. With few exceptions, the Digi-CA™ Service can be configured in the same way as Digi-CA™ Server and then offered as a managed service, specifically to meet the needs of your environment.
[1] The majority of the remainder of this online manual describes and explains the functionality and flexibility of the Digi-CA™ Server system. With few exceptions, the Digi-CA™ Service can be configured in the same way as Digi-CA™ Server and then offered as a managed service, specifically to meet the needs of your environment.
There are three classes of Digi-CA™ Server:
The principal difference between Xs, Xp and Xg in each case relates to the degree of integration and customization required. For example, Digi-CA™ Xs can be pre-configured and delivered to the customer for installation without any assistance from Digi-Sign whilst Digi-CA™ Server Xg projects can run for weeks and even months or years.
Depending on type of Digi-CA™ you order and the level of customisation and modification it requires to meet the needs of your specific environment, will dictate the best installation approach. At a basic level (and depending on your qualifications, knowledge, experience, etc.), you can probably install the required operating system and the Digi-CA™ software using help files and telephone support.
Note: If you have technical personnel that can correctly configure a network environment, install the necessary operating systems and provide secure access to the server(s), the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team [8] may be able to conduct a large part of the installation process prior to visiting your site. In some cases, the complete installation can occur without the need for Digi-CAST2™ to visit your site at all.
![]() [1] The Digi-CAST™ methodology was pioneered in 2004 and is a unique approach to simplifying the design, installation, management, certification [9] and re-certification of any CA environment.
[1] The Digi-CAST™ methodology was pioneered in 2004 and is a unique approach to simplifying the design, installation, management, certification [9] and re-certification of any CA environment.
The Digi-CAST™ methodology [8] has four distinctly separate components that are adapted and designed specifically to meet the needs of any Digi-CA™ environment:
Digi-CAST1™ and CAST2™ are used on all Digi-CA™ Server projects whereas, Digi-CAST3™ and CAST4™ are used on larger projects such as enterprise, public sector or national government environments.
The Digi-CA™ Manual covers the Digi-CAST™ methodology in more detail as does our website: www.digi-sign.com [44]
This online manual examines Digi-CAST1™ and CAST2™ in more detail here as these specific relate to issues that an Administrator or Manager would be directly concerned with.
Digi-CAST1™ is concerned with project planning excellence, cause and affect planning, 'skills pool' analysis, personnel selection and management. The most important thing to remember about all Digi-CAST™ modules is that the entire service is tailored to your specific needs. For further details download the Digi-CA™ Manual [76].
Digi-CAST2™ is concerned with detailing the actual project as documented in Digi-CAST1™. Its concern is with personnel, availability, time lines, 'choke points' and overall project delivery. Combining your resources with ours, we begin the project and work together to a common goal. For further details download the Digi-CA™ Manual.
The basic requirements for every Digi-CA™ Server installation are the same and in most instances, Digi-CAST2™ install the Digi-CA™ Server system on your server(s). As more sophisticated environments arise for Digi-CA™ Server Xp or Digi-CA™ Server Xg, the requirements increase accordingly.
![]() [1] Digi-CA™ Server Xs is Managed CA [79] for installation on a single server and comes complete with all the different sub-systems designed to run and operate efficiently on that single machine.
[1] Digi-CA™ Server Xs is Managed CA [79] for installation on a single server and comes complete with all the different sub-systems designed to run and operate efficiently on that single machine.
As a software product, Digi-CA™ Server Xs only generates client certificates [3] [Digi-IDs™] that can be used for email, two-factor authentication, secure web access, as electronic signatures, for use within a Virtual Private Networks [VPN] or for device-to-device authentication. Like all professional CA systems it allows the Administrator to set up policies and to manage all of the Digi-ID™ [21] life cycle services.
Even with all of the powerful functionality and capabilities that Digi-CA™ Server Xs offers, it is easy to install, configure and operate. A competent Network Engineer or qualified IT Technician could install a fully functional version of Digi-CA™ Server Xs and be fully competent in its operation a few days.
Digi-CA™ Server Xs can only be installed on a single server and is typically used where high availability is not a key component of the environment. As a single server installation, there is no mirroring, load balancing, fail over or synchronizing of data. All records and data are protected by periodic backups only. Typical installations would be small to medium environments where high system availability is not an issue.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp is Managed CA for installation on two servers and offers the same services as Digi-CA™ Server Xs but on a larger scale and with many additional services including Certificate deployment and renewal automation. The primary reason for selecting Xp instead of Xs is because Digi-CA™ Server Xp offers fail-over functionality.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp can also be configured to generate Secure Socket Layer [17] [Digi-SSL™ [86]] web server Certificates, Software & Code Signing Certificates [Digi-CAST™ methodology [8]] in addition to the Digi-ID™ Xp Certificates.
Most Digi-CA™ Server Xp installations are carried out by the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team. This installation may require the Digi-CAST2™ Team to physically conduct the installation on site, however, if a competent Network Engineer can provide a reliable connection to the correctly configured servers, then it may be possible to conduct the installation over the internet, without incurring travel and accommodation costs. The fully functional version of Digi-CA™ Server Xp can be completed in three to five days on average.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp is installed on two servers and is typically used where high availability is a component of the environment. As a dual server installation, there is mirroring and synchronising of data. All records and data are protected by this fail-over service. The Digi-CA™ Server Xp is split over two servers and gives the option to include a firewall and load balancing device in between. Typical installations would be large enterprise or government environments.
![]() [1] Digi-CA™ Server Xg is the CA for commercial Trust Centres [10] and other large scale PKI [7] deployments. The entire system and its components parts can be split over many servers and systems as required with a minimum of four servers and a single Hardware Security Module [HSM] being the basic deployment.
[1] Digi-CA™ Server Xg is the CA for commercial Trust Centres [10] and other large scale PKI [7] deployments. The entire system and its components parts can be split over many servers and systems as required with a minimum of four servers and a single Hardware Security Module [HSM] being the basic deployment.
Digi-CA™ Server Xg is used where high availability and reliability are a key component of the environment. As a multi-server installation, there is mirroring, fail over and synchronizing of data. All records and data are protected by this fail-over service. The Digi-CA™ Server Xg separates the CA services so that seven layers of security can be applied to the Trust Centre environment. The CA services are located in the Certificate Engine core with the RA, Certificate Revocation List [CRL], Lightweight Directory Access Protocol [LDAP] and Time Stamping [75] services located in the Outer Core (see Appendix II). Typical installations are government and commercial CA Trust Centres.
This class of Digi-CA™ Server has four levels of security including two or three levels of firewalls with fail over facilities and can incorporate hot standby, disaster recovery and a single system can operate from multiple locations.
Digi-CA™ Server Xg customization, configuration and testing is conducted off site after detailed requirements are documented and agreed with the customer. This off site work can take several weeks, or months, depending on the level and scale of the customizations required. Once configured, the fully functional version of Digi-CA™ Server Xg can be completed in five to ten days.
All Digi-CA™ Server Xg installations must be carried out by the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team and requires that the Team conduct the installation on site with the associated travel and accommodation costs.
![]() [1] The Digi-CA™ is a complete Digital Certificate [3] and certificate management system. It has three main components that are explained in more detail in their respective sub sections:
[1] The Digi-CA™ is a complete Digital Certificate [3] and certificate management system. It has three main components that are explained in more detail in their respective sub sections:
The Digi-CA™ Administration Management Console is for use by Senior Administrators. At a minimum, these should be qualified Senior Administrators with in-depth knowledge and qualifications specifically in IT and IT security networks. Suitable personnel would be the CTO, CIO, CISO, IT Director, Systems Manager, Systems Analyst, Analyst Programmer, Software Engineer, Technical Engineer and similar job functions with ‘hands on’ technical experience of five or more years. The sections of this online manual relevant to these Senior Administrators are marked in blue.
The Digi-CA™ RA Management Console is for use by RA Administrators. At a minimum, these should be qualified network Administrators with good working knowledge and qualifications specifically in IT and IT security networks. Suitable personnel would be the Technical Managers, Information Systems Manager, QA Manager, Product Manager, Systems Analyst, System Administrator, Senior Systems Engineer, Unix Administrator and similar job functions with ‘hands on’ technical experience of three or more years.
The Digi-CA™ Control Centre or LRA Management Console is for use by RA Operators. This is the most basic component of the Digi-CA™ system and the Operator needs only to have basic PC skills to adequately fulfill this role.
![]() [45] The flexibility of the Digi-CA™ [23] Certificate Authority [CA] system design means that each installation is unique and customised to the precise needs of the customer. Once the Digi-CAST™ [36] Team have agreed and documented your requirements, your Managed CA [89], Digi-CA™ Service or CA Software [90], Digi-CA™ Server, is configured and activated. In certain projects, your specific needs may require a combination of CA Software and a Managed CA, to achieve the best results. Uniquely and unlike any other Traditional CA [28] system on the market, Digi-CA™ can offer the Shared CA [91] option.
[45] The flexibility of the Digi-CA™ [23] Certificate Authority [CA] system design means that each installation is unique and customised to the precise needs of the customer. Once the Digi-CAST™ [36] Team have agreed and documented your requirements, your Managed CA [89], Digi-CA™ Service or CA Software [90], Digi-CA™ Server, is configured and activated. In certain projects, your specific needs may require a combination of CA Software and a Managed CA, to achieve the best results. Uniquely and unlike any other Traditional CA [28] system on the market, Digi-CA™ can offer the Shared CA [91] option.
The following are samples of different CA projects that use the different Digi-CA™ options and also combine other valuable services like the Digi-CAST™ Methodology [36] and consulting advice; the Total Trust Management™ [92] [TTM™] CA Management service; and the Digi-TaSC [93] on line system for CA Management and compliance.
The most substantial difference between Digi-CA™ and other Traditional CA [28]s is the flexibility and capabilities that are central to the design of the Public Key Infrastructure [PKI] system. This means that virtually any type of PKI design can be implemented using Digi-CA™ and because Digi-CA™ is probably the most modern CA available on the market, your specific design requirements can be delivered easily and cost effectively.
The following sub sections provide details of a typical project implementation and its stages. The Preliminary Analysis & Requirement Measurement stage of the project (stage I) is the first stage and this sets the project parameters and requirements from the very beginning of your project:
s
The most substantial difference between Digi-CA™ [23] and other Traditional CA [28]s is the flexibility and capabilities that are central to the design of the PKI system. This capability of transferring from a different service provider is a powerful capability that is simply not available from alternative vendor.
Digi-CA™ allows for easy migration from one data centre, or system, in an almost seamless manner. The transfer can be accomplished either physically through hardware transportation or by secure software and data migration whereby all software and database data is securely migrated in an encrypted format from one location to another.
The following sub sections provide details of the suggested project implementation stages for the transition plan. The plan is subject to decision on the re-use of existing HSMs, or the export/import of existing CA private keys and other project implementation considerations that will emerge during the Preliminary Analysis & Requirement Measurement stage of the project (stage I):
The most substantial difference between Digi-CA™ [23] and other Traditional CA [28]s is the flexibility and capabilities that are central to the design of the PKI system. This capability of transferring from a different service provider is a powerful capability that is simply not available from alternative vendor.
Digi-CA™ allows for easy migration from one data centre, or system, in an almost seamless manner. The transfer can be accomplished either physically through hardware transportation or by secure software and data migration whereby all software and database data is securely migrated in an encrypted format from one location to another.
The following sub sections provide details of the suggested project implementation stages for the transition plan. The plan is subject to decision on the re-use of existing HSMs, or the export/import of existing CA private keys and other project implementation considerations that will emerge during the Preliminary Analysis & Requirement Measurement stage of the project (stage I):
Digi-CA™ [23] is probably the most modern Certificate Authority [CA] system currently available in the market. It is modern because it leverages the many advances in open source technology including Linux, SQL and PHP.
Unlike Traditional CA [28]s, the Digi-CA™ system can create multiple instances of unique CAs in a single Digi-CAtrade; system. The Digi-CAtrade; model imposes delegation of trust downwards from CAs to their Subordinate Certification Authorities [Sub-CAs].
The same Digi-CAtrade; system also enables any CA or Sub-CA to be signed or cross signed by an external third party CA. And any number of CAs can have any number of cross signed Sub-CAs. As a result of this design principal, the Digi-CAtrade; model for trust levels increases towards the highest authority. This type of arrangement facilitates easy deployment and scalability of any PKI requirement from the smallest to the largest.
The following provides a high level overview of a typical Digi-CAtrade; Server installation at a Trust Centre [94]:
The Digi-CAST2™ [36] Team will install the Digi-CA™ PKI software and to do this the first data centre must be constructed 100%. This must include all power, cabling, fire detection, fire depressant and that the air conditioning is installed and fully tested. The air conditioning system testing is very important, as it can cause water issues if not fully tested.
The Trust Centre must then be cleaned to medical/hospital standards before any hardware is installed. The construction on the second disaster recovery data centre (if required) should start at the same time, or no more than two weeks after the first data centre. It is not required that this Disaster Recovery data centre is completed before the Digi-CAST2™ Team arrive at the Trust Centre, however it must be finished no later than one week after the Digi-CAST2™ Team arrive on site and again must be 100% finished and cleaned in that time.
Nothing will happen with the Digi-CA™ PKI software installation until the Trust Centre completion and cleaning date is confirmed. Once this date is confirmed and the hardwre is ordered, the Partner [96] should be capable fo getting all the servers, switches, network and server software, HSMs, etc delivered within 2-3 weeks of the contract being signed.
After the contract is signed the Trust Centre should be ready so that the installation of the IT infrastructure can be completed within 1 week. By the beginnning of week 4, the entire of the main Trust Centre is active and ready for the installation of the Digi-CA™ software.
Week 5 the Disaster Recovery data centre should be completed and the the Digi-CAST2 Installations Team will then arrive to begin work on the Trust Centre whilst the Digi-Trust™ Partner [96] to complete the second data centre IT infrastructutre totally and ready in one week so that by week 6, the second week for the the Digi-CAST2 Installations Team on site, they can begin the configuration of this Disaster Recovery Digi-CA™.
In week 7, after the contract is signed, the Digi-CAST2 Installations Team will be finished and can seek to have the User Acceptance Testing [UAT] sign off, to officially complete the installation process.
![]() [1] The Digi-CA™ Administrators Master Console is the central core of the entire CA system. From this Administrators Master Console the Administration of the CA is implemented and managed. The Administrators Master Console creates the Root CA, CA, Intermediate and Subordinate or Sub-CAs, the RAs and the Control Centres or LRAs.
[1] The Digi-CA™ Administrators Master Console is the central core of the entire CA system. From this Administrators Master Console the Administration of the CA is implemented and managed. The Administrators Master Console creates the Root CA, CA, Intermediate and Subordinate or Sub-CAs, the RAs and the Control Centres or LRAs.
The Digi-CA™ system model is a hierarchical trust model, in which, each entity implicitly trusts the entity above it. This model imposes the delegation of trust downwards from Root CAs to its Subordinate CAs. As a result, inherent in the design of the Digi-CA™ is the fact that the levels of trust increase as you go upwards to the higher authority. By its very design, this type of system architecture facilitates easy deployment of a large scale PKI [7]. The Administrators Master Console, its function and detailed instructions on how to use it are further described in Section 5 of this on line manual.
Read the on line Training Manual [97] for the CA AMC.
The Digi-CA™ RA Management Console is the primary management interface for a specific CA or Sub-CA. The RA Management Console provides an interface to access and manage RAs and LRAs, that are created through the CA Administration Management Console. Each RA or LRA can interface multiple CAs to allow the issuance of different types of digital Certificates through different CAs from a single central and easily manageable location. The remainder of the functions of the RA Management Console its function and detailed instructions on how to use it are further described in Section 6 of this on line manual.
Read the on line Training Manual [98] for the RA MC.
The Digi-CA™ Control Centre is more commonly known in the PKI [7] industry as an LRA and is the RA Operator interface for accessing the RA with limited features provided. For the remainder of this document and to avoid confusion, the LRA is referred too as the Control Centre. The Control Centre is a ‘stripped down’ version of the RA Console. The Control Centre is used to manage individual Certificate life cycle functions such as issuing, revoking, suspending and renewing Certificates. The remainder of the functions of the Control Centre, its function and detailed instructions on how to use it are further described in Section 5 of this on line manual.
Read the on line Training Manual [99] for the LRA Control Centre.
Depending on the configuration, policy and distribution of your Digi-CA™, some service may be publicly available. These public services are typically to enable basic end user requirements for Digital Certificates and the following sub sections describe the four main functions:
Read the on line Training Manual [100] for the RA RS.
![]() [101] The following table sets out the principal technical specifications of the Digi-CA™:
[101] The following table sets out the principal technical specifications of the Digi-CA™:
![]() [101] The Digi-CA™ PKI [7] System software suite is a multi application component based PKI system for managing cryptographic keys, Digital [X.509] Certificates and supplemental PKI related services. Each application component provides a series of defined functionalities to other PKI application components of the system, as well as to administering and operating parties, and to end entities, to whom certificates are issued. This system is built with the following modules:
[101] The Digi-CA™ PKI [7] System software suite is a multi application component based PKI system for managing cryptographic keys, Digital [X.509] Certificates and supplemental PKI related services. Each application component provides a series of defined functionalities to other PKI application components of the system, as well as to administering and operating parties, and to end entities, to whom certificates are issued. This system is built with the following modules:
All Digi-CA™ components providing core functionalities were developed using C programming language and the software operates under Unix/Linux operating system environment, which has proven to be a solid, reliable – and if not the best - platform family choice for server side applications.
Diagram below illustrates the overall logical and high level hardware architecture design of a complex PKI infrastructure that Digi-CA™ can be deployed in. This includes multi-server based system component distribution, replication and failover of various PKI services and load balancing.
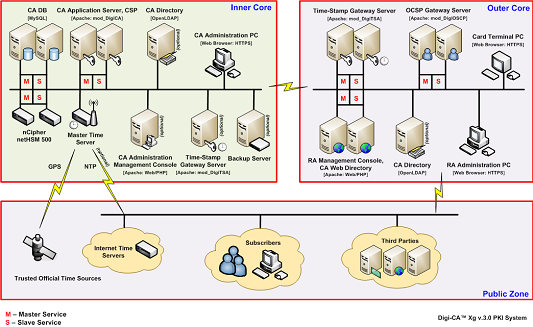
![]() [101] Whilst Digi-CA™ software can meet most complex requirements, in many scenarios it is often required to operate all PKI [7] related services on a single dedicated server hardware. Digi-CA™ can easily meet this requirement and the diagram below illustrates overall logical and high level hardware architecture design of the basic infrastructure utilizing a single server to operate all Digi-CA™ PKI services. This unique feature of Digi-CA™ software suite provides not only a flexible range of possible configuration variations but allows organizations to slowly build their own PKI infrastructure from a very small environment, thus carefully control their expenditure related to purchasing and maintenance of hardware devices.
[101] Whilst Digi-CA™ software can meet most complex requirements, in many scenarios it is often required to operate all PKI [7] related services on a single dedicated server hardware. Digi-CA™ can easily meet this requirement and the diagram below illustrates overall logical and high level hardware architecture design of the basic infrastructure utilizing a single server to operate all Digi-CA™ PKI services. This unique feature of Digi-CA™ software suite provides not only a flexible range of possible configuration variations but allows organizations to slowly build their own PKI infrastructure from a very small environment, thus carefully control their expenditure related to purchasing and maintenance of hardware devices.
Digi-CA™ PKI System provides a wide range of PKI related functionalities and introduces a variety of services and features including:
Production speed:
Key length:
Certificate validity:
Key storage:
Cryptographic Ciphers:
Signature Algorithms:
Entropy:
![]() [101] The success or failure of any project can usually be traced back to the original plans. As explained, the Digi-CAST™ methodology [8] is a unique approach to a CA project and its purpose is to ensure the successful delivery of Digi-CA™, every time.
[101] The success or failure of any project can usually be traced back to the original plans. As explained, the Digi-CAST™ methodology [8] is a unique approach to a CA project and its purpose is to ensure the successful delivery of Digi-CA™, every time.
Simply buying Digi-CA™ (or any Managed CA [79]) is not a guarantee that your environment and your project will succeed. To achieve success, the organization must actively participate in the project from the outset. To do this, you must gain a clear understanding of the Digital Certificate [3] technology and the functions, uses and capabilities of a Certificate Authority [2].
If you have not already done so, download the Digi-CA™ Manual [76] for further information.
The simplest way to select the correct Digi-CA™ for your organization is to decide how many users you have (or in some cases the number of physical devices you need to identify). This should include employees, customers, partners or suppliers and the individual people that work in each of these areas that you wish to issue a Digital Certificate [Digi-ID™ [21]] too.
Environment Requirement Users Recommended Digi-CA™
Environment B Online transaction and document signing [102] for application forms and business processes 40,000 Digi-CA™ Server Xs
Environment C Device authentication 100,000 Digi-CA™ Server Xp
Environment D Manufacturer or Large Software House with fail over Unlimited Digi-CA™ Server Xp
Environment E National Security requirement for foreign delegates 1,000 Digi-CA™ Server Xg
(customised)
Environment F National Identity Card and/or Smart Passport 25,000,000 Digi-CA™ Server Xg
(customised)
Environment G Digi-CA™ Xg Trust Centre Unlimited Digi-CA™ Server Xg
Another alternative is to look at the level of security that you wish to achieve. If the security is relating to corporate secrets, national security or can be regarded as critical, regardless of cost, then Digi-CA™ Xg may be the only option for you. The Digi-CAST1™ Team [36] of professional advisors will guide you toward the optimum solution.
The most important benefit of Digi-CA™ is that every aspect of the final solution can be tailored to meet your precise user, security and policy requirements.
The most important benefit of Digi-CA™ is that every aspect of the final solution can be tailored to meet your precise user, security and policy requirements.
The following table can be used as a guide to assist in choosing the best Digi-CA™ Server for your environment.
![]() [101] You should clearly identify if your user group is open or closed, what you want to use your Certificates for and whether you have the staff required to run and operate the Digi-CA™. If, having downloaded and read the Digi-CA™ Manual [76] that advises you on how to select your Digi-CA™ and you are still not clear, then contact the Digi-CAST1™ Team [36] and seek their advice before proceeding further.
[101] You should clearly identify if your user group is open or closed, what you want to use your Certificates for and whether you have the staff required to run and operate the Digi-CA™. If, having downloaded and read the Digi-CA™ Manual [76] that advises you on how to select your Digi-CA™ and you are still not clear, then contact the Digi-CAST1™ Team [36] and seek their advice before proceeding further.
Using the authentication and validation Certificate Policies from your Traditional CA, Digi-CA™ can migrate users automatically without requiring any IT resources or Administrators’ time.
The Digi-CA™ is probably the most flexible and capable CA system available in the market today. Unlike the other Traditional CAs, Digi-CA™ takes advantage of the many advances in technology over the past seven years and you benefit by getting the flexible, cost effective and easily integrated CA system you need.
The Digi-CA™ still uses Unix in its Certificate Engine core but by using Open Standard Architecture in other modules, the Digi-CAST2™ Team customisation and upgrade costs are substantially less than those normally associated with the complex and costly modifications of the less flexible Unix Traditional CAs.
This section explains the design principles and also gives typical examples of previous customizations . The most important feature of Digi-CA™ is that your precise requirements can be delivered, exactly as you require.
In the larger or more complex environment, the organization may require a workflow process to control the use of the Digi-CA™ usage from a cost, security or for general management reasons. The following is an example of a customization currently in use by a Digi-Sign customer for issuing Digi-SSLs™:
This type of customization is not unusual but it does add to the initial cost of deploying a Digi-CA™ system.
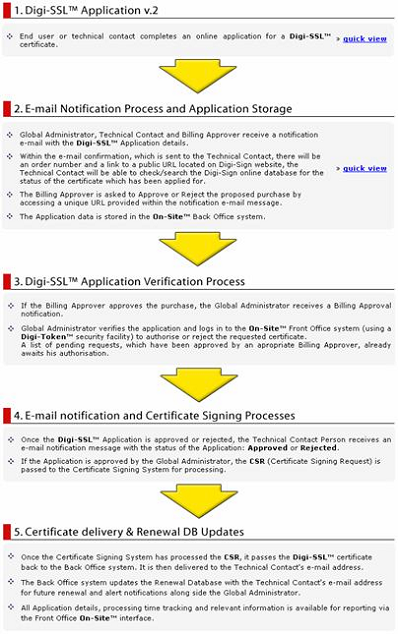
Every aspect of the Digi-CA™ can be automated. Examples of this would be where the Digi-IDs™ are being used to replace Usernames and Passwords for login to a secure website, to replace hardware tokens like SecurID®, to issue Digi-IDs™ for secure email [3] on a closed network or to replace an existing Traditional CA with Digi-CA™.
Using the Digi-CA™ flexible design technology and capabilities, it is possible to use existing LDAPs or other databases such as Oracle®, Active Directory® or any other SQL or flat file format to automate the Digi-ID™ [21] issuing, renewal, suspension and revocation processes.
Read more on why you should choose Digi-Sign [103]
![]() [101] The entire Digi-CA™ system and all of the interfaces used by the Administrators and users can be completely customized on request. Typical reasons for the graphical changes are for integrating Digi-CA™ into a larger application to make a complete package or the simpler integration of the Digi-CA™ into the organization’s web systems or extranet.
[101] The entire Digi-CA™ system and all of the interfaces used by the Administrators and users can be completely customized on request. Typical reasons for the graphical changes are for integrating Digi-CA™ into a larger application to make a complete package or the simpler integration of the Digi-CA™ into the organization’s web systems or extranet.
The specification of the Digi-CA™ at the time of going to print is available in Appendix IV. All specification updates and technical help files are updated using the online support section of the Digi-Sign website located at www.digi-sign.com [44].
Digi-CA™ offers the capability to completely localise all interfaces, help files and user screens into your local language(s). This is particularly important to organisations where English is not used. It is also possible to have multiple interfaces with multiple languages for the same system. The following two samples show the Digi-CA™ Control Centre screen in Chinese and the user enrollment screen where users can apply for a Digi-ID™ [21] in Turkish.
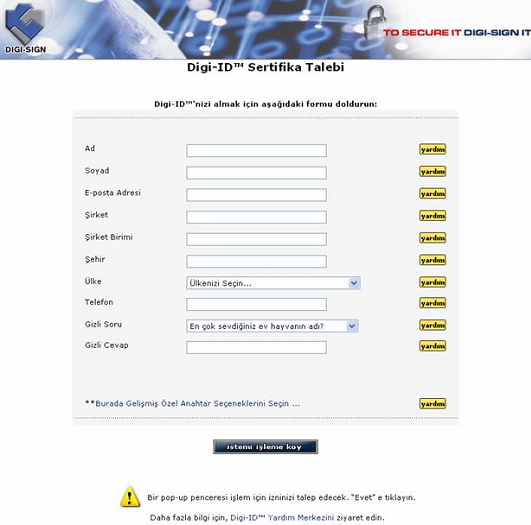
Note: Sample Only – Grammar & Diction not checked
The importance of the capability to produce the Digi-CA™ in the local language(s) cannot be over stated. It will result in faster training of the RA personnel and will significantly reduce the Help Desk Support calls (where users are seeking help to with translations from English rather than actual technical support related issues).
It is also possible to have a single Digi-CA™ configured in multiple languages so that different Digi-RAs™ in different countries can use the same Digi-CA™ Control Centre in their native language. Similarly, the users requesting Digi-IDs™ can do so from the same system but again in their native language.
To have your Digi-CA™ localized in your language, the system files and instructions are available in Appendix I.
![]() [101] The Digi-CA™ RA/API system is a highly customisable way to issue and manage x.509 Certificates issued for digital signature [3], secure email [3], two factor authentication [4] and other purposes. It:
[101] The Digi-CA™ RA/API system is a highly customisable way to issue and manage x.509 Certificates issued for digital signature [3], secure email [3], two factor authentication [4] and other purposes. It:
The Digi-CA™ RA/API system is account based, therefore in order to be able to implement and use the system, the RA API account needs to be setup first on the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core system. Before implementing the RA API you must contact the Digi-CAST™ [8] Team to ensure you have the latest version and release notes.
The entire RA/API system is based on a flat and secure communication between the RA API and the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine Core system. It is achieved using the HTTP ‘POST’ method secured with an SSL/TLS layer on top of a standard TCP/IP connection.
Depending on the specific action that needs to be completed by the Administrator, i.e.: Digi-ID™ [21] request, Digi-ID™ approval, Digi-ID™ suspension, Digi-ID™ revocation or other request, a different URL will be used for each individual action.
Relevant points below are an overview of the steps involved in the Digi-CA™ RA operations using the RA/API.
![]() [101] The user will browse to a fully customized Digi-ID™ Application Form Enrolment page. They will complete the details in the web form and click the ‘submit’ button. Depending on the chosen Certificate delivery method (Process/Package), a VB script or Java applet on the webpage can then initiate the chosen Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP] engine to generate the Private Key and Certification request (PKCS#10), before submitting all data (with the exception of the Private Key if the Process Method is chosen) to the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core system.
[101] The user will browse to a fully customized Digi-ID™ Application Form Enrolment page. They will complete the details in the web form and click the ‘submit’ button. Depending on the chosen Certificate delivery method (Process/Package), a VB script or Java applet on the webpage can then initiate the chosen Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP] engine to generate the Private Key and Certification request (PKCS#10), before submitting all data (with the exception of the Private Key if the Process Method is chosen) to the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core system.
You will need to decide the type and order of the attributes that will appear in the "Subject" field of your Digi-ID™ [21] Certificate. You may have multiple attributes of the same type (e.g. multiple ‘OU’s are common). You will also need to consider what attributes are required and which of these, if any, are optional. These settings may also be overwritten by the Digi-Policy™ applied on the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine Core system for the specific RA API. The following table is a list of the common attribute types that are currently recognized by the Digi-CA™ Certificate Engine core system:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CN |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
SN |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
C |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
OU |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
T |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
32 |
|
|
|
G |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
I |
|
1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
E |
|
1 |
|
|
|
![]() [101] The type of Digi-CA™ Server you choose for your environment will dictate what information you need to install it and if you will need assistance from the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team [36].
[101] The type of Digi-CA™ Server you choose for your environment will dictate what information you need to install it and if you will need assistance from the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team [36].
The basic requirements for installing any Digi-CA™ Server are very similar and the four main components are detailed for each case:
Before proceeding with any installation of Digi-CA™, it is strongly recommended that a thorough study of the download Digi-CA™ Manual [45] Manual is undertaken. Ultimately, Digi-CA™ is software, however, all Certificate Authorities [2] need careful planning and decision making by informed personnel if the project is to be a success.
Careful consideration should also be given to using the Digi-CAST1™ [36] professional services and from the advice received whether it is recommended that Digi-CAST2™ Installation Team support.
Digi-CA™ Server Xs is Managed CA [79] for installation on a single server and comes complete with all the different sub-systems designed to run and operate efficiently on that single machine.
The basic Digi-CA™ Server Xs software is supplied on a DVD, or as a downloadable binary file inside a .zip file from the www.digi-sign.com [44] website. Subject to ordering and purchasing, the version of Digi-CA™ Server Xs you receive may be modified to meet your specific requirements. These modifications will result in a different install sequence in some cases. To ensure the installation instructions are compatible with the customized version of your Digi-CA™ software, the specific installation guide is included in the software delivered. Once received, install it by using the ‘Digi-CA Install Guide.doc’ supplied with the specific software on the DVD, or in the .zip file.
If a secure VPN connection to the single server can be provided, it is possible that the installation of the software can be carried out virtually by the Digi-CAST2™ Installation Team if required. The benefit of this is that it reduces the cost of travel and accommodation. When examining each of the following four sub sections you can consult with the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team, at any time, to check configurations and access for you.
![]() [101] These are the minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
[101] These are the minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
Digi-CA™ Server Xs is supplied complete and ready for total install on the server but it must have a Unix or Linux Operating System [OS] pre-configured.
During the installation, the Digi-CA™ Server will use versions of the following software that will be hardened and modified by the Digi-CAST2™ Team [36] during their installation work:
The previous list is provided for information purposes only.
These are the minimum requirements for the correct installation of the single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs:
Digi-CA™ Server Xs can be installed on any Unix or Linux platform once it is compiled in advance. The Digi-CAST1™ Team will advise you on the best Operating System [OS] for your environment and here is a suggested list:
![]() [101] Digi-CA™ Server Xp is Managed CA [79] for installation on two or more servers and comes complete with all the different sub-systems designed to run and operate efficiently on these machines. Customizations and certain specific requirements can be facilitated in this class of the Digi-CA™ software and HSM hardware can also be included in the design of the CA network as required.
[101] Digi-CA™ Server Xp is Managed CA [79] for installation on two or more servers and comes complete with all the different sub-systems designed to run and operate efficiently on these machines. Customizations and certain specific requirements can be facilitated in this class of the Digi-CA™ software and HSM hardware can also be included in the design of the CA network as required.
The basic Digi-CA™ Server Xp software is supplied on a DVD, or as a downloadable binary file inside a .zip file from the www.digi-sign.com [44] website. Subject to ordering and purchasing, the version of Digi-CA™ Server Xs you receive may be modified to meet your specific requirements. These modifications will result in a different install sequence in some cases. To ensure the installation instructions are compatible with the customized version of your Digi-CA™ software, the specific installation guide is included in the software delivered. Once received, install it by using the ‘Digi-CA Install Guide.doc’ supplied with the specific software on the DVD, or in the .zip file.
As with Digi-CA™ Server Xs, if a secure VPN connection to the server environment can be provided, it is possible that the installation of the software can be carried out virtually by the Digi-CAST2™ Installation Team [36] if required. The benefit of this is that it reduces the cost of travel and accommodation. When examining each of the following four sub sections you can consult with the Digi-CAST2™ Installations Team, at any time, to check configurations and access for you.
The minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp are the same as those for [106].
These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp are the same as the specifications for [107] except 2 x Servers: Dell®/HP®/IBM®, are required.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp is supplied complete and ready for total install on the server but it must have a Unix or Linux Operating System [OS] pre-configured.
During the installation, the Digi-CA™ will use versions of the same software that is used by [106] will be hardened and modified by the Digi-CAST2™ Team during their installation work.
The minimum requirements for the correct installation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp are the same as those for [108].
As with Digi-CA™ Server Xs [109], Digi-CA™ Server Xp can be installed on any Unix or Linux platform once it is compiled in advance. The Digi-CAST1™ Team will advise you on the best Operating System [OS] for your environment.
![]() [101] The Digi-CA™ Server Xg is completely customizable and can be installed across many servers, even if they are in different locations. As stated, Digi-CA™ Server Xg customisation, configuration and testing is conducted off site after detailed requirements are documented and agreed with the customer. This off site work can take several weeks, or months, depending on the level and scale of the customisations required.
[101] The Digi-CA™ Server Xg is completely customizable and can be installed across many servers, even if they are in different locations. As stated, Digi-CA™ Server Xg customisation, configuration and testing is conducted off site after detailed requirements are documented and agreed with the customer. This off site work can take several weeks, or months, depending on the level and scale of the customisations required.
As an example, when Digi-CA™ Server Xg is used to build a Trust Centre [10], a minimum of four servers are required and if the correct internet connection and a VPN can be provided to the servers, it is possible that much of the preparation and network testing prior to the installation of the software can be carried out virtually. However, the Digi-CA™ Server Xg will require at least one site visit from a Digi-CAST2™ Team Member [36] to conduct certain specialist tasks.
The benefit of using the VPN connection as much as possible during this preparatory work is that it reduces the cost of travel and accommodation. When examining each of the following three sub sections you can consult with the Digi-CAST2™ Team at any time to check configurations and access for you.
These are the minimum suitable conditions for the correct operation of the multiple server Digi-CA™ Server Xg:
These are the minimum equipment specification for the correct operation of the dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp are the same as the specifications for [107] except 4 x Servers: Dell®/HP®/IBM®, are required and we also recommend using at least one HSM (nCipher, Utimaco, etc).
Digi-CA™ Server Xg is supplied complete and ready for total install on the server but it must have a Unix or Linux Operating System [OS] pre-configured.
During the installation, the Digi-CA™ will use versions of the same software that is used by [106] will be hardened and modified by the Digi-CAST2™ Team [36] during their installation work.
The minimum requirements for the correct installation of the Digi-CA™ Server Xg are the same as those for [108].
![]() [101] The Digi-CA™ PKI [7] System supports a variety of Unix and Linux operating systems. It was also designed to use various third party software libraries that are required to be present on your operating system prior to the beginning of the installation of any version of Digi-CA™.
[101] The Digi-CA™ PKI [7] System supports a variety of Unix and Linux operating systems. It was also designed to use various third party software libraries that are required to be present on your operating system prior to the beginning of the installation of any version of Digi-CA™.
The support and ongoing development of third party software applications and libraries that are necessary to install and operate Digi-CA™ software is not part of the system or license provided. However, for your reference, you can find a set of stable software applications and libraries provided as part of the distribution of the Digi-CA™ PKI System. A list of these applications and libraries and a set of quick installation guides for each of the necessary applications or libraries is included in this sub section.
![]() [101] As can be seen from the extensive documentation relating to the Key Ceremony [19], at the heart of every Digi-CA™ is at least one Root CA. Every Digi-CA™ Certificate is made from a Public and a Private Key. After the Root Key Ceremony procedure has produced the unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated and depending on the Certificate Practice Statement [12] [Certificate Practice Statement [12]] and Certificate Policy [CP], the generation of the Root Keys may require notarization, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples and for further details review the Root Key Ceremony [19].
[101] As can be seen from the extensive documentation relating to the Key Ceremony [19], at the heart of every Digi-CA™ is at least one Root CA. Every Digi-CA™ Certificate is made from a Public and a Private Key. After the Root Key Ceremony procedure has produced the unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated and depending on the Certificate Practice Statement [12] [Certificate Practice Statement [12]] and Certificate Policy [CP], the generation of the Root Keys may require notarization, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples and for further details review the Root Key Ceremony [19].
The Root Certificate is only ever used to sign the Intermediate Root Key(s). After signing this Key(s) the Root Key is 3-DES encrypted and split into a minimum of 4 Key shares that are each stored on 3-DES encrypted smartcard and signed with RSA SHA-1. All Key shares will have a unique password and should be stored separately in different secure locations (bank vault, safety deposit box, attorney’s office, etc). A Key generation log is kept in the system and in a separate physical log.
Important Note: the Root Certificate should not exceed a 25-Year life duration.
In order to create Digi-IDs™ from the system, at least one self-signed Digi-CA™ Root Certificate must be generated. There is a possibility in the system, depending on ordered options, to create any number of Digi-CA™ Root Certificates and Digi-CA™ Intermediate Roots with different policies and validity. The figure below represents a theoretical relationship between Digi-CA™ CA Certificates. Please consult Digi-CAST1™ [36] before setting up your specific schema.
The Intermediate CA Certificate is protected by 3-DES encryption and all key shares have unique passwords.
Important Note: the Root Certificate should not exceed a 25-Year life duration.
The Digi-CA™ PKI [7] System provides the ability to operate a Sub-CA that can be signed by a publicly recognized CA. This enables the Digi-CA™ to issue and manage Digital Certificates [3] for S/MIME and SSL, that are globally trusted throughout the Internet Community. To get a globally Trusted Root [TRoot] to sign the Sub-CA, consult the Digi-CAST™ [8] Team leader for your project.
The following pages are intended for the Network Engineer or Administrator for the Digi-CA™ system that is responsible for preparing the network and servers, prior to installation.
To avoid delays with the install of your Digi-CA™ system and to avoid the postponement or complete cancellation of your installation, follow the instructions on each of these pages very carefully.
If in doubt, or need technical assistance, email digi-cast@digi-sign.com [111] to contact a member of the Digi-CAST™ [36].
![]() [112] Usually a stable and recent enough Sendmail software is provided for your convenience by the Operating System Vendor and we recommend using the release that the Vendor included in its Operating System distribution. For further information about Sendmail or to download its most recent release, visit the Sendmail website on www.sendmail.org [113].
[112] Usually a stable and recent enough Sendmail software is provided for your convenience by the Operating System Vendor and we recommend using the release that the Vendor included in its Operating System distribution. For further information about Sendmail or to download its most recent release, visit the Sendmail website on www.sendmail.org [113].
Usually a stable and recent enough GCC compiler is provided for your convenience by the Operating System Vendor and we recommend using the release that the Vendor included in its Operating System distribution. For further information about the GNU C Compiler or to download its most recent release, visit the GNU GCC website on gcc.gnu.org.
OpenSSL 0.9.8c compiled from source code distribution with necessary patches as per the list below.
Patch Name Version Comments
Time-Stamping [114] 20060923-0.9.8c required for Time-Stamping
nCipher CHIL 0.9.8a to support nCipher HSM
Before you compile your OpenSSL toolkit, you will need to apply the Time-Stamping patch and optionally a Cryptographic Hardware Interface Library patch for interfacing nCipher HSM devices. Both patches are provided with the source distribution of Digi-CA™ and you may find them in the OpenSSL/patches sub-directory of your Digi-CA™ source distribution package. Visit OpenSSL website on www.openssl.org [115] to download the OpenSSL cryptographic toolkit. When configuring and compiling this toolkit, ensure you compile its libraries as dynamically shared. To perform a quick installation, use the Quick Installation guide provided below.
The Quick Installation Guide [QIG] for OpenSSL 0.9.8c suggests that you change working directory to the location where you saved the OpenSSL toolkit source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the OpenSSL toolkit in /usr/local/src directory.
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Using patch, apply patch to enable Time-Stamping feature:
Optionally, apply patch for Cryptographic Hardware Interface Library:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
![]() [112] The recommended URL syntax based Network Communication Tool is cURL 7.16.1 and this should be compiled from source code distribution with SSL support enabled. Visit the cURL website on curl.haxx.se to download the cURL source distribution.
[112] The recommended URL syntax based Network Communication Tool is cURL 7.16.1 and this should be compiled from source code distribution with SSL support enabled. Visit the cURL website on curl.haxx.se to download the cURL source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the cURL source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the cURL in /usr/local/src directory.
Change working directory:
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
stunnel 4.20 compiled from source code distribution with SSL support enabled. Visit the sTunnel website on www.stunnel.org [116] to download the sTunnel source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the sTunnel source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the sTunnel in /usr/local/src directory.
Change working directory:
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
The recommended Hashing & Encryption Tools and Libraries are from libmcrypt 2.5.8 compiled from source code distribution. Visit the mCrypt website on mcrypt.sourceforge.net to download the mCrypt library source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the mCrypt library source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the mCrypt library in /usr/local/src directory.
Change working directory:
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
![]() [112] GNU mHash 0.9.9 compiled from source code distribution. Visit the mHash website on mhash.sourceforge.net to download the mHash source distribution.
[112] GNU mHash 0.9.9 compiled from source code distribution. Visit the mHash website on mhash.sourceforge.net to download the mHash source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the mHash source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the mHash in /usr/local/src directory.
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
mCrypt 2.6.6 compiled from source code distribution. Visit the mCrypt website on mcrypt.sourceforge.net to download the mCrypt toolkit source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the mCrypt toolkit source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the mCrypt toolkit in /usr/local/src directory.
Change working directory:
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
Apache 2.2.6 Web Server is compiled from source code distribution with SSL support enabled. Visit the Apache website on www.apache.org [117] to download the Apache web server source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the Apache source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the Apache source distribution in /usr/local/src directory.
Change working directory:
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile and install:
![]() [112] MySQL 5.0.37 SQL Database Server and Client is compiled from source code distribution with SSL support enabled. Visit the MySQL website on www.mysql.org [118] to download the MySQL database server source distribution.
[112] MySQL 5.0.37 SQL Database Server and Client is compiled from source code distribution with SSL support enabled. Visit the MySQL website on www.mysql.org [118] to download the MySQL database server source distribution.
Change working directory to the location where you saved the MySQL source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the MySQL source distribution in /usr/local/src directory.
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Change working directory:
As super user, add new user and group:
Prepare the installation:
Compile and install:
Copy the recommended MySQL configuration file to its destination folder within your operating system:
Change working directory:
Change ownership of the working directory:
Install default databases:
Change ownership of the working directory:
Before you compile your PHP package, you will need to apply the DigiCA™ Cryptographic patch, that will enable the PHP language with additional cryptography related features required by Digi-CA™. The patch is provided with the source distribution of Digi-CA™ and you may find it in the PHP/patches sub-directory of your Digi-CA™ source distribution directory tree. Visit PHP website on www.php.net [120] to download the PHP package. To perform a quick installation, use the Quick Installation guide provided below.
![]() [112] Change working directory to the location where you saved the PHP source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the PHP source distribution release in /usr/local/src directory.
[112] Change working directory to the location where you saved the PHP source distribution release. For the purpose of this installation guide, we will assume you have saved the PHP source distribution release in /usr/local/src directory.
Using tar, unpack files from the archive:
Patch PHP source with Digi-CA™ Cryptographic Patch:
Change working directory:
Prepare the installation:
Compile, test and install:
For the PHP PEAR DB 1.7.13 and LOG 1.9.11 packages visit PHP PEAR website on pear.php.net to download the PHP PEAR DB and LOG packages. To perform a quick installation, use the Quick Installation guide provided below.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/knowledgebase.png)
Digi-CA™ is the complete certificate Authority [CA] system for organisations that would like to have their own CA. The CA issues the digital certificates that are used for two factor authentication, electronic signatures, device-to-device authentication, National ID Cards, Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD], smart cards and ID cards and many other network, online, web and physical security environments.
Digi-CA™ replaces older Legacy PKI technology and CA systems using the latest in CA technology. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Legacy CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level. The Digi-CA™ can even be ‘dropped’ on top of these Legacy CA environments and seamlessly migrate the older system’s users into this more modern and flexible replacement.
Combining the consulting and professional services offered in the Digi-CAST™ methodology with Digi-CA™ can meet all national and international standards such as: Sarbanes Oxley, SB 1386, ISO 27001, FFIEC, HIPAA, ACSI 33, 1999/93/EC, ANSI, CWA, ETSI, EAL, FIPS, RFC, ICAO, MRTD, CONOPS, ALGO, Gramm-Leach Bliley and many other compliance and certification requirements.
Small and medium sized businesses, large corporate, government, local government, Trust Centre’s, statutory bodies, security companies or any enterprise that wants to use digital certificates, should carefully examine the true benefits of using this radical technology.
The Digi-CA™ system can issue, revoke, suspend and re-sign x.509v3 certificates. The end user information and certificate request is entered through the web-based Registration Authority [RA] called the RA Master Console [RAMC]. It is the Digi-CA™ RAMC that is used to control all day-to-day administrative functions. Time stamping, Online certificate Status Protocol [OCSP], customised certificate Revokation Lists [CRLs] and many other options can be enabled in Digi-CA™ on request.
The Digi-CA™ suite of CA systems offers the following benefits:
Multiple customised Root certificates, Intermediate Root certificates and EU Qualified certificates can also be catered for. Every aspect of the digital certificate including certificate fields can all be customised to meet any x.509 standard requirement.
Digi-CA™ delivers a simple to use and operate CA that meets your precise requirements. Highly customised and complex CA environments and even a certified Trust Centre that complies with international standards can be ‘built-to-order’. And you can then decide whether to have all the required functionalities delivered as a service from outside the organisation using the Digi-CA™ Service or as installed software, using Digi-CA™ Server.
No matter how it’s delivered, Digi-CA™ is the most flexible, efficient and cost effective CA system for you and can be delivered exactly to your requirements. You can choose to have Digi-Sign do everything for you and ‘Fast Track’ your requirements, or you can be proactively involved at whatever level you like.
The Audience of this Guide should have a basic understanding of computers, how to use office software, send and receive email and how to browse the internet.
Implementing a certificate Authority is not a ‘one size fits all’ project. Your requirement might be for a few hundred users with exceptionally high security parameters or you could be looking to authenticate several million hardware devices. The commercial organisation’s requirements are typically related to cost, benefit, risk and return whilst the government project is more concerned with statutory requirements, IT standards and compliance.
No matter how small or large your requirement, you’ll have restrictions on what your current environment can cope with; availability of staff; budgetary constraints and other parameters within which you must choose the correct CA for your organisation. You may want to be very ‘hands on’ at every stage of the project and even want to conduct some of the integration and even programming or you may decide you want us to do everything for you. Just as Digi-CA™ is totally flexible, so too is the Digi-Sign approach.
‘Fast Track’ is exactly as it sounds, you want everything done as quickly as possible and you want the professionals to do it for you. This is a total ‘turn key’ approach where we take your instructions, document them and deliver the entire solution back to you in the shortest possible time. Once the Digi-CA™ is in ‘production status’, you nominate personnel within your organisation to take responsibility for it and we support them in the background.
This is where we not only ‘Fast Track your requirements through to delivery but actually assume responsibility for the total management of your CA environment for as long as you need us too.
Total Trust Management™ [TTM™] is a unique offering from Digi-Sign (although some vendors have tried to copy it) and it means that you Trust us to Totally Manage the Digi-CA™ for you. TTM™ is much more than a dedicated telephone support line, it’s a service where Digi-Sign personnel effectively work for you. We ensure that the CA technology is introduced to the end users with the minimum of fuss. All you do is agree how you want us to operate the Digi-CA™, and we do everything for you. It’s a bit like travelling First Class.
75% of our customers use TTM™ in the first year, at least, so that they can see how we do everything and then learn by watching us.
For an installation of Digi-CA™ Server (see sub section 3.7.3.2), we document your requirement, you sign the documented order and then we build, box and either ship it to you for installation or, in the case of Digi-CA™ Service (see sub section 3.7.3.1) we host it for you so that it only needs to be activated.
If your requirements include integration work or customisation, this is scheduled and delivery is subject to Production scheduling and all of this is agreed in advance.
Most Digi-CA™ systems are delivered by a member of the Digi-Sign Affiliates, Resellers & Partners [ARP] Network. The ARP member will co-ordinate all aspects of the delivery, installation, configuration and setting the system to production status for you.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ replaces older Legacy CA systems using the latest in CA and PKI technologies and benefits from combining commercial and open source software initiatives. With Digi-CA™, all of the complexities and onerous technical overhead that were required by Legacy CAs have been simplified to a ‘user-friendly’ and usable level.
By combining the consulting and professional services offered by Digi-CAST™ (see sub section 3.1) with the functions provided by Digi-CA™, can bring an organisation to a highly professional PKI level, meeting the criteria for internationally recognised accreditation standards such as WebTrust® and ISO 27001 certifications.
| Compliance to international standards | Digi-CA™ follows the international industry standards for PKI and CA systems so that is can easily fit into almost any certificated IT infrastructure and work seamlessly within that environment. This compliance to standards is important when considering current requirements and potential future requirements too | |
| Programming language | All components of the Digi-CA™ system kernel have been developed in C on Unix and this is considered the most stable, secure and efficient language and operating system for the development of PKI & CA systems | |
| Centralised Management | Web based ‘system management centre’ for all operated CAs, RAs & LRAs makes it ideal for operation as an installed standalone CA system or as a Managed CA | |
| ‘futureproof’ | By its very design, the entire Digi-CA™ system can be in house, totally out sourced or a combination of the two and this can be decided at any stage during the life of the system. So you can purchase what it needs today, safe in the knowledge that you can easily migrate and move all or part of the system to the Managed CA alternative to meet your future demands | |
| Ease of integration | Whether now or in the future, because it is LDAPv3 compliant, Digi-CA™ can publish X.509 certificates and certificate Revocation Lists [CRL] to other directories. This is a significant factor when considering integration with existing or future environments | |
| Scalability | Digi-CA™ can scale, easily and with minimal/no interrupting of live operations. This is important when considering the future growth of your requirements. It is also possible to add additional hardware to expand the system capacity and services and to conduct cross certification | |
| Continuous operation | When considering the future growth of your requirements, live production can continue uninterrupted while adding more CAs, RAs and LRAs. These capabilities ensure the CA remains operational and without interruption throughout | |
| Customisation to your requirements | Custom multi-layer CA hierarchy, RA and LRA distribution can be modified, extended and changed at any stage and again, this can be done without affecting the operation of the live environment | |
| ‘look & feel’ customisation |
The entire Digi-CA™ system interfaces and all its levels can be easily changed using Cascade Style Sheet [CSS]. This ability to completely change the ‘look and feel’ of the system eases the deployment to your end users because they know you but may not be familiar with the CA vendor. It also helps with integrating into web sites and other online systems seamlessly |
|
| Multiple Languages | Language localisation is “plug n’ play” for displaying all interfaces in your desired language(s). This further helps the deployment to end users and reduces ‘help desk calls’ (where users are really looking for translation of help files, etc) | |
| Custom profile, enrolment & DN capabilities supplied as standard | Certificate profiles and enrolment policies can be customised and therefore full custom certificate subject Distinguished Name [DN] attributes and certificate extensions are possible. This is particularly important when meeting national & international standards and the cost of providing these capabilities from other systems can be considerable | |
| CA Flexibility | Ability to operate multiple independent CA hierarchies from a single system instance without the need of installing multiple software applications on multiple server computers to run each CA hierarchy | |
| RA Flexibility | Multiple independent Registration Authority [RA] instances from a single system without needing to install multiple applications on multiple servers to run each RA | |
| 100% browser independent | 100% certificate enrolment web browser platform and operating system independency | |
| Root CA cross certification | Digi-CA™ offers the capability of cross certification between the your Root CA and any other CA | |
| Trusted Root capability | Also it can be cross certified by a Trusted Root CA of issuing trusted SSLs and secure, signed and/or encrypted email | |
| Best training & knowledge transfer | With the largest online searchable PKI & CA KnowledgeBase, the extensive documentation offered, the Digi-TaSC system and the many different types of training offered, this proposal offers the most comprehensive that programme for your personnel | |
| Overall most capable & most competitively priced | Digi-CA™ achieves the best blend of meeting your current requirements and possible future ones too. It’s highly customisable and flexible features means it will meet future demands easily, without incurring downtime, service interruption or unwieldy costs | |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/knowledgebase.png)
In the ‘real world’ passports and ID cards identify people; crests or symbols identify institutions like the police or a hospital, for example; and a seal or stamp authenticates a document. In the Digital World, we use digital certificates to do the same thing.
In the ‘digital world’ the digital certificate is used to identify the person, authority, device, website, software and/or electronic file and it is a CA that issues these digital certificates. The purpose of the CA is to provide digital identities of users, devices or files. The CA is configured and installed in accordance with the customer’s requirements and these requirements are documented in the Certificate Policy [CP] for the CA.
Every request for a digital certificate is validated and approved, or rejected, by the Registration Authority [RA]. A trained Administrator, again in accordance with the CP, can manually operate the RA or this function can be automated depending on the CA you choose. Every digital certificate issued is unique and is delivered according to the CP.
Any network where information is stored electronically needs to be secured. Up to now, the most common way of protecting such data has been through the use of usernames and passwords. This is no longer considered ‘secure’.
A single unsecured transaction could result in significant losses to an organisation. This alone makes a strong argument for using digital certificates. Digital certificates remove this risk completely.
However, the digital certificate is only as good as the security processes and procedures that surround the issuing of that certificate to the individual, or device. This is where the validations process, and its importance, must be understood thoroughly. If it is easy for one person to assume the identity of another and subsequently, as a result of poor policies and procedures, successfully apply for and receive another person’s certificate, then the value of that digital identification is effectively useless. On the contrary, a correctly managed Certificate Authority, can bring endless value and cost savings to countless digital and physical environments.
Even more compelling business arguments in favour of using digital certificates would include the reduction or removal of paper forms and workflow from an organisation. Paper business processes can be computerized and digital signatures replace handwritten signatures. The savings to organisations as a result of using this technology are well documented.
Two-factor authentication, Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD], secure email national ID cards, digital rights management, web access control, device-to-device authentication and many other business processes can benefit from significant savings by using technology smartly. Integral to all of these processes, is the requirement for digital authentication, digital identification, digital encryption, digital stamping and digital signing and being able to support these transactions with a legally binding infrastructure. This is what Digi-CA™ provides to your organisation.
If you are trying to migrate an existing environment from another Legacy CA Authority to Digi-CA™, there is a ready-to-go solution that works independently from the Legacy CA. The customer can provide the information manually, or use migration engines provided by the Digi-CAST™ team.
This is how it works:
The information provided by the customer is loaded into the Digi-CA™ system using the Digi-CA™ Control Centre;
Based on the information provided, the Digi-CA™ will send expiry reminder emails according to the expiry reminder policy and each email will contain a unique URL for the certificate renewal.
For client certificate migration, once the user enters the certificate renewal screen using the URL provided in the email, they will be prompted by the system to prove their identity using their existing/old certificate. If the old user certificate details match the pre-configured Digi-CA™ system data, the user will be allowed to renew their certificate.
For SSL certificates, the Digi-CA™ is preconfigured in the same way as for client certificates except that it doesn’t require the old certificates to be present. All that is needed is the expiry date so that the replacement occurs seamlessly.
This is the highly effective method used to replace older and more costly Legacy CA systems.
The success or failure of any project can normally be traced back to the start, where bad planning will be found. This poor initial planning will either be as a result of bad management and leadership and to a lesser extent, the selection of technically inexperienced personnel. That is why Digi-Sign insists that no matter how many 'issues' the project encounters en route, if it is properly planned initially, it will succeed.
If you want to use the internet as a tool to improve communications, take advantage of on demand cloud computing, reduce costs, improve customer service and retention, or to expand your market reach, then Digi-Sign’s products, services and solutions will help you secure these environments.
These same offerings can be used in physical border control, building access, electronic signatures and any situation where truly knowing the other person/device is a necessity to securing the transaction.
The Service Level Agreement [SLA] is critical to the continued success of the Digi-CA™ delivery model and central to this SLA is the Incident Management System [IMS]. The IMS is an automated system that escalates issues, without human intervention, and automatically notifies the user at each stage.
The IMS incorporates system and personnel reaction times with issue escalation times and then monitors each and every support issue to the successful completion as confirmed by the customer.
| IMS Level | Description | Time Before Escalation | Time Lapsed |
| Level 1 | Incident Logging | ||
| Level 2 | Severity 1 Escalation | 4 hours | 4 hours |
| Level 3 | Severity 2 Escalation | 20 hours | 24 hours |
| Level 4 | Severity 3 Escalation | 48 hours | 72 hours |
| Level 5 | Case Termination / Indefinite Suspension | 48 hours | 120 hours |
The IMS automatically provides this level of service using the SLA table of IMS Escalation Levels.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/agreement.jpg)
The IMS system is shared between your organisation and ours so that the correct delivery of the SLA is maintained. In this instance there are two components to the SLA delivery namely: the Public Interface, then the internal Support Case responsibility delineation and the IMS escalation.
Using the workflow and case escalation contained in the IMS, every case is still managed and monitored by the system, but the case may be resolved by multiple personnel in different organisations.
Further explanation of the SLA and how it is managed is available at the following URL:
www.digi-sign.com/about/service+level+agreement [121]
This level of dedication has resulted in numerous and recurring testimonials, letters of reference and increasing number of customers and members enjoying our systems and support:
www.digi-sign.com/about [122]
Numerous Governments around the world and countless internationally recognised organisations have commented on the effectiveness of the IMS.
Digi-CA™ has different certificate application options for each type of digital certificate it produces. In low volume situations, such as SSL certificates, the application process is conducted manually. Alternatively, when issuing thousands of client certificates to end users, part or all of the application process can be automated.
The three application options are completely manual, completely automated or partial automation, as required.
There are two primary ways that the end entity certificates are delivered. Either the certificate is delivered as a package [Package Method] or it is delivered as a result of a series of steps in a process [Process Method].
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx /digi-ca/introduction/
There are two primary ways that the end entity certificates are delivered. Either the certificate is delivered as a package [Package Method] or it is delivered as a result of a series of steps in a process [Process Method].
Using the
There are two primary ways that the end entity certificates are delivered. Either the certificate is delivered as a package [Package Method] or it is delivered as a result of a series of steps in a process [Process Method].
In the 'real world' passports and ID cards identify people, crests or symbols identify institutions like the police or a hospital and a seal or stamp authenticates a document.
In the online world, a digital certificate can be used to identify a person, an authority or device like a web site and/or an electronic file or piece of software. The CA issues digital certificates that provide digital identities and/or to prove the authenticity of users, devices or files. The digital identities are proven by use of the digital certificates.
The digital certificate is the unique identifier that allows individuals and devices to be irrefutably linked to their actions, transactions and communications. In the case of an organisation or corporate body, the Digi-SSL™ acts as a seal or crest of authenticity. For an individual, the digital certificate acts as the electronic equivalent of the passport or driver's license.
Another use for the digital certificate (also called an electronic signature) is for digitally signing electronic files and data just as a person’s signature or official seal is used to authenticate paper documents. This dual functionality of both identification and authentication enables many different types of electronic transactions.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
CA Software is a software product that is installed, either in a data centre or at the Customer site. This CA Software charges a once-off fee upfront that is based on the cost of the software, its configuration and installation and then the number of digital certificates required over the life of the product's use. The only other fee the Customer pays is an annual license fee to cover upgrades, patches and application telephone support required to keep the CA operational. Digi-CA™ Server is CA software.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/software.jpg)
The CA Software user creates and controls their own CA environment but in so doing must have reliable internet connections, hardware, hardware support, compliance documents, Administrator’s and its own technical support help desk.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
The Shared CA, Digi-CA™ Shared, is a concept and capability that is unique to Digi-CA™. It is made possible by the component design and flexibility that is at the core design of Digi-CA™ and is not available from any other CA vendor.
The concept is simple: The benefits of outsourcing the entire CA to a Trusted Third Party [TTP] as a Managed CA may meet most of your main business objectives. In a second scenario, your organisation may require total ownership of the CA in which case the Managed CA is more suitable. But there is a third scenario where you want to own the critical assets but do not wish to manage everything internally. In this case, the Digi-CA™ Shared system is the solution.
In instances where critical assets, such as the use of a Hardware Security Module [HSM], databases, key storage and other functions must be retained by your organisation and the day-to-day administration, support, help desk, ‘critical response’ and other ‘non critical’ components can be outside your organisation, then Digi-CA™ will be your choice.
Digi-CA™ Shared offers all the technical backup and support components of your CA requirements and ‘fills in any gaps’ in your current environment. The external infrastructure, the team of professionals and specialist you require and other critical resources such as Disaster Recovery, critical response and Service Level Agreement [SLA], components can be outsourced with ease. At the same time, the principal assets and integrity you wish to own and control can remain inside your organisation.
Digi-CA™ Shared can be designed and delivered to meet your precise requirements and can combine physical IT assets, personnel, help desk, internal and external networks and servers. For further details contact a member of the Digi-CAST1™ Technical Advisor Team and they will advise you accordingly.
To decide on the best CA system for your environment, there are three key considerations you need to take into account:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ Server is the CA Software that is installed on a server in a data centre or at the customer site. As explained in 2.6.3, Digi-CA™ charges a once off license fee in advance that is based on the cost of the software, its configuration and installation and then the number of certificates required over the life of the product's use. The only other fee you pay is the annual license fee to cover upgrades, patches and application telephone support (see sub section 3.14 for more details).
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ Shared was a concept conceived by Digi-Sign in 2006 that has only recently been acknowledged by potential customers as a real alternative in the provisioning of CA services. Although implementations of this concept CA are limited, the capability and the option are important.
Typical enquiries come from large industry or government agencies where ownership of the entire CA is not a requirement, but ownership of specific components is preferred (e.g. data files, HSMs or the requirement to have a complete, hosted disaster recovery system). When considering Digi-CA™, the availability of this concept may not be of paramount importance, but its availability may be very useful during the continued growth and expansion of the total environment.
Digi-CA™ is delivered either as CA Software or as a Managed CA and it is available in three classes:
There are four principal variations of Digi-CA™ Service and each variation can be provided as a single variant and multiple combinations are also possible. The four main variants are:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ssl.png)
When issuing and managing multiple Digi-SSL™ certificates, the Digi-CA™ Service system is the recommended management system. Almost every Digi-SSL™ certificate is issued from a TRoot and therefore this is offered form this Managed CA service .
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-access.png)
When securing with Digi-Access™ two factor authentication, we recommend using Digi-CA™ Service, because it is issued and managed by the Digi-CAST™ team and it is much faster to configure and deploy. However, the is also the option to install the Digi-CA™ Server software if there is a strong requirement and business case for it .
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-id.png)
When considering multiple Digi-ID™ certificates, careful consideration to the usage, environment and overall requirement should assist you in deciding wh is the best Digi-CA™ system to choose. Seek advice from the Digi-CAST™ team before making this important selection
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-mail.png)
When issuing and managing multiple Digi-Mail™ certificates, the Digi-CA™ Service system is the recommended management system. Almost every Digi-Mail™ certificate is issued from a TRoot and therefore this is offered form this Managed CA service .
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/manage.jpg)
Digital certificates can be used in a variety of different security situations, however the common uses are for proving identity, digitally signing/sealing files and encrypting data. These important capabilities are integral parts of any secure environment.
As can be seen from the diagram below, digital certificates come from the certificate Engine core and it issues the various types of digital certificates.
Digital certificates are issued and managed using a certificate Authority or CA. There are two different types of CA systems and, uniquely, with Digi-CA™ there is a third option:
The Managed CA is supplied as an online service from outside your organisation.
We call this Digi-CA™ Service.
The CA Software can be installed at your premises or at your data centre.
We call thisDigi-CA™ Server..
All digital certificates come from a certificate Authority [CA] that is a computer system that is capable of issuing these different types of digital certificate.
Digital certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority [CA]. Any organisation can opt to operate its own CA and typically the types of organisations that have a CA are either commercial CAs that offers their services to other organisations as an external service, or organisations that purchase the necessary systems for their own use.
The computer system that issues the different types of digital certificate does this from the central system core of the CA system and this core is called the certificate engine.
Regardless of the type of CA system or how it is operated, the certificate Engine for the system has at least one Root certificate. The certificate Engine core uses the Root certificate to sign the various types of digital certificates the CA issues.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/manage.jpg)
The rules, methods and guidelines that specify how the digital certificate is distributed to the end user are documented in the Certificate Policy [CP]. The CP is the ‘Who, What, Where and How’ document that describes the principles of the digital certificate usage and how they are to be distributed. This CP is agreed before the CA is operational and all digital certificates must be deployed in accordance with the CP.
The Registration Authority [RA] decides what users are permitted to receive a certificate. The RA can be a Systems Administrator or other responsible member of the organisation, or the process can be automated using a database and a series of automated checks and controls, each one of which is designed to reduce the error possibility or the risk of deception.
There are three main types of digital certificates, they are:
All certificate revokations are initiated either by the user or by the Administrator. Revokations are required for a number of reasons, for example:
| 1 | the user has lost the PC or media where the certificate was stored. | ||
| 2 | the user no longer has any affiliation with the organisation that issued the certificate | ||
| 3 | the user changed position in the organisation and no longer has any right to the certificate | ||
| 4 | the Administrator believes a certificate has been misused. | ||
| 5 | the Administrator believes a certificate used to misrepresent the organisation that issued the certificate | ||
The following sub sections detail how Revokation requests are made and the resulting actions and uses for this important feature.
The following diagram explains the events that occur within the Digi-CA™ and how a revokation request is executed:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/revok.jpg)
For end entity certificates there are two different Storage Types and several devices that need careful consideration when choosing how your certificates will be deployed. The correct selection is critical to the ease of operation combined with the level of security you need to achieve.
The end entity certificates can be stored on two different types of device, one that has Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP] capabilities and the other that doesn’t. Most web browsers and specific Smart Cards [Digi-Cards™], USB Tokens [Digi-Tokens™] have CSP software installed. These devices are easily identified because the product’s specification will refer to its cryptographic capabilities.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/usb.jpg)
If the end user is required to enroll for their certificate and the storage device is their PC, then the CSP within the Microsoft Internet Explorer browser will use its own CSP capabilities during the procedure.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/csp.jpg)
Other types of storages device that don’t have CSP capabilities can still be used to store the certificate, just as they would any computer file. These devices can include Smart Cards and USB Tokens that don’t have CSP capabilities.
When selecting your storage device, you should consider its immediate intended use and also other future possible uses too. For example the end entity certificate that’s being used to access an online banking system today could also be used to sign funds transfer transactions in the future. The protection for the access to the application will not be as great as the protection required to transfer funds, so you need to decide in advance what solution will work today but also grow with the needs of tomorrow.
Then there are the issues of ‘portability’ and cost. Digi-Tokens™ are an excellent solution because the end entity certificate can be used in any PC anywhere but as the most expensive storage device, it may not be the most practical. The Digi-Card™ offers multiple functions like doubling for an ID card, but it assumes there are smart card readers available and again cost may be an issue here. The least expensive option is the user’s own PC but may not suit your requirement for complete portability.
The Digi-CAST1™ Team of professional advisors are there to assist you in making the best choice for your environment and remove the element of risk from your purchase.
When a CSP is used in the ‘manufacture’ of the Public and Private Key Pair that is used when generating the certificate, then there is the option to use two end entity certificate Storage Methods:
Digi-CA™ offers both of these Types of Storage.
Export Storage means that when the Public and Private Key Pairs are generated and then signed, the entire end entity certificate package that includes the Key Pairs and the certificate can be exported from the original storage device as a PKCS#12. So the certificate is not ‘fused’ into the device.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/key.jpg)
In the most common case where the end entity certificates is stored in the certificate Store of the Desktop Profile for the user, there is a wizard for exporting the entire file so that it can be reinstalled elsewhere.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/case.jpg)
Digital certificates can be used to identify a person or a device. Once identification is established, the certificate is most frequently used to prove one person’s, or device’s, identity to another person or device. Because of the RSA system, they both know each other. The digital certificate can now be used for signing and/or encrypting email or for providing two-factor strong authentication.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/certificate.jpg)
Using the dual-key cryptography algorithm, the digital certificates allow users to exchange public keys to secure and authenticate each other.
There are two main uses for digital certificates are for:
And when considering using digital certificates you need to consider:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-cast1.png)
The Digi-CAST™ practices for digital certificates and the provisioning of Certificate Authority [CA] systems differs substantially for other Traditional CA providers. The methodology itself is unique to Digi-Sign and was conceived in 2004 after many years of examining alternative system implementations and poorly conceived projects. The principle differences are achieved by the ‘open collaboration & your active participation’ that is then supported by our extensive experience.
The four corner stones of the Digi-CAST™ approach are:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-code.png)
Digi-Codes™ are Code Signing certificates and are used for securing and authenticating:
Digi-Codes™ are not a high volume item and most organisations only need one or two each year.
Digi-Code™ is offered in a single Class only: Digi-Code™ Xs and is used for software and code signing.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-access.png)
Securing any on line system with usernames and passwords may not offer the level of protection and security your organisation needs. You improve the security by adding a 'second layer' of protection called 'two factor authentication'. This means adding another method of authenticating your users, on top of the existing username and password access.
Digi-Access™ adds this two factor authentication security and is the most popular and fastest growing certificate we provide currently.
Digi-Access™ certificates are available in the Xs and Xp Classes and are used for cloud based on demand computing, Software-as-a-Service [SaaS], secure web portals, online gaming compliance, financial service (e.g. online banking and broking), etc. In fact, anywhere where a username and password is used to gain access to any application or service using your browser.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-id.png)
Digi-ID™ certificates are most commonly used for identification and digital signature and are single application certificates. A single application certificate is designed to perform a single action like providing identification on an ID card or for digitally signing a document, e.g. a PDF.
If a single Digi-ID™ is required to perform multiple functions (and this isn’t always possible), then a Digi-ID™ Xg is used because the single Digi-ID™ Xg certificate is a multi-application certificate that can be used to perform multiple actions (i.e. both identification and digital signing).
Digi-ID™ certificates are available in Xs, Xp and Xg Classes and are used for digital identification and/or electronic signatures. Digi-ID™ Xs are entry level certificates used for pilot projects, test environments or in small, single application environments only.
Digi-ID™ certificates are very popular when considering EU legislation, workflow systems or indeed anywhere that a digital signature is being used to replace paper based signatures. The reason for this is because digital identity and non-repudiation of transactions is now considered critical. Also, the demand for Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD], electronic invoicing and other document signing solutions have underpinned the use of Digi-ID™ certificates.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-mail.png)
Digi-Mail™ certificates are available in the Xs and Xp Classes and are used for digitally signing and encrypting email. The practice of signing email is commonly used in healthcare, financial and government environments, where the authenticity of an email is of paramount importance to the organisation.
Digi-Mail™ certificates are available in Xs and Xp Classes and are used for secure email only. Digi-Mail™ Xs are entry level certificates used for pilot projects, test environments or in small, single end users only
Digi-ID™ Xp is the most commonly used commercial certificate and it is also a single application certificate. A single application certificate is designed to perform a single action like securing email or providing two factor authentications.
User A and B exchange public keys and use the other person’s public key to encrypt messages back to each other. Only User A has the Private Key that can decrypt any the messages encrypted with User A’s matching public key.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/user.jpg)
In the case where a web server has a highly secure area and wishes to give restricted and controlled access to the information stored on it, then usernames and passwords do not offer sufficient protection. Adding two factor authentications to this insecure login method with a Digi-Access™ certificate solves this problem.
There are two types of Digi-Access™ authentication systems:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
The Digi-CA™ system is a complete system containing all of the necessary Operating System [OS], modules, directories and engines required to operate a fully functional CA system. For the technical specifications of the software, refer to the Digi-CA™ Administrator Manual.
Your complete system design, the modules that are needed, their specification and configuration and preparation for delivery can be completely delivered by the Digi-CAST1™ Team of professional advisors. After consulting with you, every aspect of the project is documented and submitted back to you for approval.
Once approved, the Digi-CAST2™ will deliver the ‘turn key’ solution as specified in by the Digi-CAST1™ documentation.
Digi-CA™ has been designed by some of the foremost experts in Internet Application Security. All modules are contained in one Linux / Unix based system. Specific care has been taken in the design of Digi-CA™ to ensure that no outside intrusion can take place and that all the private Keys for the Digi-CA™ are secure (if they are not stored on a HSM).
To ensure the uniqueness of the keys in the certificates, Digi-CA™ uses its own entropy system. Digi-CA™ can create Key lengths up to 9192-bits. It can also support all key ciphers and signature algorithms.
Depending on the level of security required, Administrators must be authenticated by either a smart card [Digi-Card™], a USB Tokens [Digi-Tokens™] and/or a biometric reader.
The entire Digi-CA™ system infrastructure is formed mainly around x.509 certificates produced with accordance to the internationally recognised RFC 2459 standard and is maintained in accordance to the same internationally recognised RFC 3647 standard.
The design of a typical x.509 certificate includes the following cryptographic algorithms that are approved for commercial use by governments and related agencies and institutions around the world.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
The Digi-CA™ is probably the most flexible and capable CA system available in the market today. Unlike the other Legacy CAs, Digi-CA™ takes advantage of the many advances in technology over the past seven years and you benefit by getting the flexible, cost effective and easily integrated CA system you need.
The Digi-CA™ still uses Unix in its certificate Engine core but by using the Open Standard Institute [OSI] initiative in other modules, Professional Services and upgrade costs are substantially less than those normally associated with the complex and costly modifications of the less flexible Unix Legacy CAs.
This section explains the design principles and also gives typical examples of previous customisations . The most important feature of Digi-CA™ is that your precise requirements can be delivered, exactly as you require.
In the larger or more complex environment, the organisation may require a workflow process to control the use of the Digi-CA™ usage from a cost, security or for general management reasons. The following is an example of a customisation currently in use by a Digi-Sign customer for issuing Digi-SSLs™:
This type of customisation is not unusual but it does add to the initial cost of deploying a Digi-CA™ system.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/process.jpg)
Every aspect of the Digi-CA™ can be automated. Examples of this would be where the certificates are being used to replace Usernames and Passwords for login to a secure website, to replace hardware tokens like SecurID®, to issue certificates for secure email on a closed network or to replace an existing Legacy CA with Digi-CA™.
Using the MCAM™ technology and capabilities, it is possible to use existing LDAPs or other databases such as Oracle®, Active Directory® or any other SQL or flat file format to automate the certificate issuing, renewal, suspension and revokation processes.
Using the authentication and validation certificate Policies from your Legacy CA, Digi-CA™ can migrate users automatically without requiring any IT resources or Administrators’ time.
The entire Digi-CA™ system and all of the interfaces used by the Administrators and users can be completely customised on request. Typical reasons for the graphical changes are for integrating Digi-CA™ into a larger application to make a complete package or the simpler integration of the Digi-CA™ into the organisation’s web systems or extranet.
The specification of the Digi-CA™ at the time of going to print is available in Appendix IV. All specification updates and technical help files are updated using the online support section of the Digi-Sign website located at www.digi-sign.com [44].
Digi-CA™ has different delivery options for each digital certificate it produces. The most common use for Digi-CA™ is to deliver end entity certificates. Prior to the installation of the Digi-CA™, the CP is documented and this determines what Method of Delivery is used for issuing a digital certificate.
The two principle Methods are the Package Method and the Process Method. An end entity certificates can be issued in different ways depending on the method of delivery chosen. A single issuing process can be decided on, or a combination of processes.
There are two primary ways that the end entity certificates are delivered. Either the certificate is delivered as a package [Package Method] or it is delivered as a result of a series of steps in a process [Process Method].
Methods of Delivery:
Digi-CA™ offers both of these Methods of Delivery.
Using the Package Method, the public and Private Keys are generated at the RA or Administrator’s PC. The public key is signed by the Digi-CA™ Engine and the entire end entity certificate is packaged in a single file and either sent to the end user or is installed on a Smart card, USB Token or any other suitable end entity certificates storage device. This package is also referred to as a PKCS#12, a .pxf or a .p12 Private Key Container Package.
Using suitable Digi-Cards™, Digi-Tokens™ or other suitable CSP storage device, a Private Key is generated and remains on the device and never leaves the user. When requesting an end entity certificates, the device generates the certificate Signing Request [CSR].
When the user enrolls at the web application form, the form data entered and the CSR are transferred to the Digi-CA™. The transfer occurs over a HyperText Transfer Protocol Secured [HTTPS]. On receiving the CSR, the Digi-CA™ Engine signs it and creates the x.509 certificate.
Usually, an email is then sent to the user to collect the end entity certificates. When the user clicks on the hyperlink within the email, using the TCP/IP Protocol, the certificate is installed on the user’s device.
As stated, the Digi-CA™ offers both of these Methods of Delivery.
Almost every Digi-CA™ installation has one or more customised features added to the system to meet the customer’s specific requirements. The requirements range from overall certificate management and control, to system integration, automation and/or accounting requirements.
Digi-CA™ Service as the Managed CA solution and Digi-CA™ Server as the Software CA product ‘in a box’, both use the same browser–based interfaces. To get a better understanding of how Digi-CA™ is controlled and Administered manually (much of the Administration can be automated in the Xp and Xg systems), its basic functionality, features and benefits, visit the following URL:
www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca [123]
…and see an online demonstration of how the Digi-CA™ system works.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ is the core software that includes the interfaces, modules and applications [IP] that are common to both the Digi-CA™ Server software and the Digi-CA™ Service. The importance of this common IP is unique to Digi-CA™ and makes it possible for the Service and the Server versions of Digi-CA™ to be interchangeable. Therefore, starting with one version of Digi-CA™ and migrating to the other, as your requirements grow, will not
require a complete system replacement (as is the case with legacy CAs) and thereby saves you considerable costs, should such a requirement arise.
The Digi-CA™ System provides a full scale of services necessary for the management of X.509 certificates. At its core, the Digi-CA™ software was designed for Unix and Linux operating systems that provide a robust and stable operating environment. The simplicity of the architectural design of the complete Digi-CA™ system means, that the same software can be deployed on a single server device and later scaled for enterprise or Internet PKI use with minimum or no disruption.
Typically, scaling may start from single server, or 'handful' of servers acting in a cluster or
fail-over mode. This setup can be later extended to reach greater capacity and performance by introducing additional servers as required, almost without or completely without interrupting the operation of the existing production environment. This is a critical component when deciding on a CA that may scale considerably over time and allows organisations to carefully plan their investment costs whilst still achieving all its functional goals.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/design.jpg)
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/cp.png)
The rules, methods and guidelines that specify how the Digi-CA™ will issue its certificates and these processes and procedures are documented in the certificate Practice Statement [CPS] and certificate Policy [CP]. The CP is the ‘Who, What, Where and How’ document that describes the principles of the digital certificate usage and how they are to be distributed.
This CP is agreed before the Digi-CA™ is operational and all digital certificates must be deployed in accordance with the CP. Appendix I is a questionnaire designed to assist in creating your CP.
There are three different types of Digi-CA™ system:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-access.png)
Digi-Access™ Service is the simple to deploy and manage two factor authentication secure access method that can’t be compromised. In most cases, the issuing and management of the Digi-Access™ Service is simpler than administering a database of usernames and passwords. There are no specialist skills needed to incorporate it into your system(s) as most IT
systems are x.509 compliant and are already configured to work with Digi-Access™.
Digi-Access™ uses digital certificates to authenticate individual users to the server. More than 27 different server software systems that are compatible with Digi-Access™ (including most OEM versions). Within minutes, the server can be configured without the need for any additional software or specialist programming skills. Once activated, whatever section of the network or server needs protecting, all that is required is a simple Login button.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/login.jpg)
Once this Login button is clicked, the browser automatically activates the client authentication dialog (a piece of software that is already embedded in most web browsers)
Digi-Access™ competes directly with asynchronous number and One-Time Password [OTP] tokens like RSA® SecurID®, but this older technology. There have been many improvements since the original SecurID® idea, but the technology is still basically the same. In their favour, tokens are easy for the user to understand (it’s just a more powerful password) but the initial and ongoing costs are prohibitive. Tokens do provide good two factor authentication, but that’s it.
More and more organisations are moving towards digital certificates to solve their authentication issues because they are more flexible and provide additional functions (albeit they may not be needed immediately). If your Storage Type is the certificate Store within the browser, there are significant cost savings to consider.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-id.png)
The Digi-ID™ Service is used when you require digital signatures for workflow, forms and/or digital documents. Digi-ID™ certificates are also used for ID cards and tokens. With Digi-ID™ Service, each service you require is configured according to your precise requirements and tested before activation.
Digital signatures are becoming a regulatory requirement when considering digital documents and workflows in specific communities (e.g. European Union, gaming industry, HIPPA, etc.). There is no substitute, either your organisation continues to operate cumbersome paper based systems, or you digitise and authenticate them with a Digi-ID™.
Within the EU in particular, there is a specific requirement to use qualified electronic signatures that are a very specific type of Digi-ID™ that must be delivered on a Secure Signature-Creation Device [SSCD]. Digi-ID™ SSCD are issued for the Digi-ID™ Service system only, unless your organisation is prepared to achieve ISO 27001 certification and is willing to invest considerable sums in creating your own dedicated Trust Centre. If your organisation wishes to achieve qualified certificate status, then Digi-CA™ Server can deliver the PKI system you need to issue your own Digi-ID™ SSCD.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-service.png)
The Digi-CA™ Service is the Managed CA and as explained in 2.6.2, it is the service that is provided online using the Application Service Provider [ASP] or Software-as-a-Service [SaaS] delivery model. There is no hardware or software requirement at the customer site.
The Digi-CA™ Service is charged on an annual recurring fee based on the number of digital certificates issued each year and this covers all maintenance, administration and the support that is required to keep the Digi-CA™ operational.
You can choose to start with Digi-CA™ Service, migrate to Digi-CA™ Server and then further migrate back to Digi-CA™ Service with ease. This is because the Digi-CA™ Service and Digi-CA™ Server systems share a common architecture and the same Digi-CA™ certificate Engine.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/manage.jpg)
No other vendor offers this high degree of flexibility; migration and integration capabilities (see sub section 3.13 for more details).
The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/dual.jpg)
The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/dual1.jpg)
A standard process for issuing an end entity certificate involves the following stages:
- Using the Digi-CA™ RAMC, the Administrator initiates a certificate invitation email message that is sent to the intended recipient (user)
- The recipient (user) enters the online certificate application form using the URL provided in the invitation email message;
- The user completes the online certificate application form by providing personal information such as:
- A key-pair (Private and public key) and a PKCS#10 certificate Signing Request [CSR] code is generated on the user PC using a local Cryptographic Service Provider [CSP] engine installed on the user’s computer. It can be either a built-in Microsoft CryptoAPI software engine or a hardware USB Token or Smart Card CSP engine;
- Using HTTP POST method over SSL/TLS all the user data is transferred securely to the RA [Registration Authority] Server;
- The system Administrator/Validations Officer verifies and validates the user application data and depending on the content of the application, it is either approved or rejected;
- If the certificate application is approved, the application data is passed to the certificate Engine core server and the CSR is signed by the Certification Authority certificate;
- The certificate Engine core server generates a unique key/PIN number and sends a certificate activation email message to the end user. The message contains a URL to activate and install the certificate;
- The recipient (user) enters the certificate activation screen from the URL provided in the certificate activation email and completes the installation of the certificate by clicking the installation button on the screen;
- The certificate is collected from directly the certificate directory via a background TCP/IP connection and installed on the user’s PC using the CSP engine chosen at the time of the certificate application;
- The user may now use the certificate.
End entity certificates are requested by using the online certificate application form or by the Administrator (on the users behalf) using the Digi-CA™ RAMC.
From the Digi-CA™ Control Centre, all certificate requests are either entered into the database on an individual basis, using a batch upload file or automatically, depending on the Class of Digi-CA™ you are using. Similarly, all requests for end entity certificates are accepted, rejected or deferred either manually or automatically, depending on the Class of Digi-CA™ you are own, using the RAMC console of the Digi-CA™.
The Digi-CA™ system automatically generates a certificate Signing Request [CSR] if the requesting party did not already supply one and then generates the end entity certificate. The generation is done in batch processes according to schedules set in crontab. The default is to run the process every hour.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/inter.jpg)
After generation, the certificate is activated at the users PC or it can be delivered by email as a .p12 file. Storage of the certificate can be on the PC or any suitable media such as a Digi-Card™ or a Digi-Token™. Similarly, the Administrator can pre-install the certificate on the Digi-Card™ or Digi-Token™ prior to dispatch. This is particularly convenient where the Administrator wants ‘Zero Touch’ at the user’s location.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/inter1.jpg)
The method of distribution is set in the database at the time of the validation. The default is that certificates are distributed over the web, with the certificate holder getting an email containing a one-time password needed to pick it up.
If the billing module is installed, this module is updated with information and then passed on to your billing system.
| PROCESS A | User enrolls at the web application form and in submitting the form creates the Private Key on the device (PC Digi-Card™ or Digi-Token™). The Private Key is not exportable and requires a password every time it’s used. Application is validated and approved and the user receives a second email to activate the certificate. This is an example of a Fused Process Method with High User Protection. | |
| PROCESS B | User enrolls at the web application form. Application is validated and approved and the user receives an email with a certificate container package (containing both the public and Private Key). A second activation email containing a password is sent and used in opening the package to install the certificate on the device (PC Registry, Smartcard, USB Token or other suitable certificate storage media device). This is an example of an Export Package Method. | |
| PROCESS C | User receives a Smartcard, USB Token or any other certificate storage media device with the certificate pre-installed. The user completes the web application form. The Private Key is not exportable. Application is validated and approved and the user receives an email with a password to activate the device. This is an example of a Fused Package Method. | |
| PROCESS D | User receives a pre-printed Smartcard with their photograph and other details and follows METHOD A to complete the process. This is an example of a Fused Process Method with High User Protection. | |
| PROCESS E | A security printed P.I.N. number is delivered via registered courier or postal service. This is the same procedure as in METHOD B except that the user must enter the P.I.N. number when enrolling at the web application form stage. This is an example of an Export Package Method. | |
| PROCESS F | Parts of METHOD A and Method E combined except that the P.I.N. number is also required when installing the certificate. This is an example of a Fused Process Method with High User Protection. |
As stated, these are just some issuing processes and parts of one process can be combined with parts of another to meet the CP requirements.
Using the Solution Advisor Table will help you select the best solution your environment or use the interactive version available at www.digi-sign.com/advisor [124]
| Digi-SSL™ Service | Digi-Access Server™ | Digi-Mail Service™ | Digi-CA™ | Digi-Code™ | |
| Secure Multiple Servers (Using SSL) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Secure Multiple Emails (Closed Group) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Secure Multiple Emails (Internet Public) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Multiple Email Encryption (Closed Group) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Multiple Email Encryption (Internet Public) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Two Factor Authentication (without tokens / smart cards) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Two Factor Authentication (with tokens / smart cards) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Secure Login (Web Applications) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Secure Login (Desktop Applications) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Device-to-Device Authentication (Specialist / Proprietary) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Secure Messaging (Closed Group) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Secure Messaging (Internet Public) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| MRTD (e Passport / National ID) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| certificate Authority (Closed Group) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| certificate Authority (Accredited Trust Centre) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Digital Signature (Workflow & Business Process) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| electronic signature (e Signature & Compliance) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Strong Authentication (without tokens / smart cards) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Strong Authentication (with tokens / smart cards) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
||||
| Software & Code Signing (Applications, Downloads & Applets) | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tick.jpg) |
When deciding on whether the Managed CA or the CA Software is most suited to you, you should understand the difference between an open and a closed user group. From a CA perspective, this relates to the extent of end user control you have. If the CA exercises some degree of control over the end user’s environment then it is a closed user group and if it doesn’t, it is in an open group.
The following are examples of the two types of user group:
It is not always immediately obvious whether a group is open or closed and it is important that this is determined accurately if your CA is to meet your precise requirements. If there is any doubt, contact the Digi-CAST™ Team and ask them to advise you.
If the user group is closed, then you may be able to use either CA. There are two exceptions to this when you want to secure:
In 99% of cases an SSL certificate must be Trusted and if there is any possibility that the secure email is required outside the closed group, then the Trusted certificate is required here too. In both of these special cases, the Managed CA is your only choice.
The third consideration needed to help you select the correct CA for your organisation is the availability suitably trained and experienced technical personnel required to run and operate a CA. Most organisations don’t have this type of specialist staff within their organisation and therefore are best advised to use a Managed CA to deliver the required service.
The issue of Key Management is an important consideration when selecting any CA system. To understand the importance of this subject, you must first understand the real difference between the key-pair and the certificate. The key-pair is used to provide the authentication and the unique identity of the end user. The certificate, that is used to sign this key-pair, tells you that it is valid and ‘not out of date’. Together the key-pair and the certificate create the ‘package’ that makes up the digital certificate.
When considering whether you need (or want) Key Management, you should clearly understand the total environment that your digital certificates will be used in and, in particular, your end users. This requires that you pay special attention to the following three ‘Top Considerations’ when selecting the correct CA for you:
Three Top Considerations
The Fourth Top Consideration
Certificate/Key Backup can be a valuable service where there is a risk that if a user looses their digital certificate, or if the certificate is corrupted for any reason, this may cause serious issues for the CA administrator, or the organisation. Typically, this concern only exists where a user certificate is being used to encrypt data. With Certificate Backup, the user can request a replacement for the lost keys that were used when their digital certificate was generated.
Certificate/Key Backup can be likened to leaving the spare key for your house with a trusted neighbour so that if anything happens to the original, you know you have a spare. This type of help from your trusted neighbour could also be referred too as key backup. Alternatively and using the same analogy, it might be just as good to have a backup key stored elsewhere. The CA equivalent of this is called the digital certificate backup.
Backing up computer data is now understood as a routine responsibility and including the user’s digital certificate backup in this routine is a simple task that your network administrator should provide for you on request.
Key Management is often mistakenly linked to the Certificate/Key Backup service and should be clearly understood as a separate service that many CAs provide so that users can manage multiple key-pairs and certificates.
Key Management is only necessary when users have multiple Keys and this only occurs when the Disposable Binding Option (see sub sections 3.8.4 and 3.8.4.1) is chosen. To understand why Key Management is only needed in these certain special cases, you must first understand the x.509 elements that are used when generating the digital certificate.
Understanding the principles of Dual Key Cryptography , the Public and Private Key form the key-pair that is used to authenticate the user. This key-pair is generated using the RSA algorithm and once created, the certificate signs the key-pair with the information that you see when you open the digital certificate. This singing procedure inextricably ‘binds’ the specific key-pair to the specific certificate that was used to sign it. This is what makes up the elements of the digital certificate.
The production of any digital certificate, from any provider, uses the same x.509 elements and the method that is used to inextricably link the key-pair to the certificate we call the ‘Binding Option’. There are two different Binding Options that can be used when generating digital certificates and each one produces an inherently different CA environment.
With Digi-CA™, you can choose what type of Binding Option you prefer once you have a clear understanding of your environment and the affect of your choice. Digi-CA™ refers to the Binding Options as Disposable or Renewable and classifies the options in two distinctly different certificates:
With Digi-CA™, you can choose the Disposable Certificate Binding Option most frequently used in Legacy CAs or you can use the more modern Binding Option that creates the Renewable Certificate.
The Disposable Binding Option stipulates that every time you require a new certificate, you need both a new key-pair and a new certificate. Once the certificate expires, you simply dispose of it and issue a new certificate (i.e. a new key-pair and a new certificate are issued every time). The certificate that uses this type of Disposable Binding Option is referred too as a disposable certificate
The Renewable Binding Option stipulates that you keep the original key-pair and only need a new certificate for the renewal. Once the certificate expires, you simply need a new certificate to renew it (i.e. only a new certificate is issued every time). The certificate that uses this type of Renewable Binding Option is referred too as a Renewable Certificate.
The Renewable Binding Option stipulates that you keep the original key-pair and only need a new certificate for the renewal. Once the certificate expires, you simply need a new certificate to renew it (i.e. only a new certificate is issued every time). The certificate that uses this type of Renewable Binding Option is referred too as a Renewable Certificate.
As is the case with sub section 5.4, Digi-CA™ offers the capability to completely localise all interfaces, help files and user screens into your local language(s). This is particularly important to organisations where English is not used. It is also possible to have multiple interfaces with multiple languages for the same system. The following two samples show the Digi-CA™ Control Centre screen in Chinese and the user enrollment screen where users can apply for a certificate in Turkish.
The importance of the capability to produce the Digi-CA™ in the local language(s) cannot be over stated. It will result in faster training of the RA personnel and will significantly reduce the Help Desk Support calls (where users are seeking help to with translations from English rather than actual technical support related issues).
It is also possible to have a single Digi-CA™ configured in multiple languages so that different Digi-RAs™ in different countries can use the same Digi-CA™ Control Centre in their native language. Similarly, the users requesting certificates can do so from the same system but again in their native language.
To have your Digi-CA™ localized in your language, the system files and instructions are available in Appendix V.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/language.jpg)
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/language1.jpg)
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-mail.png)
As a business tool, email is the easiest one to manipulate and alter. Once sent, the information is extremely easy to intercept and copy whilst en-route. The best way to protect email is with Digi-Mail™.
Digi-Mail™ is a simple solution that totally protects email information. All email can be digitally signed and the sensitive information can also be encrypted for total security.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/mail.jpg)
Using the capabilities within the certificate, Digi-Mail™ works with all versions of email software without any additional configuration or specialist skills required to make it work. Digi-Mail™ can be used within an organisation or across a user group that includes suppliers, customers, advisors and employees alike.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/mail1.jpg)
Once deployed, all members of the user group can be assured that all communications are bona fide and have not been tampered with or intercepted. With the simple click of a button, those sensitive emails can be encrypted so that only the intended recipients can open them.
When the email arrives, it is displayed in the recipient’s inbox, clearly marked as being digitally signed. In checking the details of the certificate, the credentials of the sender and the integrity of the communication can be verified:
Digi-Mail Service™ provides the certificates designed to provide the secure email you need and as it comes from the TRoot, it will work in either a closed or an open user group.
All you require is a single internet enabled PC with Internet Explorer® 5.5+ and to decide whether to store the Digi-Access™ certificate used to access the system on a Digi-Card™, a Digi-Token™ or in the certificate Store of that PC.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-service.png)
A Managed CA is a service that is provided online using the Application Service Provider [ASP] delivery model. There is no software or hardware requirement. This Managed CA is charged on an annual recurring fee, based on the number of digital certificates issued each year. The Customer pays this fee to cover all maintenance, administration and support required to keep the CA operational. The Digi-CA™ Service is a managed CA.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/ca.jpg)
The Managed CA Administrator connects securely to the larger CA environment run and operated by the CA Provider or what is called the CA Trust Centre.
Managed CAs is operated by professional organisations that specialise in digital certificates and have been certified to issue trusted certificates. Managed CAs that offers trusted certificates run and operate Trust Centres.
Digi-CAST™ is factual, high-quality, digital certificate and CA advice from experienced personnel that can show you how your CA should be implemented, integrated and maintained. The C-A-S-T? method was pioneered by Digi-Sign in 2004 after many years of developing and deploying CAs around the world.
The Digi-CAST™ methodology has four distinctly separate components that are adapted and designed specifically to meet your needs:
Where Digi-CAST1™ should be used on every project, CAST2™ to CAST4™ are normally used on medium to large-scale projects such as enterprise or public sector environments.
Just as there is no such thing as a typical IT environment, there is no such thing as a typical Digi-CAST™ service. Some Digi-CAST1™ projects (where we are assisting or advising on a project before it starts) can last only a few hours, whilst other projects have 4-6 weeks durations.
Digi-CAST1™ is concerned with project planning excellence, cause and affects planning, 'skills pool' analysis, personnel selection and management. The most important thing to remember about Digi-CAST™ is that the entire service is tailored to your specific needs.
Depending on the findings of Digi-CAST1™ regarding the available personnel and their skills, you might decide that you need us for some or all of the project implementation phase. As explained in the Digi-CAST1™ phase, all of this is decided at the project evaluation and planning stage.
Digi-CAST2™ is concerned with detailing the actual project as documented in Digi-CAST1™. Its concern is with personnel, availability, time lines, 'choke points' and overall project delivery. Combining your resources with ours, we begin the project and work together to a common goal.
Digi-CAST3™ is concerned exclusively with compliance and certification. The most common requests for certification are for ETSI 101 456, ISO 17799, ALGO and 1999/93/EC. There are many other requirements that can include accreditation in your country by the national accreditation board, the national telecom regulator or other third-party organisations.
These requirements are typical of a CA that wants to issue Digi-IDs™ for Machine Readable Travel Documents [MRTD], e Passports, National ID cards, Trust Centres or large scale certificate deployments for government, health, finance, insurance or banking.
National and international accreditation is normally based on ETSI, ISO, ANSI, ICAO or other standards. BS 7799 (Part 2) or ISO 17799, 1999/93/EC, ETSI 101 456, HIPAA, Sarbanes Oxley, SB 1386, Gramm-Leach Bliley, EAL, ETSI, CWA, ALGO, ICAO for MRTD and many others are all possible with Digi-CA™.
The real objective with Digi-CAST4™ is to ensure as much knowledge transfer as possible. Using the 'Train the Trainer' approach, it is expected that your organisation should be capable of maintaining your own environment and its accreditation to the highest of standards and to do this without assistance.
The following technical installation diagram outlines a typical network requirement to run and operate a dual server Digi-CA™ Server Xp system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/multi.jpg)
The solution to the problem of online identification, authentication and privacy in computer based systems lies in the field of cryptography. Due to the non-physical nature of electronic communication, traditional methods of physically marking transactions with a seal or signature are useless. So an alternative mark must be coded into the information itself in order to identify the source and provide privacy against eavesdroppers.
One widely used tool for privacy protection is what cryptographers call a “secret key.” Log-on passwords and cash card PINs are examples of secret keys. Consumers share these secret keys only with the parties they want to communicate with, such as an online subscription service or a bank. Private information is then encrypted with this password, and it can only be decrypted by one of the parties holding that same password.
Despite its widespread use, this secret-key system has some serious limitations. As network communications proliferate, it becomes very cumbersome for users to create and remember different passwords for each situation. Moreover, the sharing of a secret key involves inherent risks. In the process of transmitting a password, it can fall into the wrong hands, or one of the sharing parties might use it maliciously and then deny all action or liability.
Digital certificate technology addresses these issues because it does not rely on the sharing of secret keys. Rather than using the same key to both encrypt and decrypt data, a digital certificate uses a matched pair of keys that are unique complements to one another. In other words, what is done by one key can only be undone by the other key in the matching pair.
Digi-CA™ generates these digital certificates using the patented Rivest, Shamir & Adelman [RSA] cryptographic algorithm. This algorithm is a mathematical formula that creates a dual key algorithm that is used to create the digital certificate.
In this type of key-pair system, the “Private Key” can only be accessed by you. Your “public key” gets widely distributed as part of the certificate. Customers, partners or employees who want to communicate privately with you can use the public key in your certificate to encrypt information, and you are then the only one who can decrypt that information. Since the public key alone does not provide access to communications, you do not need to worry about who gets hold of this Key.
Your certificate tells customers and correspondents that your public key in fact belongs to you. The certificate contains your name and identifying information, your public key and electronic signature as certification.
| Number of certificates: | 200 up to 200,000,000 | |
| Production speed: | Without HSM up to 5,000 1024-bits certificates/hour With HSM up to 10,000 1024-bits certificates/hour |
|
| Key length: | Root and Intermediate certificates 9196-1024 bits Client certificates 1024-2048 bits Symmetric Keys 56 to 256 bits |
|
| Key validity: | Root Key 1 to 25 years Intermediate Keys 1 to 10 years Client Keys 1 to 10 years (as per CP) |
|
| Key storage: | Root Key off-line and stored in several separate pieces Intermediate (signing) keys access through HSM, biometric client certificates, smart card or USB tokens | |
| Cryptographic Ciphers: | AES, Blowfish, CAST5, DES, 3DES, IDEA, RC2, RC4, RC5 and RSA | |
| Signature Algorithms: | MD2, MD4, MD5, MDC2, SHA1 (DSSI) and RIPEMD-160 | |
| Entropy: | 2127 | |
The authentication, privacy and integrity of the digital certificates is governed by several factors:
SSL and TLS are protocols that are used to provide secure Web communications on intranets and the Internet. TLS is the standardized (by the Internet Engineering Task Force [IETF]) version of SSL and is also referred to as SSL version 3.1, whereas the most commonly used SSL version is 3.0. Both protocols can provide the following basic security services:
Mutual Authentication verifies the identities of both the server and the client through the exchange and validation of their digital certificates.
Communication Privacy encrypts information exchanged between secure servers and secure clients using a secure channel.
Communication Integrity verifies the integrity of the contents of messages exchanged between the client and the server, which ensures that messages haven’t been altered en route. Digital certificates are an integral part of a total environment. Whether it is a simple case of using them to secure email or using them for authentication purposes in a larger workflow business process, in all cases, Digi-CA™ certificates are easy to deploy.
You can own and operate a Digi-CA™ system without ever putting in place any statutory documents or standards compliance and many organisations because their application is commercial and doesn’t need third part accreditation. ‘Best Practice’ means you should consider having a CP and we would recommend the following:
Having specific fields added to your certificates is normally not required unless you are seeking accreditation or are issuing to millions of users and is a common practice when considering National IDs, e Passports, Health IDs, etc. At the deepest level, this may include Object ID [OID] fields and the need to register these OIDs with the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority [IANA]. Digi-CAST1™ will advise you on this should it be required and carry out this level of customisation and registration where appropriate.
| Status: | Active | ||
| Expiry Date: | 2007-02-14 00:00:00 GMT | ||
| Serial Number: | 04A80417E8B3D35AE8B480FFAFCD3274 | ||
| Invited on: | 2006-02-02 17:40:17 GMT | ||
| Invited by: | bob.smith@digi-sign.com | ||
| Invitation Name: | Mary Brown | ||
| Invitation Email: | mary.brown@domain.com | ||
| Requested on: | 2006-02-02 18:51:09 GMT | ||
| Approved on: | 2006-02-12 18:55:52 GMT | ||
| Approved by: | mylissa.monton@hostname.com | ||
| Activated on: | 2006-02-13 19:00:33 GMT | ||
| Revoked on: | ![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/revoke.jpg) |
||
| Common Name: | Bob Smith | ||
| Email: | bob.smith@digi-sign.com | ||
| Organisation: | Services Group | ||
| Organisational Unit: | 14029 | ||
| Locality/City: | Pompano Beach, FL | ||
| Country: | US | ||
| Secret Question: | Favourite pet's name? | ||
| Secret Answer: | Johnny Cash |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/cer.jpg)
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/cp.png)
The CP for the Digi-CA™ is an important document because it clearly identifies the processes and procedures of your CA operation in a single document. It also adds to the credibility, security and acceptance when getting the people to accept and use your digital certificates. There is a standard recognised format for writing a CP but we suggest that you don’t need to follow this RFC format unless your CA requires certification or accreditation.
In sub section 2.5.7.3, the CP is the ‘Who, What, Where and How’ document that describes the principles of the Digi-CA™ usage and how they are to be distributed. This CP is agreed before the Digi-CA™ is operational and all certificates must then be deployed in accordance with the CP.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/cps.png)
CPS control using your own CPS is only required if you are building a Trust Centre using Digi-CA™ Server Xg. The CPS should follow the RFC 2527 format in compliance with European Telecommunications Standards Institute [ETSI] 101 456. The Digi-CAST1™ Team will advise your legal technical teams on the best approach using these internationally recognised standards.
Creating your own CPS is a time consuming and complex process that will require several specialist consultants and may take several months to complete. Referencing an existing CPS such as the one used by Digi-Sign is probably the most practical approach. You should only consider drafting your own CPS if you are setting up a national or international Trust Centre.
Public keys and Private Keys ‘recognize’ each other and because the public key can be freely distributed, the web server can store all the public keys belonging to its list of authorized users and match the Keys for users seeking access. This is called On-to-One authentication.
User A’s public key is stored on the web server. When User A attempts to gain access to the server, the server asks User A’s browser’s certificate Store to confirm that it has the matching Private Key to the public key stored on the server. If the match is confirmed, User A is granted access.
In simpler deployments, you might only need to identify groups of users in which case the One-to-Many implementation is faster to implement and easier to manage.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/keys.jpg)
In One-to-Many Authentication, the entire group of users or several sub-groups are formed. The server is then configured to seek the Signing certificate only, in which case, the server doesn’t need a copy of each individual’s public key.
This is easier to deploy and manage because the server doesn’t require a unique configuration for each Digi-ID™ that will be used to access it. By its simplicity, the server is configured once and any number of users can access it without any further intervention and still the individual user can be revoked so that access is denied on the individual basis as needed.
Consider the following questions carefully:
| Q1. | When you visit a web site, like your Bank’s for example, how do you know that it really is their web site? |
| Q2. | When you download software from the Internet, how can you be sure that it really is from the original Publisher? |
| Q3. | If you are sending a confidential email to someone, how can you be sure that they are the only person that can open it? |
| Q4. | Your company has a Virtual Private Network [VPN], how can you replace password security with a stronger alternative? |
| Q5. | When you make a payment over the Internet using your credit card, how can you be assured a hacker won’t steal it during transmission? |
| Q6. | If your organisation wishes to use the internet to have business forms / documents (legally binding) signed on line, how can you do this? |
| Q7. | Your organisation wishes to put some or all of its systems on line for suppliers, customers, etc. How can you securely control access to them? |
Digital certificates can be used in a variety of different security situations; however the most common uses are for proving identity, digitally signing/sealing files and encrypting data or two factor authentications.
This is how digital certificates answer the above questions:
| A1. | If the Bank is serious about security, they will use a Digi-SSL™ Secure Web Server certificate to prove its online web site identity. |
| A2. | Using a Digi-Code™ Software/Code Signing certificate, a pop up dialog box assures the user of the Publisher’s identity prior to download. |
| A3. | If the email is first encrypted using an email certificates [Digi-Mail™], and then only the intended recipient can decrypt the email. |
| A4. | Passwords can be copied and misused, however, if each user has a Digi-Access™ certificate, security and identification is assured because this is strong two factor authentication. |
| A5. | The same Digi-SSL™ that confirms the identity of the website automatically encrypts any data that is submitted through it. |
| A6. | Again using the Digi-ID™, because the identity of the owner has been verified, they can use it to sign any digital file. |
| A7. | Using a Digi-CA™ combined with Digi-Access™, the systems can be secured and all users can be verified before offering them the correct access level. |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-cast3.png)
At the heart of every Digi-CA™ are at least one Root Key(s) or Root certificate(s) and one Intermediate Root certificate(s). Every Digi-CA™ certificate is made from a Public and a Private Key. A Root Key Ceremony is a procedure where a unique pair of Public and Private Root Keys is generated. Depending on the CP, the generation of the Root Keys may require notarization, legal representation, witnesses and ‘Key Holders’ to be present. This process is best explained with some examples:
Example A: Strong identification & non-repudiation for email & web access
Unless the information being accessed or transmitted is valued in terms of millions of dollars, it is probably sufficient that the Digi-CAST2™ Team conduct the Root Key Ceremony within the security of the Digi-CAST2™ Laboratory. The customer may opt to have the Root Key stored on a Luna Card or HSM, but in most cases the safe storage of the Root Key on a CD or hard disk is sufficient. The Root Key is never stored on the Digi-CA™ server.
Example B: Machine Readable Travel Document [MRTD] ID Card or e Passport
This type of environment requires much higher security than a commercial one. When conducting the Root Key Ceremony, the Government or Organization will require rigorous security checks to be conducted on all personnel in attendance. Those that are normally required to attend the Key Ceremony will include a minimum of two Administrators from the organisation, two signatories from the organisation, one lawyer, a notary and two video camera operators in addition to the Digi-CAST2™ Team.
The actual Root key-pair generation is normally conducted in a secure vault that has no communication or contact with the outside world other than a single telephone line or intercom. Once the vault is secured, all personnel present must prove their identity using at least two legally recognised forms of identification. Every person present, every transaction and every event is logged by the lawyer in a Root Key Ceremony Log Book and each page is notarized by the notary. From the moment the vault door is closed until it is re-opened, everything is also video recorded. The lawyer and the two organisation’s signatories must sign the recording and it too is then notarized.
Finally, as part of the above process, the Root Key is broken into as many as twenty-one parts and each individual part is secured in its own safe for which there is a key and a numerical lock. The keys are distributed to as many as twenty-one people and the numerical code is distributed to another twenty-one people.
Important Note: Example A and B are at opposite ends of the security spectrum and no two environments are the same. When considering the Root Key Ceremony, the Digi-CAST1™ Team of professional advisors can assist you in deciding on the most efficient level of security to reflect the level of protection required.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/images/knowledgebase.png)
In the same way that a Grandfather can be traced back from the Grandson (and if needed the true legal identity proven using DNA analysis); a web server certificate can be traced back to its Root and by definition this relationship is tested, verifiable and cannot be compromised.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/types.jpg)
Depending on the type of CA system, the Root certificate used in by certificate Engine to sign the certificates below it can be:
An SSRoot is a Root certificate that is signed by itself or is Self-Signed. This means that the Root certificate was created during the CA system installation and was not signed or cross certified by any other certificate (i.e. this certificate is the certificate at the top of the certificate chain).
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/root.jpg)
In every browser, there is a Trusted Root certificate store so that the important relationship from web server or person back to the TRoot can be checked every time the certificate is accessed.
This TRoot is used to sign all digital certificates below it. Much in the same way there is a natural Grandfather, Father and Son relationship; there is a chained relationship between a TRoot certificate, an Intermediate Root certificate and a Personal, or web server certificate.
Digital certificates signed in this way are part of the Trusted Chain and are said to offer public non-repudiation. Non-repudiation means that the validity of the certificate can be proven and that the recipient has been validated and verified in accordance with internationally recognised standards of practices and procedures for issuing Trusted certificates. This can also mean that they have legal standing in a court of law and therefore can act as a legal instrument or seal for digital transactions.
Only a Trusted Third Party [TTP] that operates a Trust Centre can issue a Trusted certificate because only a TTP has access to the TRoot certificate needed to sign the certificates they issue so that they can be trusted.
Only a certified commercial CA organisation or certified independent organisation can achieve the status necessary to own and operate the TRoot CA in a Trust Centre.
Trust Centres are Commercial CAs and are usually operated by accredited TTP organisations. The TTP is an organisation that has been certified in accordance with international standards as being suitable and capable of issuing digital certificates. To attain the status of being a TTP, the organisation must have at its disposal a secure data centre that conforms to the Web Trust or similar Standards (an internationally recognised authority that certifies TTPs)
This typically includes that the data centre meets the same military standards for the physical facilities, personnel, procedures, practices, security controls and allocations used when storing nuclear missiles and is therefore highly secure. Once the TTP has been certified and its Root certificates accepted by the major browsers, they can issue Trusted certificates.

Secure Socket Layer [SSL] server certificates are installed on a server. This can be a server that hosts a website like www.digi-sign.com [44], a mail server, a directory or LDAP server, or any other type of server that needs to be authenticated, or that wants to send and receive encrypted data.
Code signing certificates are used to sign software or programmed code that is downloaded over the Internet. It is the digital equivalent of the shrink-wrap or hologram seal used in the real world to authenticate software and assure the user it is genuine and actually comes from the software publisher that it claims.
Client certificates or Digital IDs are used to identify one person to another, a person to a device or gateway, or one device to another device. Client certificates are issued in their thousands and millions each year and would be the principle reason for purchasing a CA.
A person that is given access to a secure online service like a cloud service, an extranet or web portal will be authenticated to the gateway or entry point using a client certificate. This type of strong two factor authentication replaces less secure usernames and passwords currently in use on many websites.
If two routers or a Virtual Private Network [VPN] connection needs to authenticate each other, a client certificate can be used and exchanged to prove the connection is trusted. This type of client authentication occurs deep within the application and is not usually visible to the end user. This type of device-to-device authentication often uses a particular IPSec client certificate.
Also, bespoke applications and hardware seeking to utilize IP technology securely can use digital certificates to authenticate the application and/or for device-to-device authentication.
Digital signatures are used to authenticate documents, files and emails and are the electronic equivalent of a handwritten signature. Digital signatures are issued in their thousands and millions each year and would be another use for a CA.
For example, two people communicating by email will used a client certificate to authenticate or digitally sign their respective communications. This digital signature will assure each person that the email is genuine and comes from the other person. And the same digital signature can be used to sign forms, PDF documents, workflow processes, etc.
The simplest way to select the correct Digi-CA™ for your organisation is to decide how many users you have (or in some cases the number of physical devices you need to identify). This should include employees, customers, partners or suppliers and the individual people that work in each of these areas that you wish to issue a digital certificate [Digi-ID™] too.
Another alternative is to look at the level of security that you wish to achieve. If the security is relating to corporate secrets, national security or can be regarded as critical, regardless of cost, then Digi-CA™ Xg may be the only option for you. The Digi-CAST1™ Team of professional advisors will guide you toward the optimum solution.
The most important benefit of Digi-CA™ is that every aspect of the final solution can be tailored to meet your precise user, security and policy requirements.
The following table can be used as a guide to assist in choosing the best Digi-CA™ Server for your environment.
| Environment | Requirement | Users | Recommended Digi-CA™ | |
| Environment A | Strong two factor identification for web access | 2,500 | Digi-CA™ Server Xs | |
| Environment B | Online transaction and document signing for application forms and business processes | 40,000 | Digi-CA™ Server Xs | |
| Environment C | Device authentication | 100,000 | Digi-CA™ Server Xp | |
| Environment D | Manufacturer or Large Software House with fail over | Unlimited | Digi-CA™ Server Xp | |
| Environment E | National Security requirement for foreign delegates | 1,000 | Digi-CA™ Server Xg (customised) |
|
| Environment F | National Identity Card and/or Smart Passport | 500,000,000 | Digi-CA™ Server Xg (customised) |
|
| Environment G | Digi-CA™ Xg Trust Centre | Unlimited | Digi-CA™ Server Xg |
As explained in sub section 2.6.5.1, you should clearly identify if your user group is open or closed, what you want to use your certificates for and whether you have the staff required to run and operate the Digi-CA™. If, having read sub section 2.6.5 that advises you on how to select your Digi-CA™, you are still not clear, then contact the Digi-CAST1™ Team and seek their advice before proceeding further. You should also read the ‘Top Considerations’ when selecting your CA
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
The principal difference between Xs, Xp and Xg in each case relates to the degree of integration and customisation required. For example, Digi-CA™ Server Xs can be pre-configured and delivered to the customer for installation without any assistance from Digi-Sign whilst Digi-CA™ Server Xg projects can run for several days or a few weeks.
Important Note:If you have technical personnel that can correctly configure a network environment, install the necessary operating systems and provide secure access to the server(s), the Digi-CAST2™ installations Team may be able to conduct a large part of the installation process prior to visiting your site. In some cases, the complete installation can occur without the need for Digi-CAST2™ to visit your site at all.
Digi-CA™ Server Xs is CA Software for installation on a single server and comes complete with all the different sub-systems designed to run and operate efficiently on that single machine (see Appendix II).
As a software product, Digi-CA™ Server Xs only generates client certificates that can be used for email, two-factor authentication, secure web access, as electronic signatures, for use within a Virtual Private Networks [VPN] or for device-to-device authentication. Like all professional CA systems it allows the Administrator to set up policies and to manage all of the certificate life cycle services.
Even with all of the powerful functionality and capabilities that Digi-CA™ Server Xs offers, it is easy to install, configure and operate. A competent Network Engineer or qualified IT Technician could install a fully functional version of Digi-CA™ Server Xs and be fully competent in its operation within three days or less.
Digi-CA™ Server Xs can only be installed on a single Pentium® server and is typically used where high availability is not a key component of the environment. As a single server installation, there is no mirroring or synchronising of data. All records and data are protected by periodic backups only. Typical installations would be small to medium environments where high system availability is not an issue.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp is CA Software for installation on two servers and offers the same services as Digi-CA™ Server Xs but on a larger scale and with many additional services including certificate deployment and renewal automation (see Appendix II). The primary reason for selecting Xp instead of Xs is because Digi-CA™ Server Xp offers fail-over functionality.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp can also be configured to generate Secure Socket Layer [Digi-SSL™] web server certificates, Software & Code Signing certificates [Digi-Code™] in addition to Digi-Access™, Digi-ID™, and Digi-Mail™ certificates
The Digi-CA™ Server Xp installation must be carried out by Digi-CAST2™ professional services. This installation may require the Digi-CAST™ Team to physically conduct the installation on site, however, if a competent Network Engineer can provide a reliable connection to the correctly configured servers, then it may be possible to conduct the installation over the internet, without incurring travel and accommodation costs. The fully functional version of Digi-CA™ Server Xp can be completed in seven days or less.
Digi-CA™ Server Xp is installed on two Pentium® servers and is typically used where high availability is a component of the environment. As a dual server installation, there is mirroring and synchronising of data. All records and data are protected by this fail-over service. The Digi-CA™ Server Xp is split over two servers and gives the option to include a firewall in between. Typical installations would be large enterprise or government environments.
Digi-CA™ Server Xg is the CA for commercial Trust Centres. The services can be split over as many as 16 servers but a typical installation would use four servers and a single Hardware Security Module [HSM]. This CA has four levels of security including two or three levels of firewalls with fail over facilities and can incorporate hot standby, disaster recovery and a single system can operate from multiple locations.
The Digi-CA™ Server Xg installation must be carried out by Digi-CAST2™ professional services and requires the Team to physically conduct the installation on site with the associated travel and accommodation costs. Once configured, the fully functional version of Digi-CA™ Server Xg can be completed in ten days or less.
Digi-CA™ Server Xg is used where high availability and reliability are a key component of the environment. As a multi-server installation, there is mirroring and synchronising of data. All records and data are protected by this fail-over service. The Digi-CA™ Server Xg separates the CA services so that seven layers of security can be applied to the Trust Centre environment. The CA services are located in the certificate Engine core with the RA, certificate Revocation List [CRL], Light Directory Access Protocol [LDAP] and Time Stamping services located in the Outer Core (see Appendix II). Typical installations are government and commercial CA Trust Centres.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-server.png)
Digi-CA™ Shared is where you actually purchase the Digi-CA™ Server software but we host it for you. This is particularly of use to organisations that know their long-term requirement is for Software CA but their immediate personnel and technical resources are insufficient to meet their needs.
The Digi-CA™ Server is configured, integrated and designed to meet your future environment and Digi-Sign hosts the software on a dedicated platform for you. As soon as your resources are at the appropriate levels, we migrate the entire system (without service interruption) to your site.
The service approach is based on three principles:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ca-service.png)
The principal difference between Digi-CA™ Service Xs, Xp and Xg is the level of integration and customisation you require. For example, Digi-CA™ Service Xs is provided as a standard Service and there is no customisation or integration offered. The Digi-CA™ Service Xp offers language localisation of the Digi-CA™ Control Centre and the end user interfaces and Xg could be a highly integrated Service involving various databases, synchronisation and other features.
There are four versions of Digi-CA™ Service, each with self-explanatory names:
Each of these services is explained in detail in the following sub sections and the principal difference between Digi-CA™ Service Xs, Xp and Xg in each case relates to the type of digital certificate it issues and the degree of integration and customisation required.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ssl.png)
You may be seeking a simple solution for getting SSL certificates or perhaps you have a larger and more specific set of requirements. You need many different digital certificates for several organisational divisions and locations. Whether your requirement is large or small, Digi-SSL Server™ easily meets your needs.
Traditionally, organisations have to wait hours or even days for SSL certificates. Other certificate solutions are cumbersome, labour intensive and expensive. With Digi-SSL™ Service these issues and others are completely removed.
You provide us with a list of domains that you need secured and before the Digi-SSL™ Service is activated these names are thoroughly Validated. All domain name validations are provided free-of-charge and once active, the Administrator is able to issue and revoke any Digi-SSL™ for any domain name in the system.
Digi-SSL™ Service has out performed even its best-known rivals by using the latest in digital certificate and Internet technologies offered by the Digi-CA™ certificate Engine core. It offers you a totally flexible, fast, convenient and easy to use Service.
Moving from your current SSL ordering system to the Digi-SSL™ Service couldn’t be easier. The Digi-CA Assistant™ can create a list of your SSLs automatically and then upload this list to the Digi-SSL™ Service system. The migration process occurs as part of your normal SSL Renewal process and this means that all your existing certificates remain valid until they need to be replaced. Using the Digi-CA Assistant™, the Digi-SSL™ Service automatically ensures that the migration process is child’s play
The Signature Algorithm uses RSA and DSA and as these algorithms are always used in conjunction with a one-way hash function, the following hash functions can be applied:
The Signature Key generation algorithms use RSA and DSA (Digi-CA™ Server only).
The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system without a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/single.jpg)
The following technical installation diagram outlines the typical network requirement to run and operate a single server Digi-CA™ Server Xs system with a HSM. Backup server is optional.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/single1.jpg)
The x.509 certificate can be used for many purposes, such as: electronic signature, two factor authentication, client authentication, email signing and encryption and many other applications.
The most common and most frequently used purposes can be included using further layers of security protocols and cryptographic algorithms, the most common of which are:
Digi-CA™ has been verified to comply with more than 70+ standards and here is a list of the most commonly requested standards that Digi-CA™ complies with:
| Digi-CA™ standard compliance list | ||
| RSA Public Key Cryptography Standards | PKCS#1, PKCS#3, PKCS#5, PKCS#7, PKCS#8, PKCS#9, PKCS#10, PKCS#11, PKCS#12 | |
| Internet Engineering Task Force RFC standards or standard candidates | RFC 373, RFC 1231, RFC 1422, RFC 2246, RFC 2315, RFC 2459, RFC 2510, RFC 2527, RFC 2560, RFC 2587, RFC 2630, RFC 2634, RFC 2818, RFC 2898, RFC 2986, RFC 3039, RFC 3161, RFC 3279, RFC 3280, RFC 3628, RFC 3629, RFC 3647, RFC 3739, RFC 4514, RFC 5280 | |
| US Federal Information Processing Standards | FIPS 46, FIPS 180-2, FIPS 186-2, FIPS 197, FIPS 198 | |
| European Telecommunications Standards Institute standards | ETSI TS 102 280, ETSI TS 102 042, ETSI TS 102 040, ETSI TS 102 023, ETSI TS 101 861 | |
| CEN Workshop Agreement standards | CWA 14167-1, CWA 14172 (1-8) | |
| ISO & Other standards | ITU X.509, ITU-T X.520, ISO 27001, ISO 7816 Parts (1 – 5), ISO 7816 (Parts 7 – 9), ISO 15408, GridPMA, EAL4, EAL4+, XKMS XML, NIST SP 800-38C, NIST SP 800-38B, NIST SP 800-90 | |
Digi-SSL™ and Digi-Code™ certificates require browser compatibility. Digi-ID™ certificates require browser compatibility and also compatibility with Adobe® PDF whilst email software compatibility is required when being using Digi-Mail™ certificates.
The following is a list of browsers that are compatible with Digi-SSLs™, Digi-Codes™ and Digi-ID™ certificates:
The following is a list of browsers that are compatible with the certificates used for Digi-Mail™:
Proof of Identity – When the end user first applies for the certificate, in most cases they must prove their identity. The information or documents required to provide ‘proof of identity’ are decided by the issuing authority and may include official papers and/or other documents. The precise requirement will be clearly identified in the CP.
Application Form - An application form must be completed.
Data Check – Once the end user’s application form details are received, the Registration Authority [RA] cross checks or validates the data for accuracy and authenticity.
Approval/Rejection – The RA either approves or rejects the application.
Notification – End user is notified that their certificate is available for collection or it is sent out automatically.
Collection – The end user receives the certificate and can use this to prove their identity.
Renewal – All certificates are renewed at fixed intervals, usually each year or every second year.
Proof of Identity – When the end user first applies for a certificate, the information or documents required to provide ‘proof of identity’ are decided in the CP.
Application Form - An online application form must be completed.
Data Check – Once the end user’s application form details are received, the Registration Authority [RA] cross checks or validates the data for accuracy and authenticity.
Approval/Rejection – The RA either approves or rejects the application using the online RA Control Centre.
Notification – End user is notified that their certificate is available for collection as the final part of the Process or it is simply sent out automatically in a Package.
Collection – The end user receives the certificate and can use this to prove their identity.
Renewal – All certificates are renewed at fixed intervals, usually each year or every second year.
Typically the renewal process is simply a case of presenting the previous certificate and a new one is issued to replace it.
There are four consoles in the Digi-CA™ system, namely:
| Error! Reference source not found. | CAMC | www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/camc [125] | ||
| Error! Reference source not found. | RAMC | www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/ramc [126] | ||
| Error! Reference source not found. | EERS | www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/eers [127] | ||
| Error! Reference source not found. | CCDS | www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/ccds [128] |
The focus of this document is on the Digi-CA™ Management Console [CAMC]. Separate documents and online support resources provide detailed information on the Registration Authority Management Console [RAMC]; the End Entity Registration Service [EERS]; and the Active Content Dissemination Services [CCDS].
The CA Administrator’s Management Console [CAMC] is the web based Certification Authority management module that enables the CA Administrator to control the principal services of the Digi-CA™ system.
The RA Management Console [RAMC] Service Module is the central graphical user interface [GUI] for operating Registration Authorities and managing End Entity Certificates. For further details, please visit www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/ramc [126]
The End Entity Registration Service [EERS] is the GUI where end entities (e.g. users, devices and services) interface with the digital certificates and digital signatures issues by the Digi-CA™ system. For further details, please visit www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/eers [127]
The Certificate & CRL Dissemination Services [CCDS] is a software application as described in various European Telecoms Standards Institute [ETSI] and CEN Workshop Agreement [CWA] Standards. Ultimately the CCDS provides dissemination for end entity public key certificates, key pairs, Certificate Revocation List [CRL] and Online Certificate Status Protocol [OCSP] services. For further details, please visit www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/acds [129]
The Digital Signature and message encryption implementation on email messages is achieved by mechanisms implemented directly in the email client software and that follows the S/MIME standard.
Both S/MIME message encryption and Digital Signatures are based on encryption technologies. Message body encryption creates a completely unreadable message body and Digital Signature. The diagram below shows how the encryption process generates a one-time Symmetric Key (also called a Session Key) that encrypts the message body.
The Symmetric Key is then encrypted with each recipient’s public key so that only the recipient can decrypt the Symmetric Key. The message is then sent. On the recipient end, the Private Key is used to decrypt the Symmetric Key, which is then used to decrypt the message. This process is transparent to the user and is performed with no interaction between clients. Symmetric encryption is much faster than asymmetric encryption. The reason is because symmetric encryption encrypts the data (message body) in bulk.
In the diagram on the following page, it illustrates the message encryption and decryption process. The four main steps detailed in the illustration are as follows:
| 1 | Message is encrypted with Session Key. | |
| 2 | Session Key is encrypted with recipient’s public key. | |
| 3 | After encrypted message is received, recipient decrypts Session Key with the recipient’s Private Key. | |
| 4 | Message is decrypted with Session Key. | |
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/tec.jpg)
When you add a Digital Signature to a message, a hash value of the message contents is computed. User Keys aren’t used to compute the hash value and the hash doesn’t identify anyone. The hash is only a small, unique digital fingerprint of the message. This hash value is then encrypted with the sender’s Private Key, and can be decrypted with the public key found in the sender’s certificate.
The recipient decrypts the original hash value with the sender’s public key, which might be sent with the signed message or can be found in the sender’s certificate. Your client verifies signatures. For encrypted messages, it decrypts the message first. The client computes a new hash value based on the text received and compared to the original hash value. If they match, you can trust the content’s integrity and the sender’s identity.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/ttm.png)
Total Trust Management™ [TTM™] is a unique offering from Digi-Sign (although some try to copy it) and it means that you Trust us to Totally Manage the Digi-CA™ for you. TTM™ is much more than a dedicated telephone number for support; it’s a service where Digi-Sign personnel effectively work for you.
We ensure that the Digi-CA™ is introduced to your end users with the minimum of fuss. All you do is agree how you want us to operate the system and we do everything for you. It’s a bit like travelling ‘First Class’.
75% of Digi-CA™ owners use TTM™ in the first year, at least, so that they can see how we do everything and then learn by watching us. We assume the RA responsibility and solve any technical and Help Desk support issues from the end users.
Training an RA Administrator how to use the Digi-CA™, explaining the principles and importance of the CP and providing sufficient Administrator knowledge to undertake their work in a professional manner, can take time. Manuals, technical documentation, on site training and subsequent second and third level external support can assist the Administrator, but too often, the organisation does not have these vital, and necessary, resources available.
As with all new technology implementations in any organisation, the initial deployment and piloting of a project is critical to its success. Many CA installations have failed because this important principle was either misunderstood or miscalculated.
To solve all of these issues, in 2001 Digi-Sign pioneered the TTM™ service so that CA deployment is a simple execution. Since then, other organisations have attempted to 'copy' the TTM™ offering with varying degrees of success. However, to completely understand why TTM™ is so unique, an understanding of the technology used in Digi-CA™ is required.
Incredibly, most CAs available in the market today still use Legacy CA technology. The technology that was used to design what is at the very heart of these CAs is 1990's technology. The best way to illustrate the affect this has for Legacy CA users is to draw a comparison between Legacy CAs and the Desktop PC. Consider the difference between Windows® 3.1 with today’s versions of Windows® and the differences are obvious. The same is true of Legacy CAs.
Digi-CA™ uses the latest in CA technology and this enables Digi-Sign to offer the most comprehensive TTM™ service. The organisation that owns the Digi-CA™ is provided with read-only access to the system so that they can see the TTM™ service in 'real time' and learn from the actions carried out by the Digi-CA TTM™ Administrators.
Over time, the initial deployment and pilot projects are completed and full scale implementation is well advanced. In many cases, the organisation only uses the TTM™ service for the first year and by this time, digital certificates are already part of the organisation's total IT infrastructure.
With TTM™, the total implementation and adoption of certificates within the organisation can sometimes happen almost without anyone noticing. Some owners have even extended the TTM™ service to include the Total Trust Management of their Digi-SSL™ requirements too.
Digi-Sign offers three types of digital certificate and both types of CA. With exception of Digi-Code™, these are offered in three Classes depending on your requirements.
The three types of digital certificate are:
| Digi-SSL™ | SSL certificates | |
| Digi-Code™ | Code signing certificates | |
| Digi-ID™; Digi-Access™; Digi-Mail™ | Client certificates |
And there are several Classes for each of these certificates, e.g. Xn, Xs, Xp, Xe, Xg, etc. The three standard Classes are the Xs, Xp and Xg, where Xs is the basic Class and offers no real flexibility to the user and Xg is at the other end of the spectrum and is the most flexible.
The following sub sections detail the different Types of certificate and the correct Class depending on your requirement.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/imagefield_thumbs/digi-ssl.png)
Digi-SSLs™ are Secure Socket Layer [SSL] certificates and are used for securing and authenticating the following:
Digi-SSLs™ are the most commonplace digital certificate in use today. Web sites and other servers use Digi-SSLs™ in their thousands each year. If your requirement is predominantly for SSL and SSL Management, we recommend the Digi-SSL™ Service.
Digi-SSL™ provides you with two functions:
Every application for any class of Digi-SSL™ is subjected to the Triple-Check Validations procedure. This means that two or more Validations Officers physically check your details and entitlement to get the Digi-SSL™ before it is issued to you. This rigorous checking procedure protects you from someone else stealing your online identity because the Digi-Sign Triple-Check Validations™ has a 100% track record of never issuing a digital certificate to the wrong party. Once this Digi-SSL™ is put on your website, visitors know your site is genuine.
The same Digi-SSL™ that authenticates your site to visitors can also be used for encrypting data and it is here that the Xp/Xg and Xs difference occurs. The main difference between Xp/Xg & Xs is that the Digi-SSL™ Xs is for low/no value transactions and Xp/Xg is for corporate users and commercial websites.
The Digi-Sign Certificate Practice Statement [CPS] v3.7, Sub section 2.4.1.a and 5.32.1 both state that the maximum warranty associated with a Digi-SSL™ Xs certificate is €0.01. So if your information is worth more than €0.01 and you require warranty protection, you should only use the Xs certificate to authenticate your website. This does not mean you can’t use the Xs for encrypting data, it only means that in the event of a fault in the Digi-SSL™, you have no warranty.
The maximum warranty associated with the Digi-SSL™ Xp or Xg certificate is €10,000. The CPS v3.7, Sub section 2.4.1.b and 5.32.2, both state clearly that this is for corporate or professional use and carries a warranty in the event of failure.
Other Differences between Xp/Xs & Xg would be that:
Digi-SSL™ Xg certificates are only supplied in specific cases where multiple hosting specifications require flexible naming within the Digi-SSL™. This specialist configuration can include multiple Common Names within the same certificate, wildcard facilities or a combination of these requirements.
Fused User Protected Storage
In the case where the end entity certificates is stored in the Microsoft Internet Explorer certificate Store of the Desktop Profile for the user, there is an option in the Digi-CA Sever™ system to offer further security levels by enabling the User Protected setting. Depending on the CP, this can be offered to the end user as an option or it can be enforced. The security levels are:
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/key1.jpg)
The Low setting is the same as no User Protection and the check box remains unchecked. The Medium setting is where every time the certificate is required by any application a simple pop-up dialog appears so that the user is notified and must accept the request to use the certificate by clicking the OK button. And in the High setting, a pop-up dialog appears so that the user must enter a password before any request to use the certificate will be permitted.
If a High User Protection is enforced by the CP, or the user selects it, then the pop-up dialog will require them to enter a password to protect the end entity certificate.
This final setting where the user must enter a password is referred to a Two Factor Authentication, because the user must have an end entity certificates and know its password before they can use it. So something you have and something you know provides this Two Factor Authentication.
When choosing your Storage Type, careful consideration should be given to a number of factors. If the Private Key is not exportable and its life cycle is set to be valid for ten years, then will the device it is stored on still work 10 years from now? What happens if the device is lost, stolen or destroyed? Alternatively, if you decide that the Private Key can be exported, how do you prevent it being shared by several users? What is the disadvantage should sharing occur?
If you decide to enforce High User Protection, what happens if the user forgets their password and the certificate is rendered permanently unusable thereafter? On the other hand, if there’s no password, how easy would it be for someone else to use that certificate?
The Digi-CAST1™ Team of professional advisors are there to assist you in making the best choice for your environment and to help remove the element of risk from your purchase.
x.509 and cryptographic standards make it impossible that two identical certificates can be issued from the same Digi-CA™. Every certificate is unique.
A person’s ‘proof of identity’ can be proven using various traditional methods. For example: private information that only that specific person could know; a letter from a notary, lawyer, accountant, employer or Peace Commissioner identifying that person; bank, passport, national ID card or insurance number; eye scan, finger print, biometrics; etc. Every person is unique.
The whole purpose of the certificate is to identify the specific person or device in the digital world. Once the unique identity is proven using traditional methods, then the unique certificate can be issued.
The process of mapping the unique certificate to the unique person or device is called the Validation Process. The Validation Process is based on the specific CP for the specific certificate and is set out when Digi-CA™ is first designed and installed.
The Digi-CA™ is the digital equivalent of an identification authority like an employee ID card, a passport office or a national identity card issuer. In all of the above cases, the identity of the end user is checked and an ID is issued to certify that the person is who they claim to be. In the case of the Digi-CA™, it issues the certificate to each end user after their ‘real world’ identity has been verified.
The process of issuing the certificate is similar to the steps used to issue an employee ID card, passport or national ID card.
How an end entity certificate is validated is central to the security and legality of the certificate and the Digi-CA™. If the Validation Policy is weak or can be easily circumvented, then personal identity theft or impersonation is possible. In other words, there is no way to ‘tie’ the certificate to the user.
Every time a user sends an email it travels across the internet or World Wide Web. It is called the World Wide Web because the internet is made up of thousands of servers or a ‘web of servers’. Each and every communication visits a minimum of 8 and a maximum of 32 servers before it reaches its intended destination. Each of these points of contact represents a security risk. Scripts, viruses, hackers and other devices can intercept the data at any time and can copy or alter it unnoticed.
Device-to-device authentication, two-factor authentication, transaction signing and the inherent ‘digital identity’ within the digital certificate means that you know who and what you’re communicating with.
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/world.jpg)
Encrypting information is only one aspect of security, the other is knowing the identity of the person. If two people choose to communicate by email, how can they be sure that any of the communications were transmitted without being tampered with? Equally, if a website owner wants to be sure that only a specific user gains access to secured information, how can this assurance be provided?
![Digi-CA™ the complete Certificate Authority [CA] system](/files/pass.jpg)
The simple answer is that digital certificates are the digital equivalent of a passport or signature. By opening a user’s digital certificate much of the information that would be available in a passport or drivers license can be viewed in the certificate. The person’s name, the organisation that they work for (or the organisation that issued the certificate) and other information is clearly legible. A digital certificate cannot be compromised or ‘cracked’, this provides the assurance necessary to assure the recipient that the person is genuinely who they claim to be.
![]() [1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90].
[1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90].
![]() [1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the CA Administration Management Console [CA AMC] component of the system.
[1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the CA Administration Management Console [CA AMC] component of the system.
Depending on the configuration, policy and distribution of your Digi-CA™ system, some services may be disabled. The following is an overview of the key elements of the system:
These and other functions of the CA Administration Management Console [CA AMC], how to use each interface, what your System Administrators, Certificate Administrators and Registration Managers need to know and other training materials are listed in the sub sections below.
![]() [1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the RA Management Console [RA MC] component of the system.
[1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the RA Management Console [RA MC] component of the system.
Depending on the configuration, policy and distribution of your Digi-CA™ system, some services may be disabled. The following is an overview of the key elements of the system:
These and other functions of the RA Management Console [RA MC], how to use each interface, what your System Administrators, Certificate Administrators and Registration Managers need to know and other training materials are listed in the sub sections below.
![]() [1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the Limited RA [LRA] - Control Centre component of the system.
[1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the Limited RA [LRA] - Control Centre component of the system.
Technically, the Digi-CA™ Control Centre inherits its design and all its features from the RA Management Console [RA MC]. However the Control Centre does introduce flexible configuration mechanisms that allow Registration Authorities to distribute RA roles and individual RA Management Console features to different organisational units, branches, partner channels and so on.
Depending on the configuration, policy and distribution of your Digi-CA™ system, some services may be disabled. The following is an overview of the key elements of the system:
These and other functions of the Limited RA [LRA] - Control Centre, 'Step-by-Step Instructions' on how to use each interface, what your System Administrators, Certificate Administrators and Registration Managers need to know and other training materials are listed in the sub sections below.
![]() [1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the Control Centre Public Services – RA Registration Service [RA RS] component of the system.
[1] This is the on line training manual for the installed Certificate Authority [CA] Software, Digi-CA™ Server [90] and the Control Centre Public Services – RA Registration Service [RA RS] component of the system.
Depending on the configuration, policy and distribution of your Digi-CA™, some services may be publicly available. These public services are typically to enable basic end user requirements for Digital Certificates and have four main functions:
These and other functions of the Registration Authority Registration Service [RA RS], how to use each interface, what your end users need to know and other training materials are listed in the sub sections below.
Links:
[1] https://www.digi-sign.com/order/digi-ca-admin/accept.php
[2] http://www2.digi-sign.com/certificate+authority
[3] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digital+certificate
[4] http://www2.digi-sign.com/two+factor+authentication
[5] http://www2.digi-sign.com/id+card
[6] http://www2.digi-sign.com/electronic+identification
[7] http://www2.digi-sign.com/public+key+infrastructure
[8] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast
[9] http://www2.digi-sign.com/compliance/introduction
[10] http://www2.digi-sign.com/trust+centre
[11] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/online+certificate+status+protocol
[12] http://www2.digi-sign.com/repository/certificate+practice+statement
[13] http://www2.digi-sign.com/downloads/aacd-manual
[14] http://www2.digi-sign.com/aacd
[15] http://www2.digi-sign.com/service/certificate+authority+management+services#ttm
[16] http://www2.digi-sign.com/downloads/digi-ca-manual
[17] http://www2.digi-sign.com/ssl+certificate
[18] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-mail
[19] http://www2.digi-sign.com/key+ceremony
[20] http://www2.digi-sign.com/e+passport
[21] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-id
[22] http://www2.digi-sign.com/support/digi-ssl/generate+csr
[23] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca
[24] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-id/distribute/policy
[25] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-id/distribute/invite
[26] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-id/distribute/enrol
[27] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-id/distribute/activate
[28] http://www2.digi-sign.com/certificate+authority/traditional+ca
[29] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/introduction/migration
[30] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+components
[31] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+modules
[32] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+console#ra-mc
[33] http://www2.digi-sign.com/
[34] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/index
[35] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/transition
[36] http://www2.digi-sign.com/service/digi-cast
[37] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/information+database
[38] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/information+database#control+centre
[39] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/information+database#crl
[40] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-access
[41] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/customisation/index
[42] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/aacd
[43] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/migration
[44] http://www.digi-sign.com
[45] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-ca-pdf
[46] http://www2.digi-sign.com/compliance/list+standards
[47] http://www2.digi-sign.com/arp
[48] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast#digi-cast1
[49] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administration/transition
[50] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast#digi-cast2
[51] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/products
[52] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-bill
[53] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-code
[54] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-id
[55] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-id/qualified
[56] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-access
[57] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-seal
[58] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-mail
[59] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/service
[60] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/server
[61] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-ca
[62] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/ocsp
[63] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/hsm
[64] http://www.digi-sign.com/products
[65] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/server
[66] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/products/digi-ca
[67] http://www.digi-sign.com/product/digi-ca
[68] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/shared
[69] http://wwwtest.digi-sign.com/products/
[70] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-ca-deployment-pdf
[71] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/deployment/modules
[72] http://www2.digi-sign.com/www.digi-sign.com/about/compliance
[73] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+console#control-centre
[74] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+console#ca-amc
[75] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/time+stamp
[76] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-ca-pdf alt=
[77] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/digi-ca
[78] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/managed+ca
[79] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/software+ca
[80] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/digi-ca+xs+xp
[81] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/digi-ca+xg
[82] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast/1
[83] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast/2
[84] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast/3
[85] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-cast/4
[86] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ssl
[87] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+console
[88] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+console#ra-rs
[89] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/service
[90] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/server
[91] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/shared
[92] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/total+trust+management
[93] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-tasc
[94] http://www2.digi-sign.com/en/digi-trust/trusted+services+provider
[95] http://www2.digi-sign.com/books
[96] http://www2.digi-sign.com/en/about/third+party
[97] http://www2.digi-sign.com/training/digi-ca/server/ca+amc
[98] http://www2.digi-sign.com/training/digi-ca/server/ra+mc
[99] http://www2.digi-sign.com/training/digi-ca/server/lra
[100] http://www2.digi-sign.com/training/digi-ca/server/ra+rs
[101] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-ca-admin-pdf
[102] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digital+document
[103] http://www2.digi-sign.com/about/choosing+digi-sign
[104] http://www2.digi-sign.com/demos/digi-ca+presentation
[105] http://www2.digi-sign.com/support/knowledgebase
[106] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+environment
[107] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+environment#equipment
[108] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+environment#network
[109] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+environment#os alt=
[110] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/certificate+authority+environment#os
[111] mailto:digi-cast@digi-sign.com
[112] http://www2.digi-sign.com/downloads/digi-ca admin
[113] http://www.sendmail.org
[114] http://www2.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/administrator/time+stamp
[115] http://www.openssl.org
[116] http://www.stunnel.org
[117] http://www.apache.org
[118] http://www.mysql.org
[119] http://www.perl.org
[120] http://www.php.net
[121] http://www.digi-sign.com/about/service+level+agreement
[122] http://www2.digi-sign.com/www.digi-sign.com/about
[123] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca
[124] http://www2.digi-sign.com/www.digi-sign.com/advisor
[125] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/camc
[126] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/ramc
[127] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/eers
[128] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/ccds
[129] http://www.digi-sign.com/digi-ca/acds